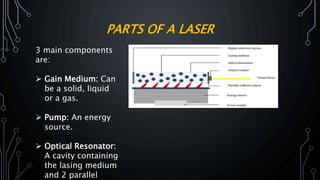
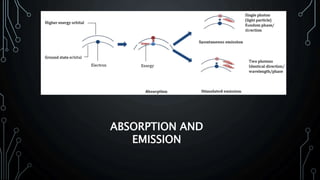
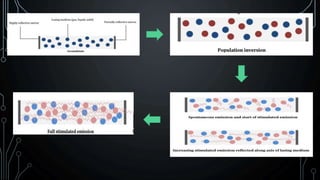
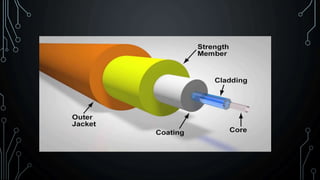
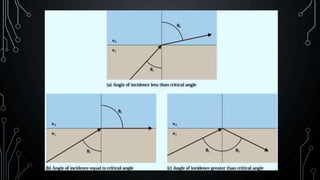
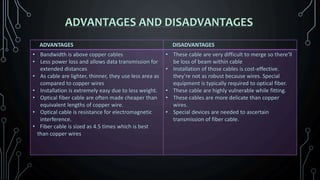
Lasers and fiber optics are used for optical communication. Lasers emit light that is monochromatic, coherent and collimated. The three main components of a laser are the gain medium, pump and optical resonator. Fiber optics use total internal reflection to transmit light through fibers made of glass or plastic. They have a core and cladding, with the core having a higher refractive index. Fiber optics have advantages like higher bandwidth, less power loss and resistance to electromagnetic interference compared to metal wires.