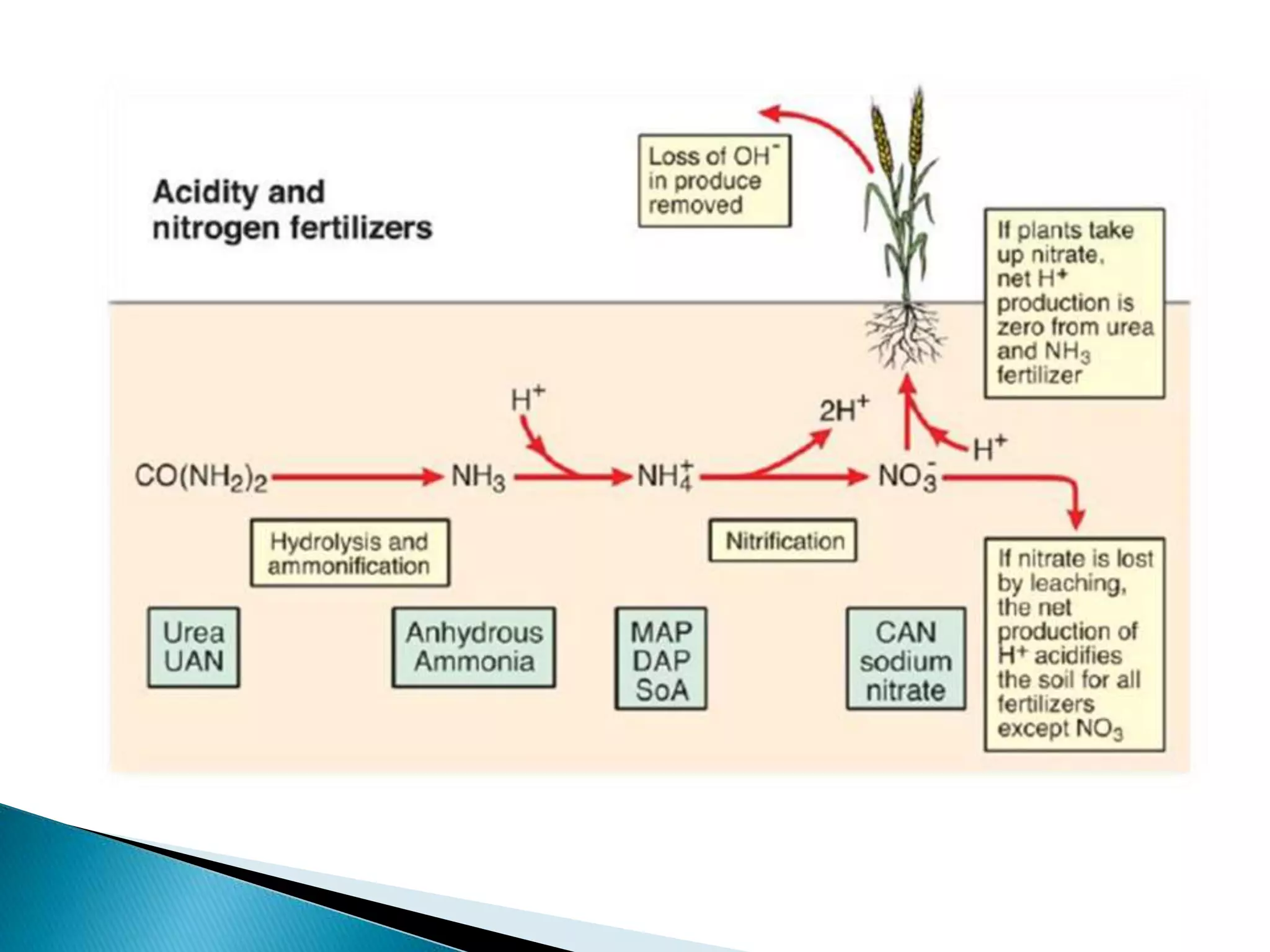
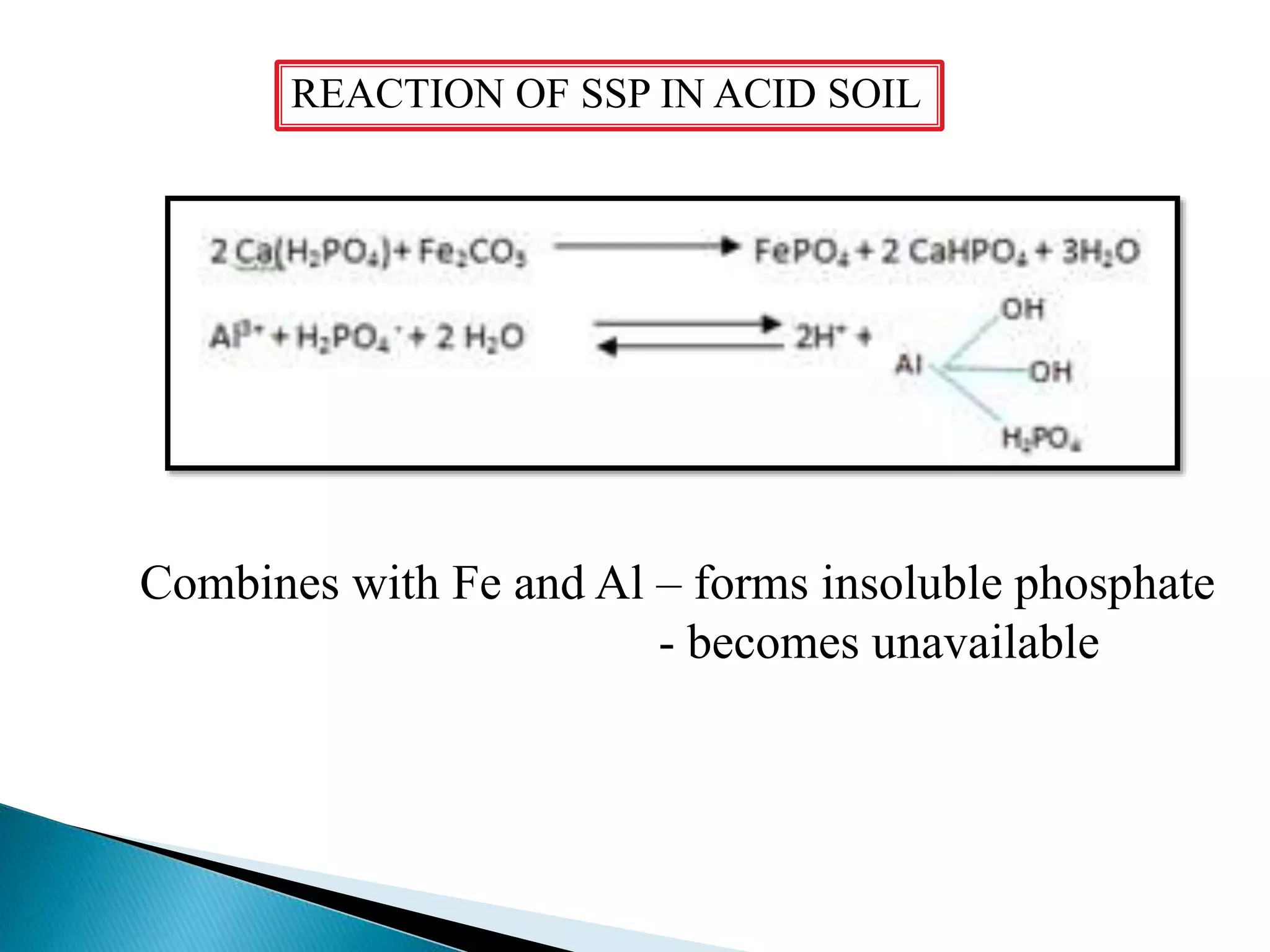
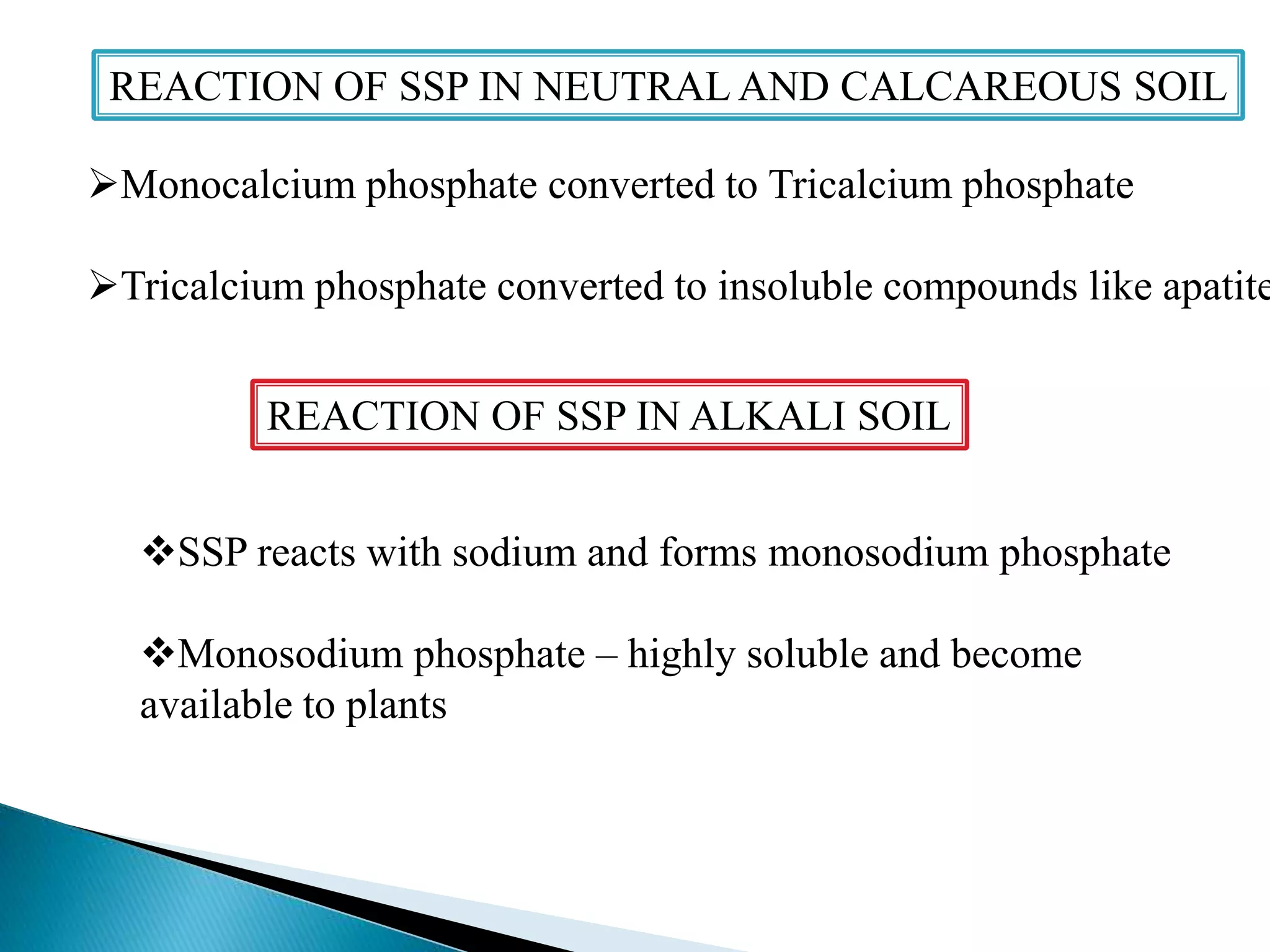
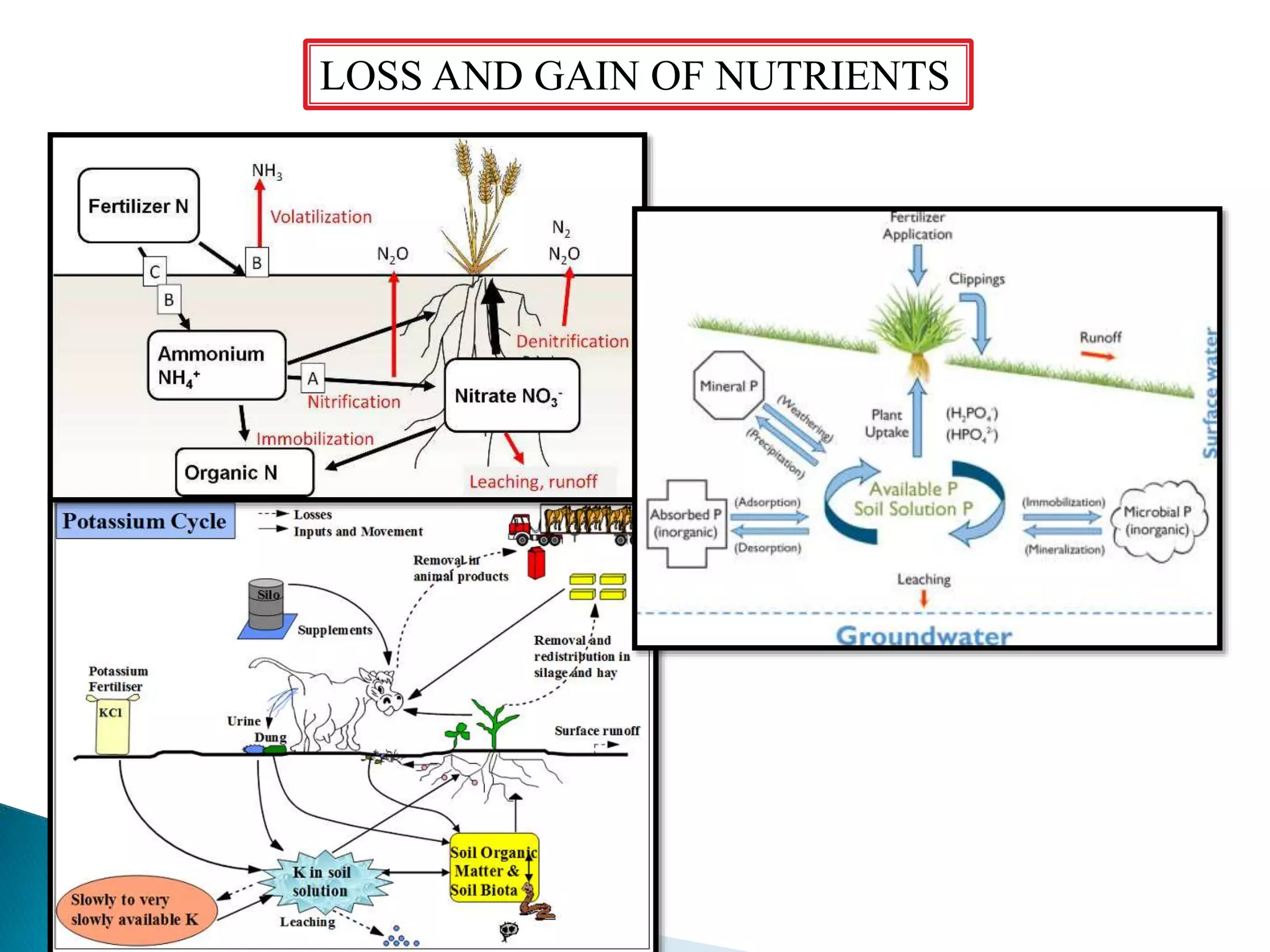
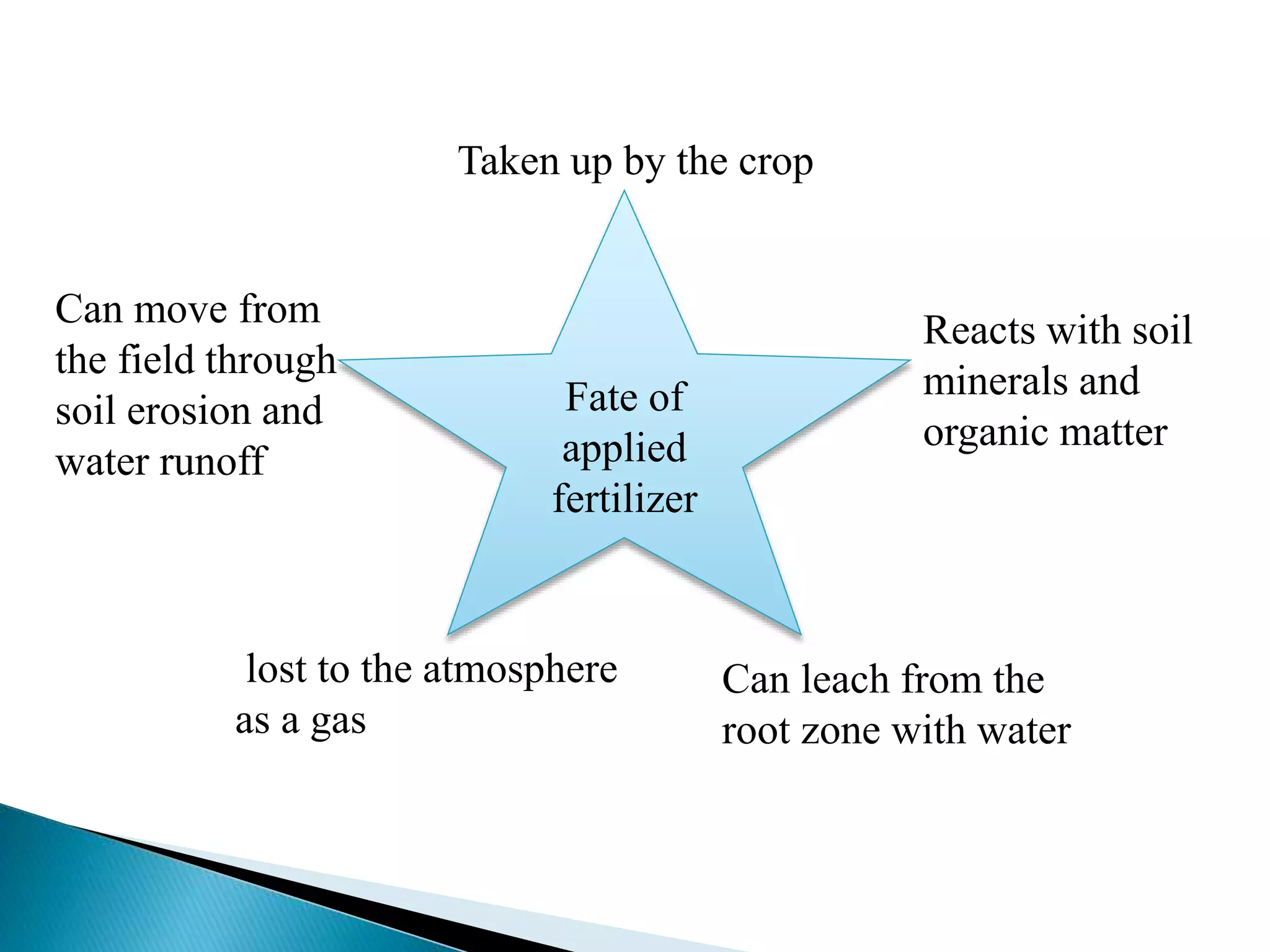
Fertilizers undergo various chemical reactions in soil that determine their availability to plants. Nitrogenous fertilizers like ammonium sulfate and urea release ammonium ions through cation exchange or hydrolysis reactions. These ions can then be further transformed by soil microbes. Phosphate fertilizers like single superphosphate dissolve in soil water but can precipitate or react with soil minerals to form insoluble compounds depending on the soil pH. Potassium fertilizers like potassium chloride and potassium sulfate readily dissolve to release potassium ions for plant uptake. After application, the nutrients in fertilizers may be taken up by crops, react with the soil, leach below the root zone, or be lost through erosion, runoff or gas emission.