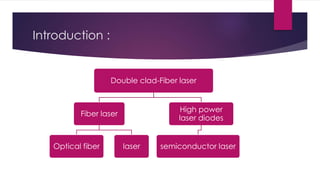
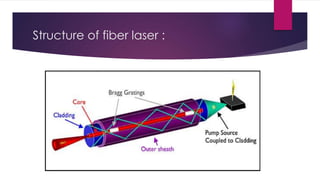
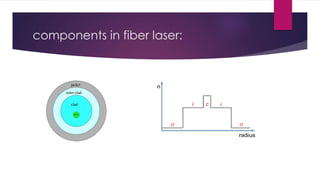
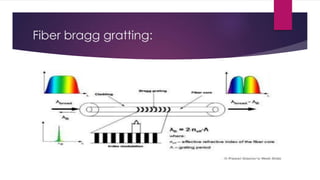
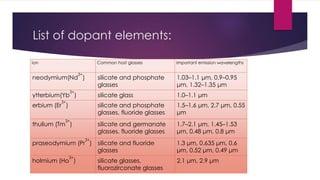
This document provides an overview of fiber lasers, including their basic components and advantages over conventional solid-state lasers. It discusses the history of fiber lasers beginning with Maiman's demonstration of the ruby laser in 1960 and Snitzer's development of the first fiber laser in 1961. The key components of a fiber laser are described, including the double-clad fiber structure, fiber Bragg gratings, and common dopant elements such as neodymium, ytterbium, and erbium that produce important emission wavelengths. Advantages of fiber lasers include high power capability due to efficient cooling, stability, reliability, lower cost, and insensitivity to environmental changes. Remaining challenges include designing new host and dopant