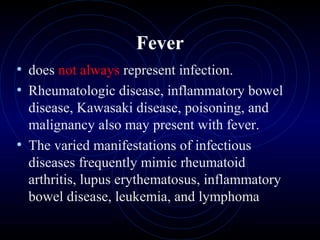
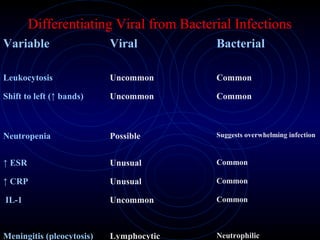
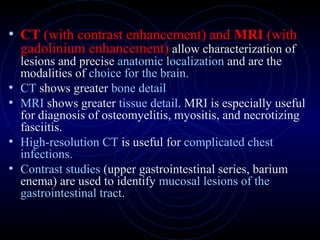
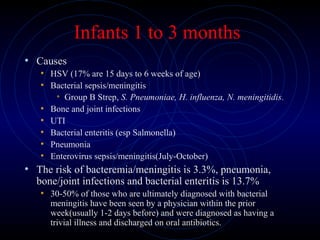
This document provides information on fever in infants and children, including:
1) It describes the differences between true fever caused by the body's set point being increased due to infection or inflammation, versus false fever which does not directly increase the set point.
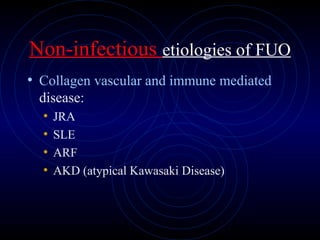
2) Evaluation of the febrile infant or child involves obtaining a thorough history, physical exam, and screening tests like CBC, blood cultures, and lumbar puncture if meningitis is suspected, to identify potential causes and focus of infection.
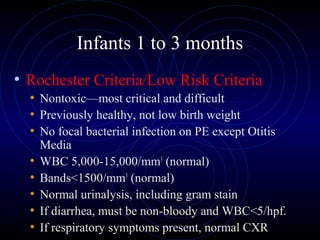
3) Management depends on the age of the child. Neonates less than 1 month require full sepsis workup and antibiotics if febrile. Infants 1-3 months can potentially be treated as out