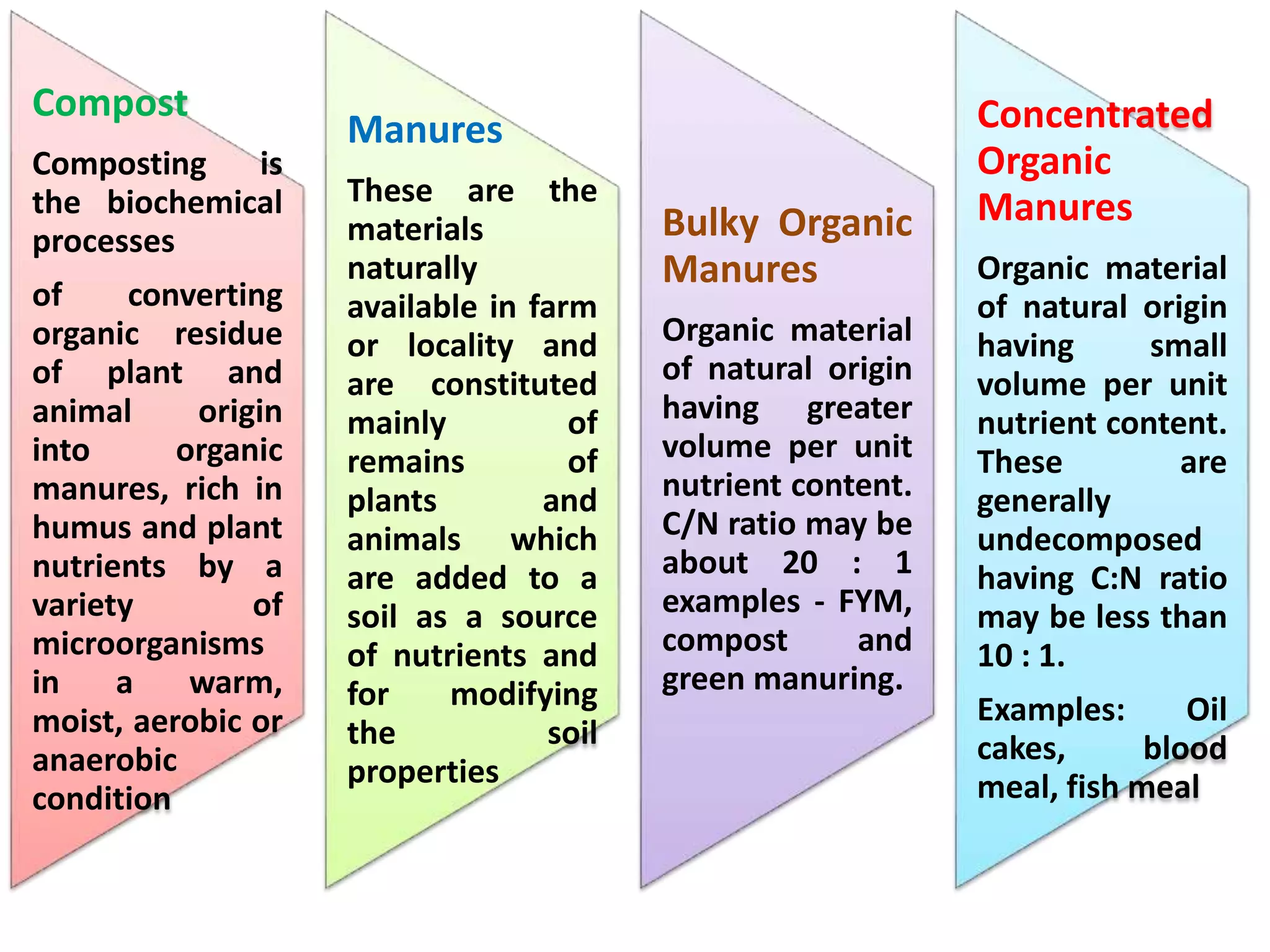
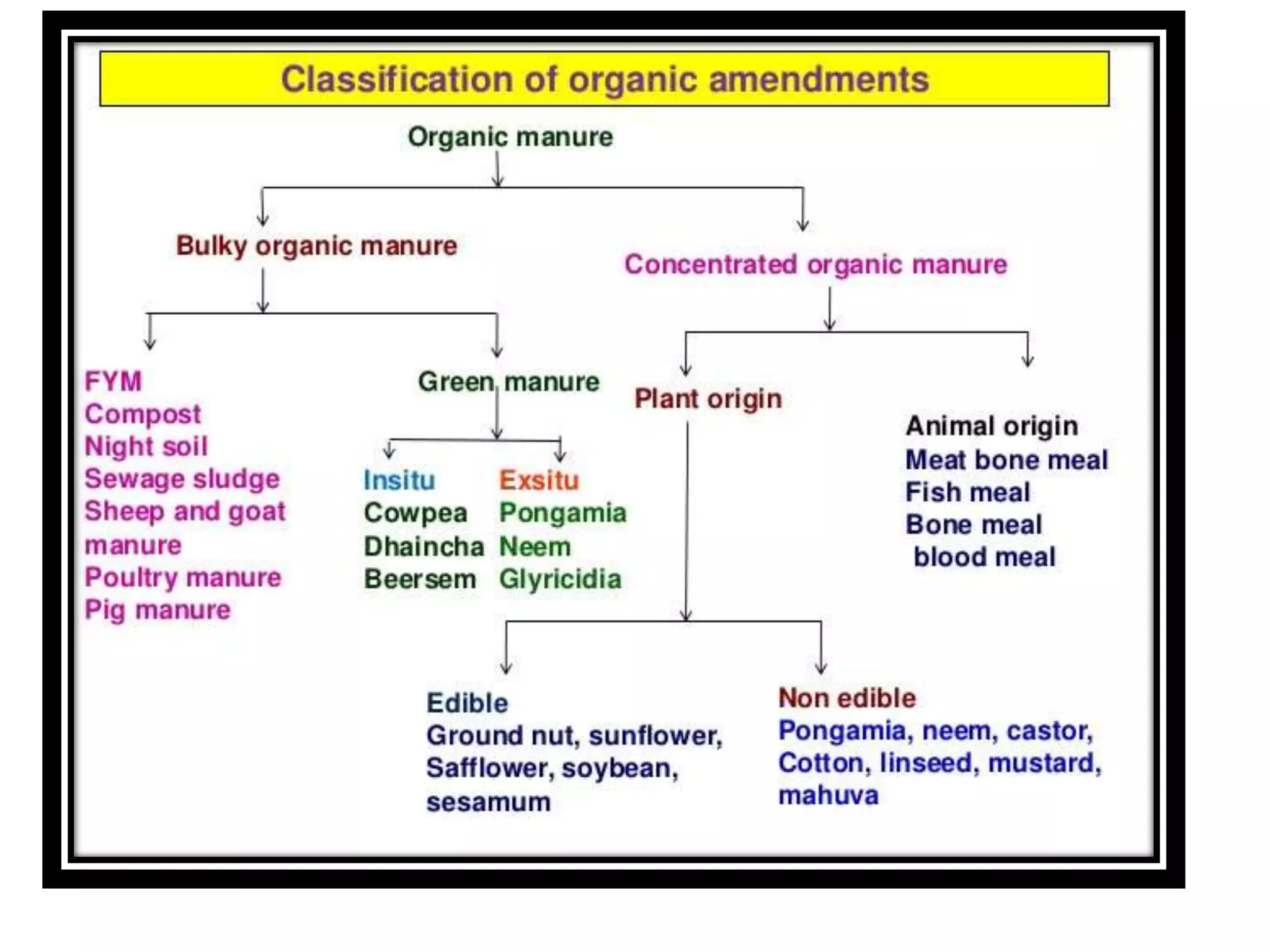
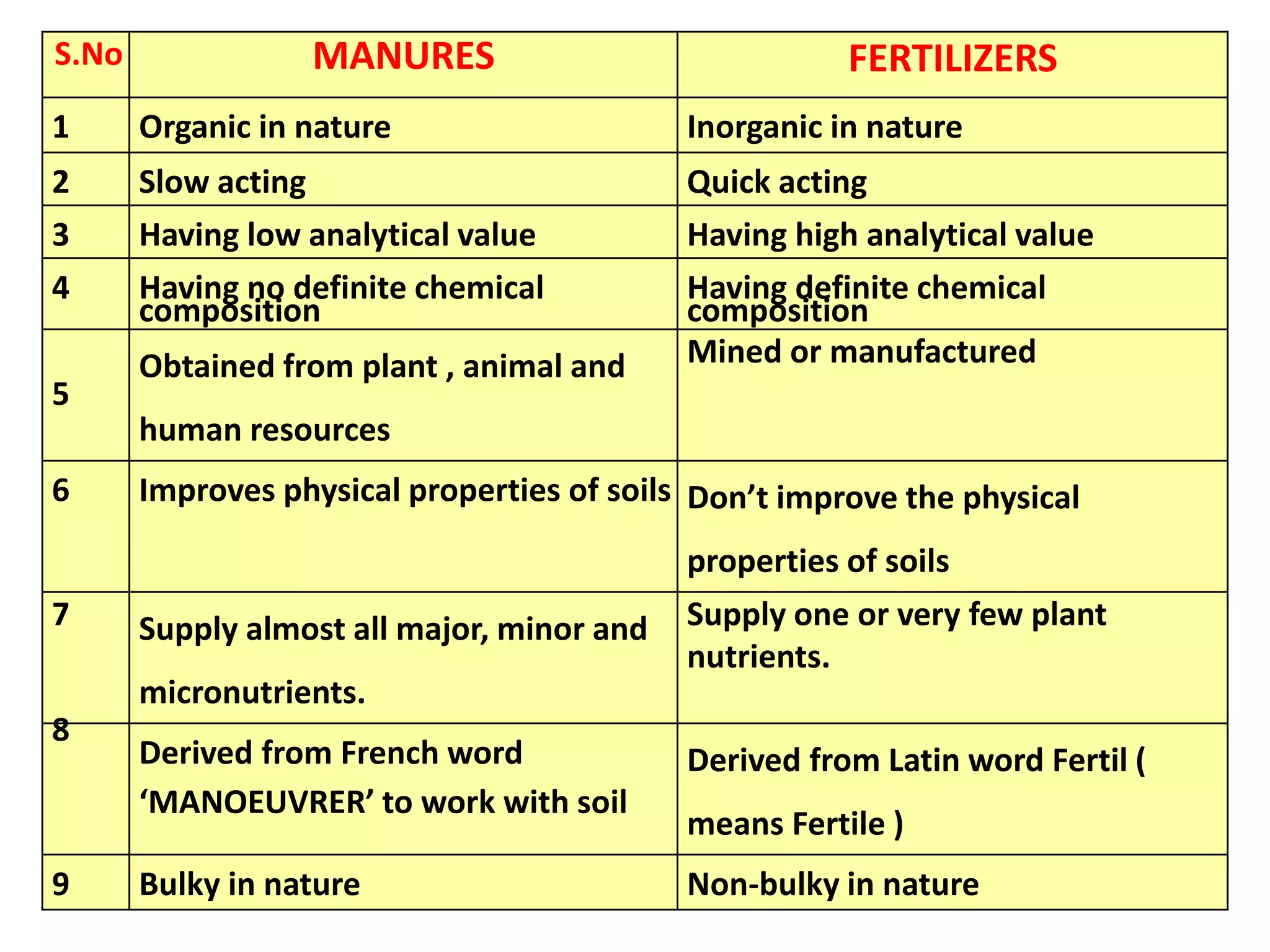
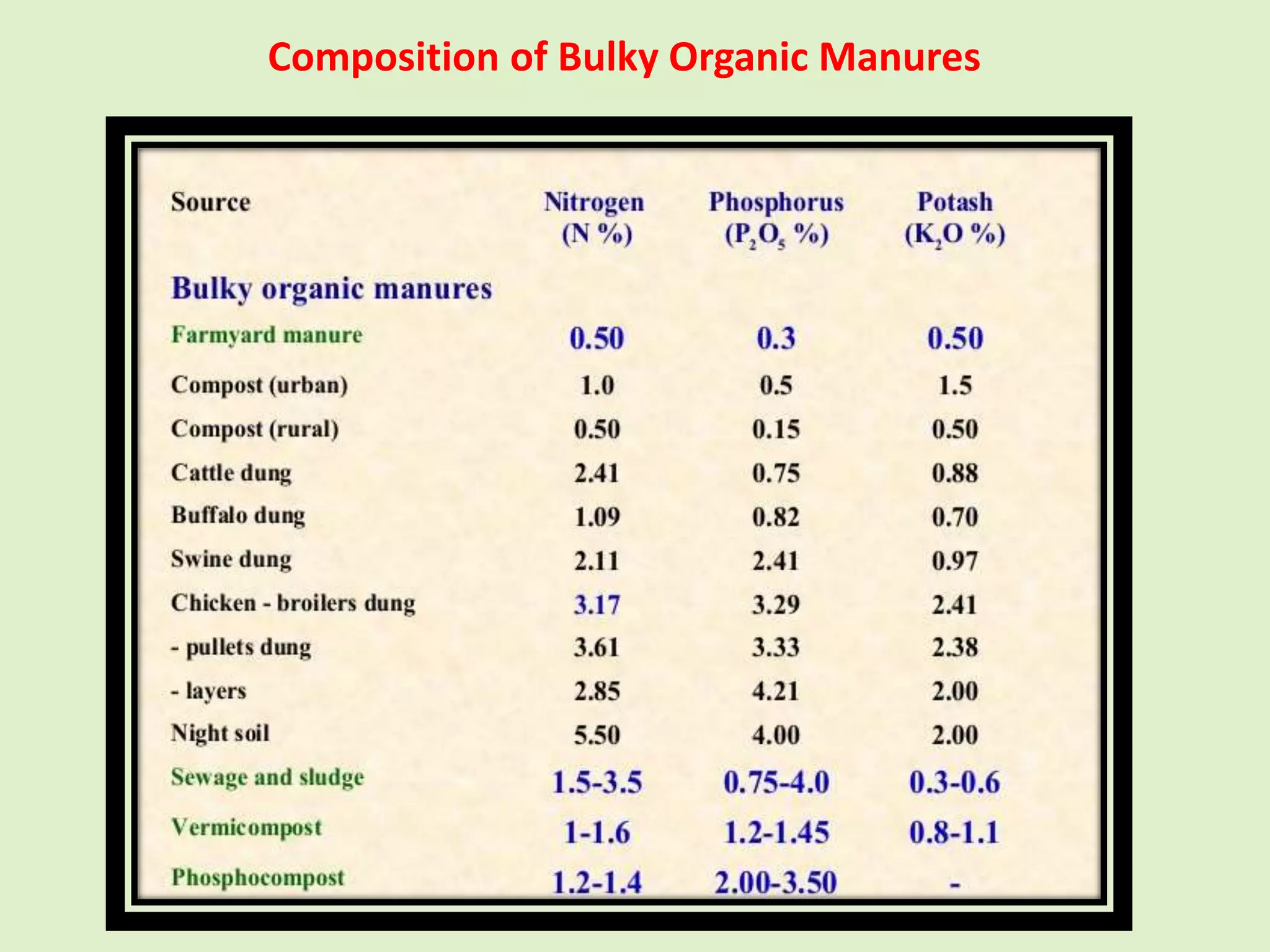
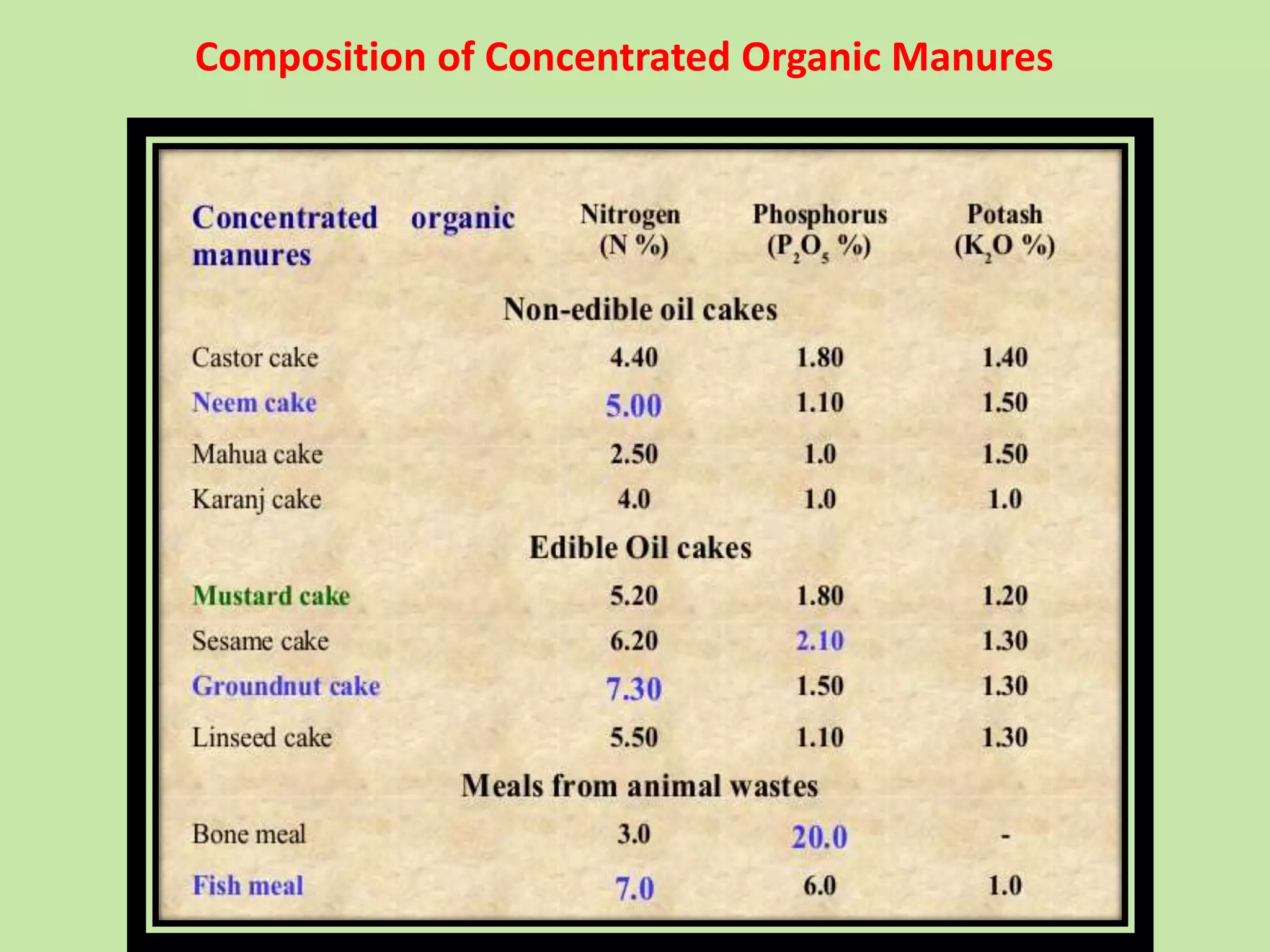
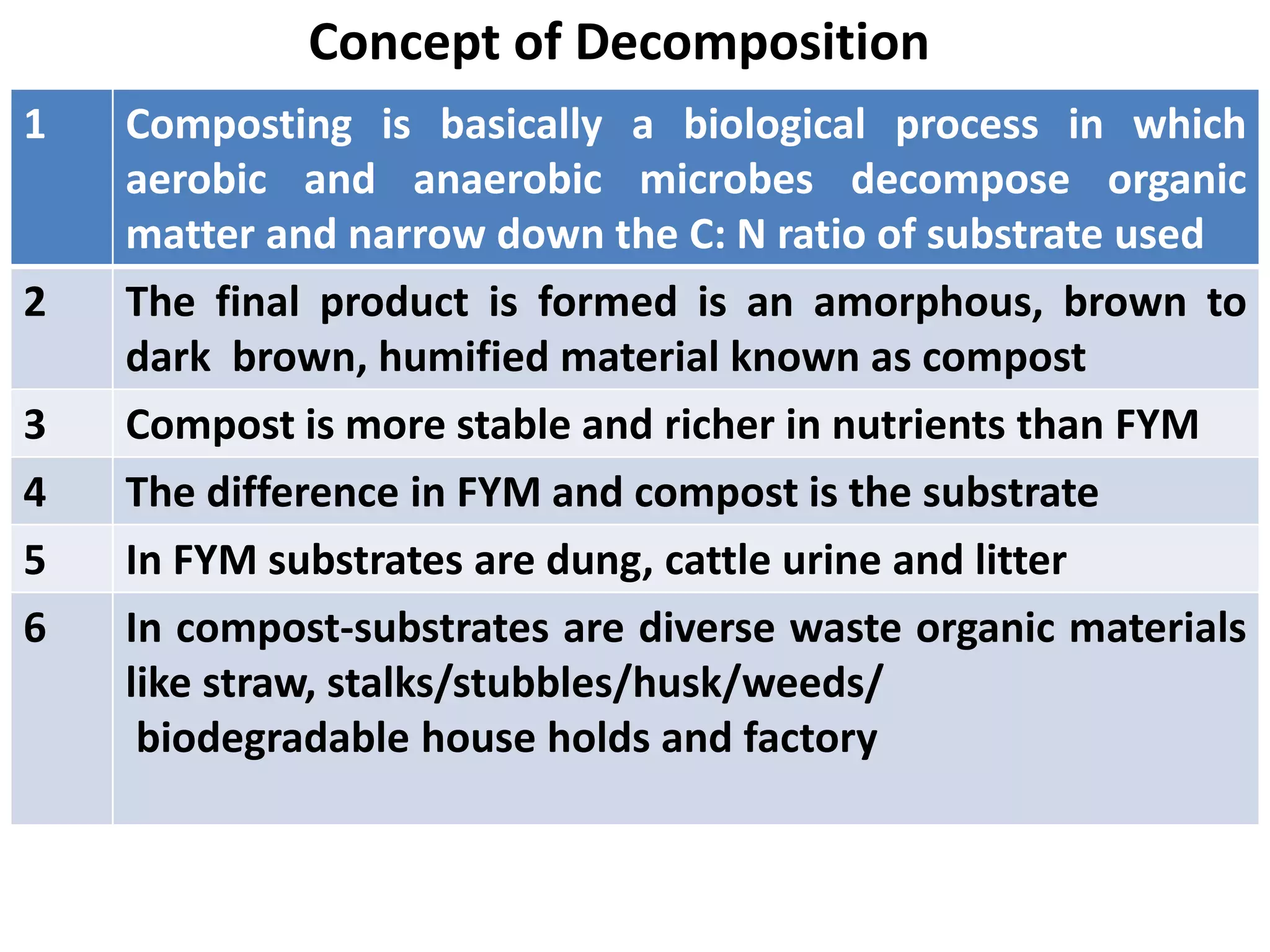
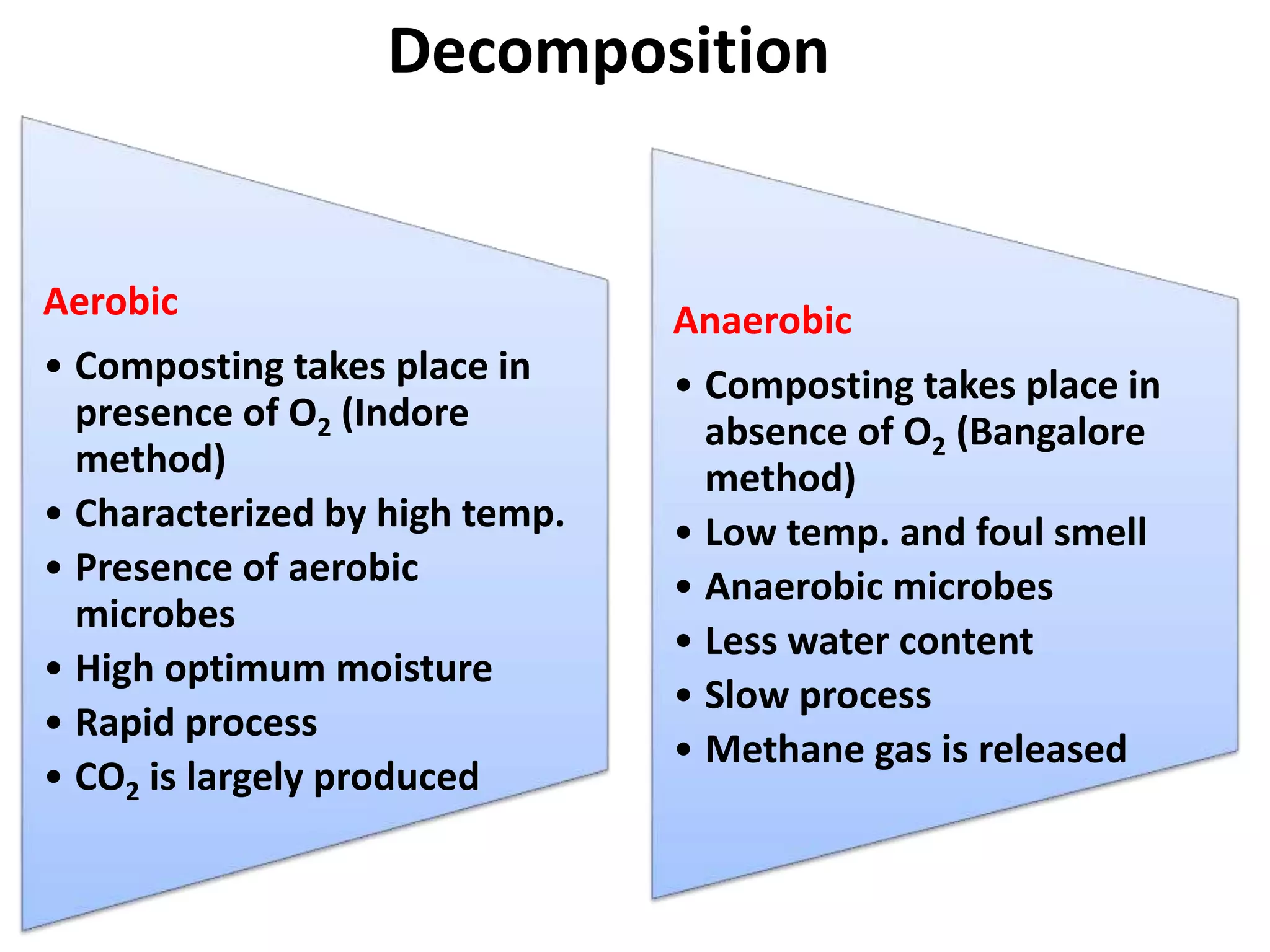
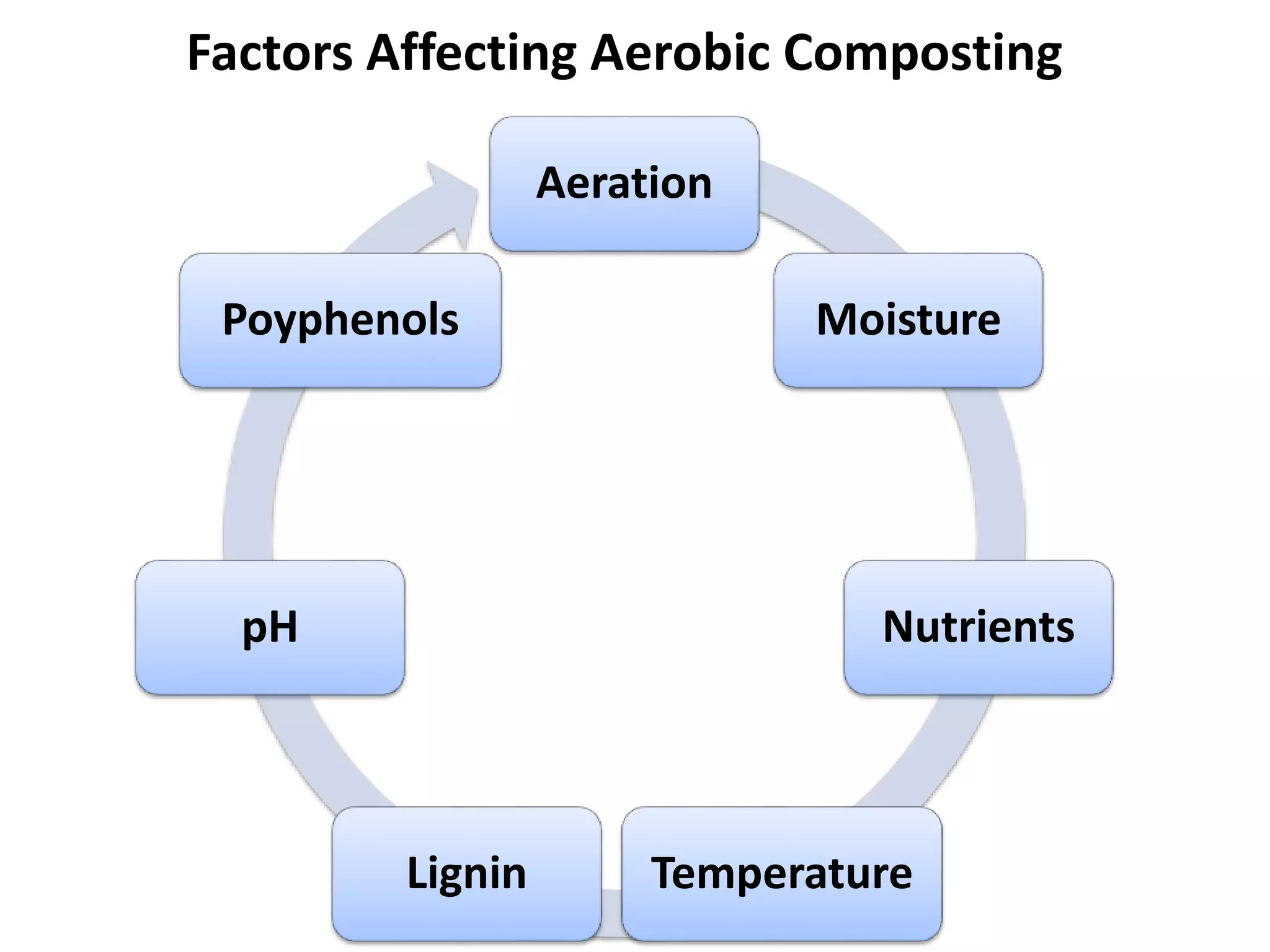
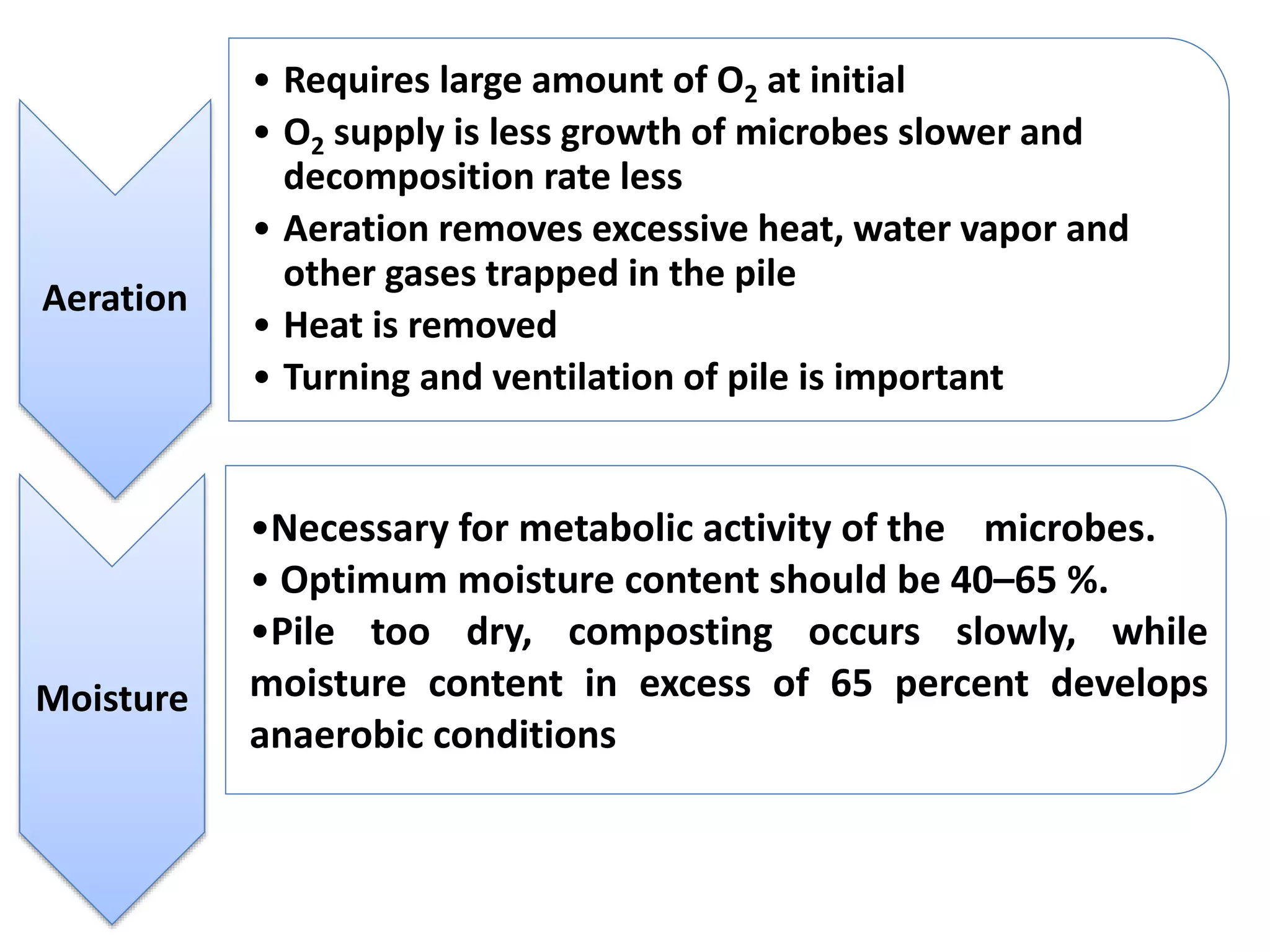
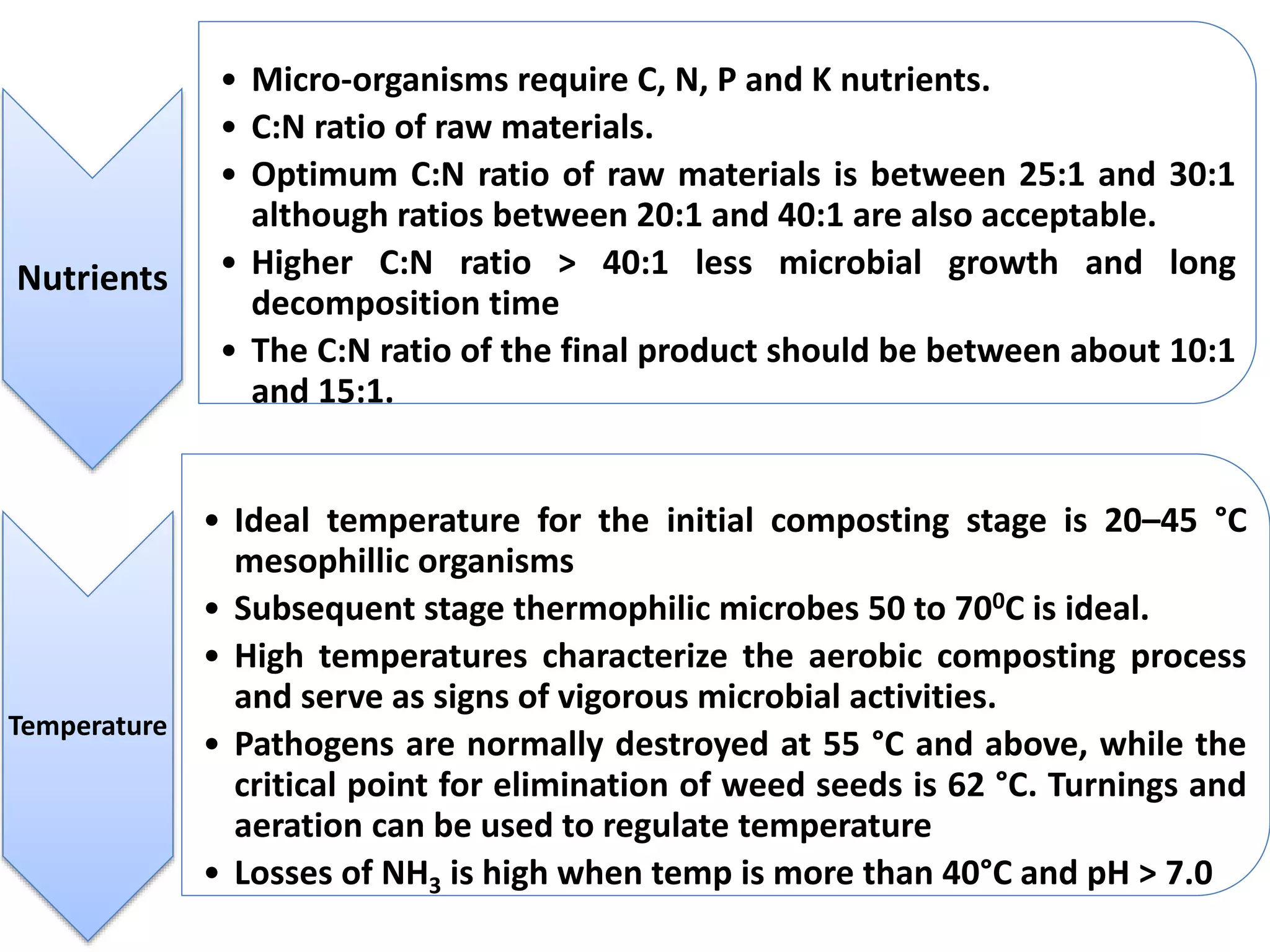
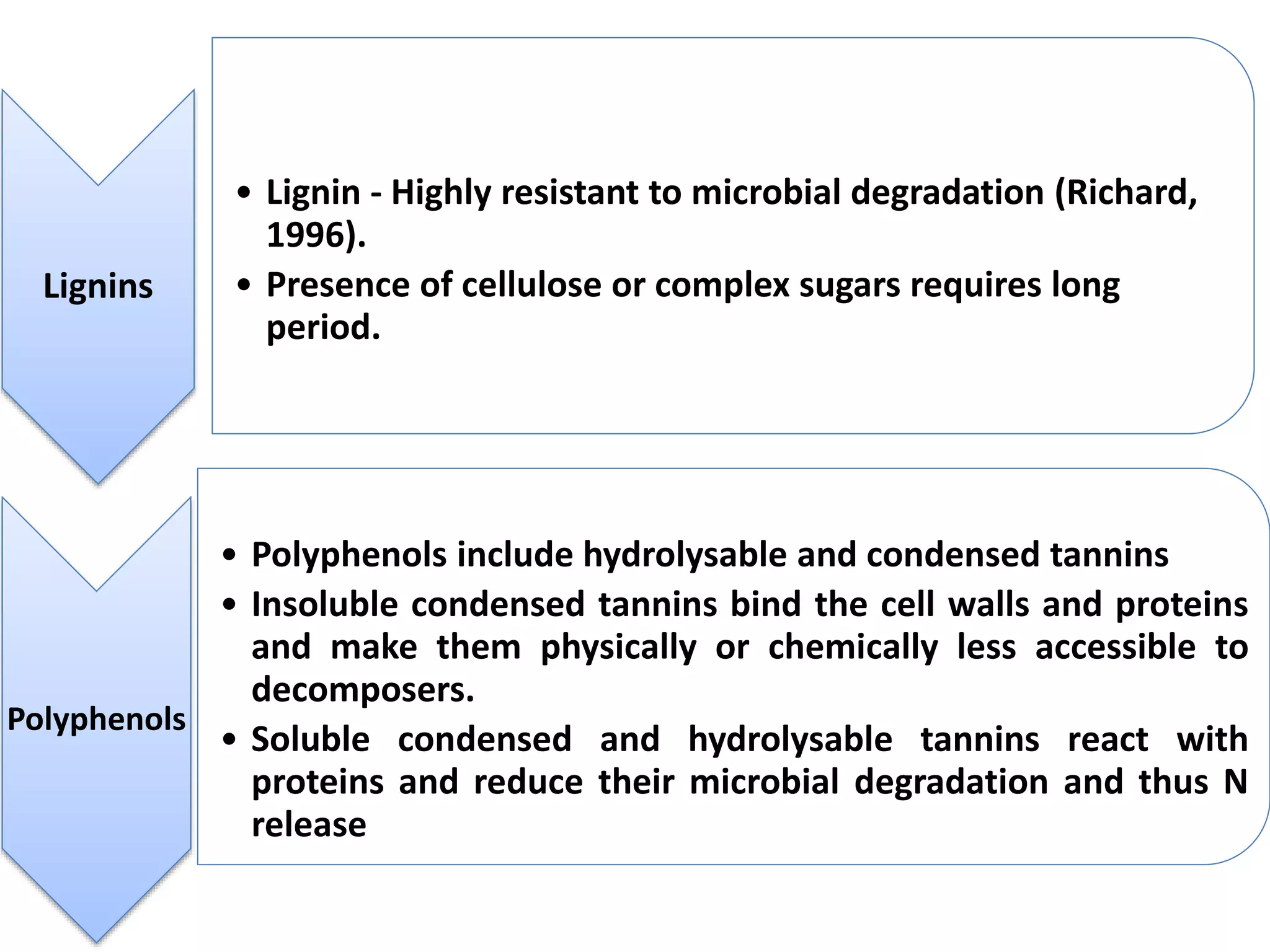
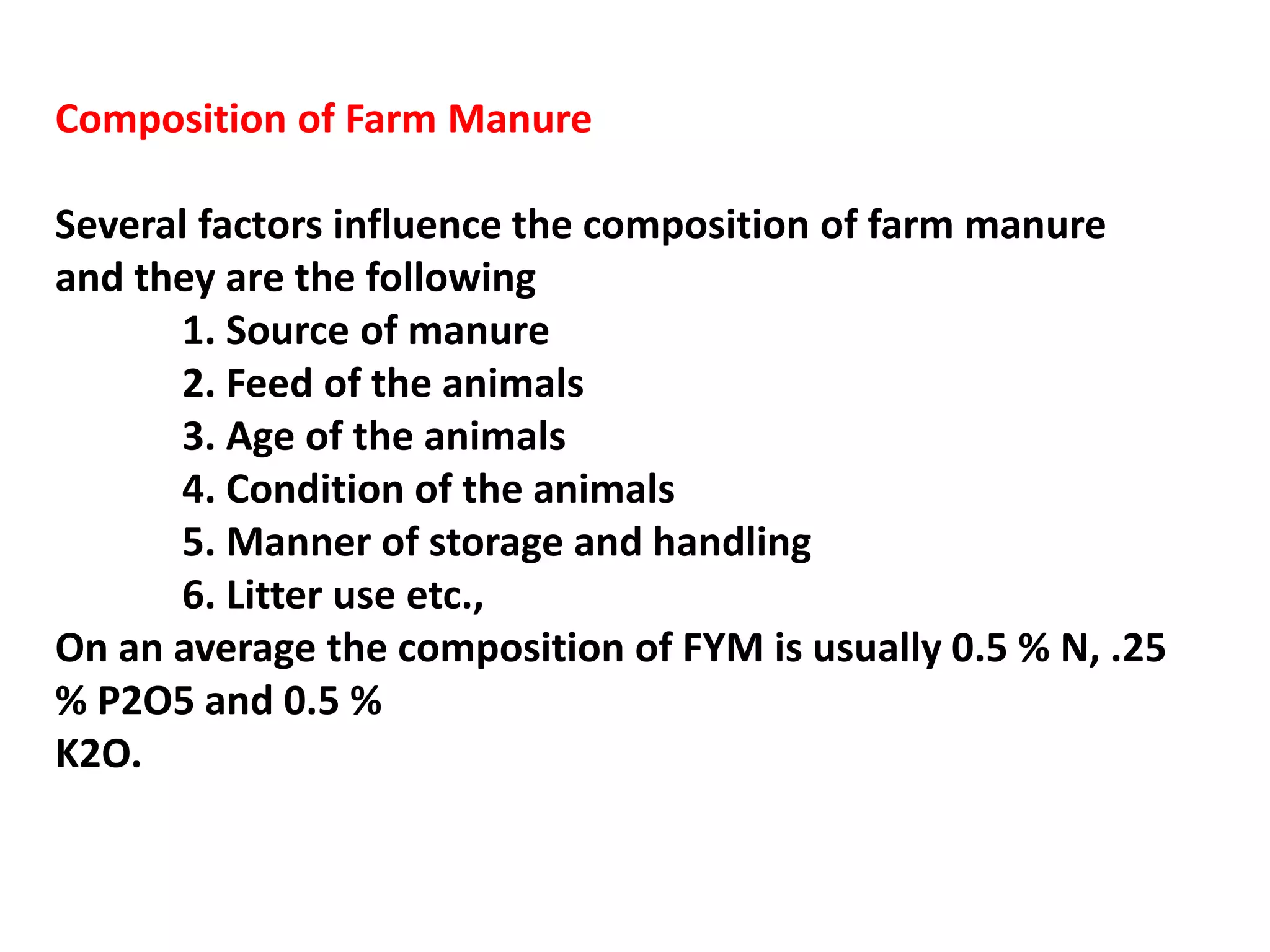
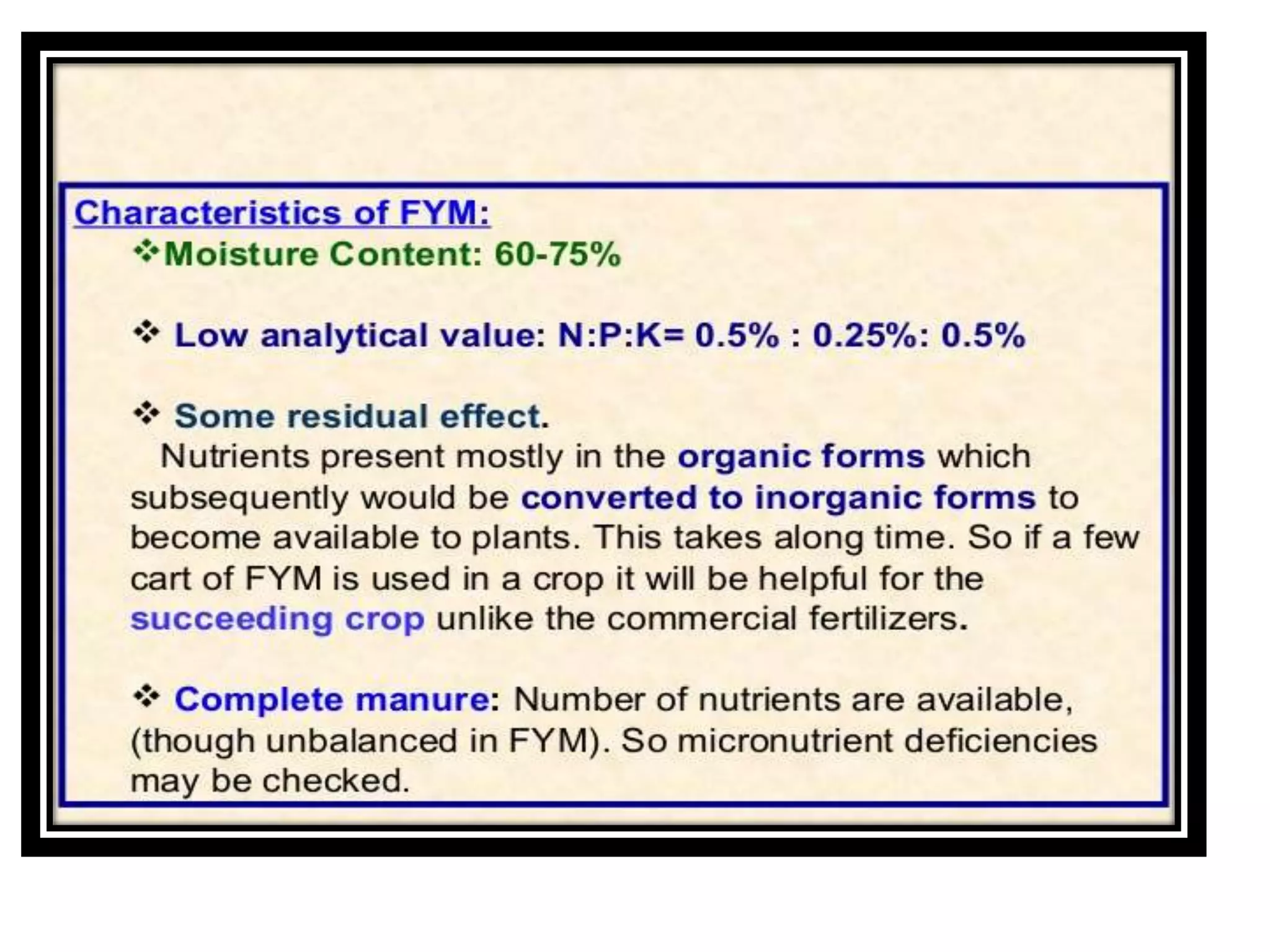
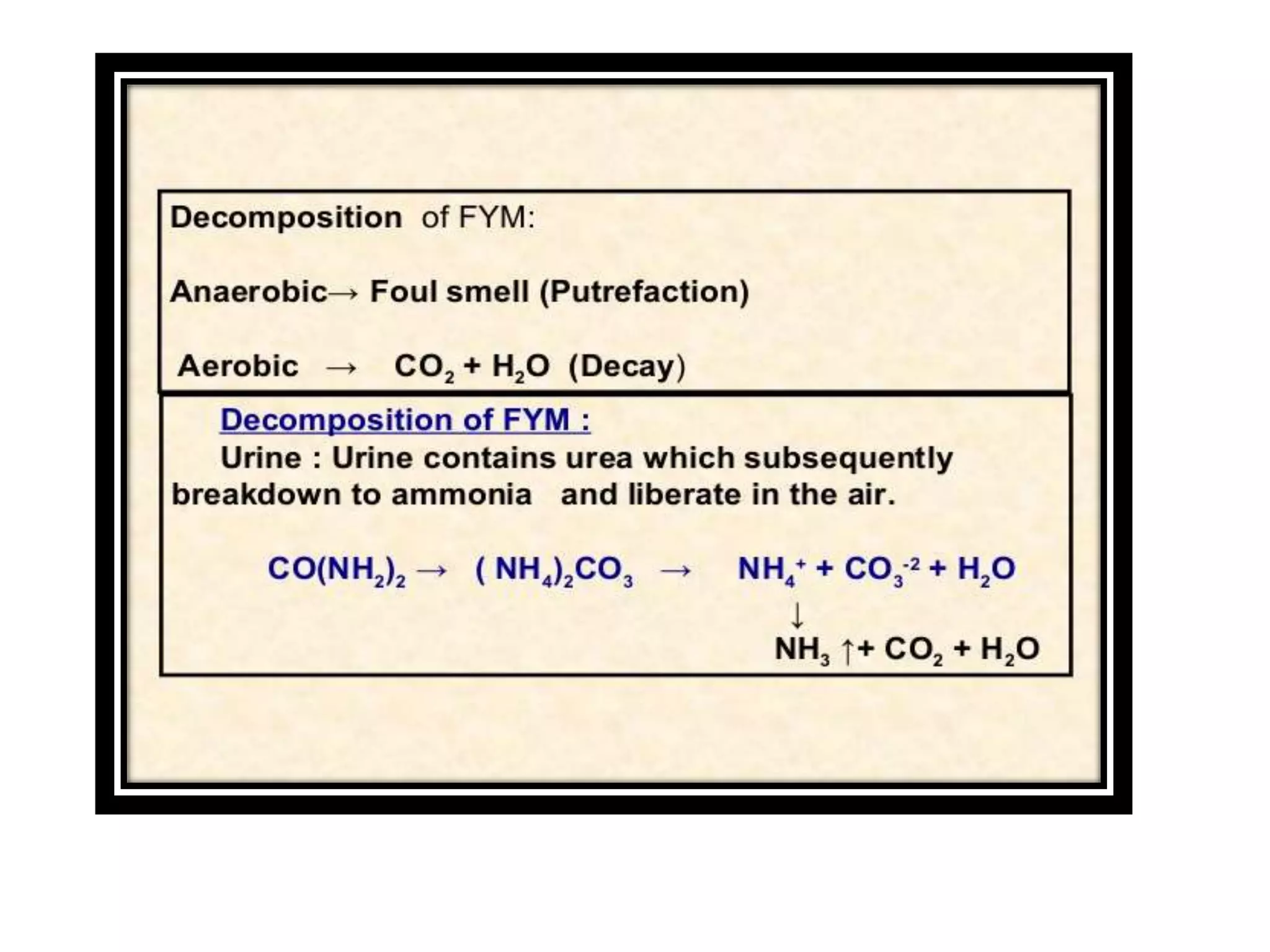
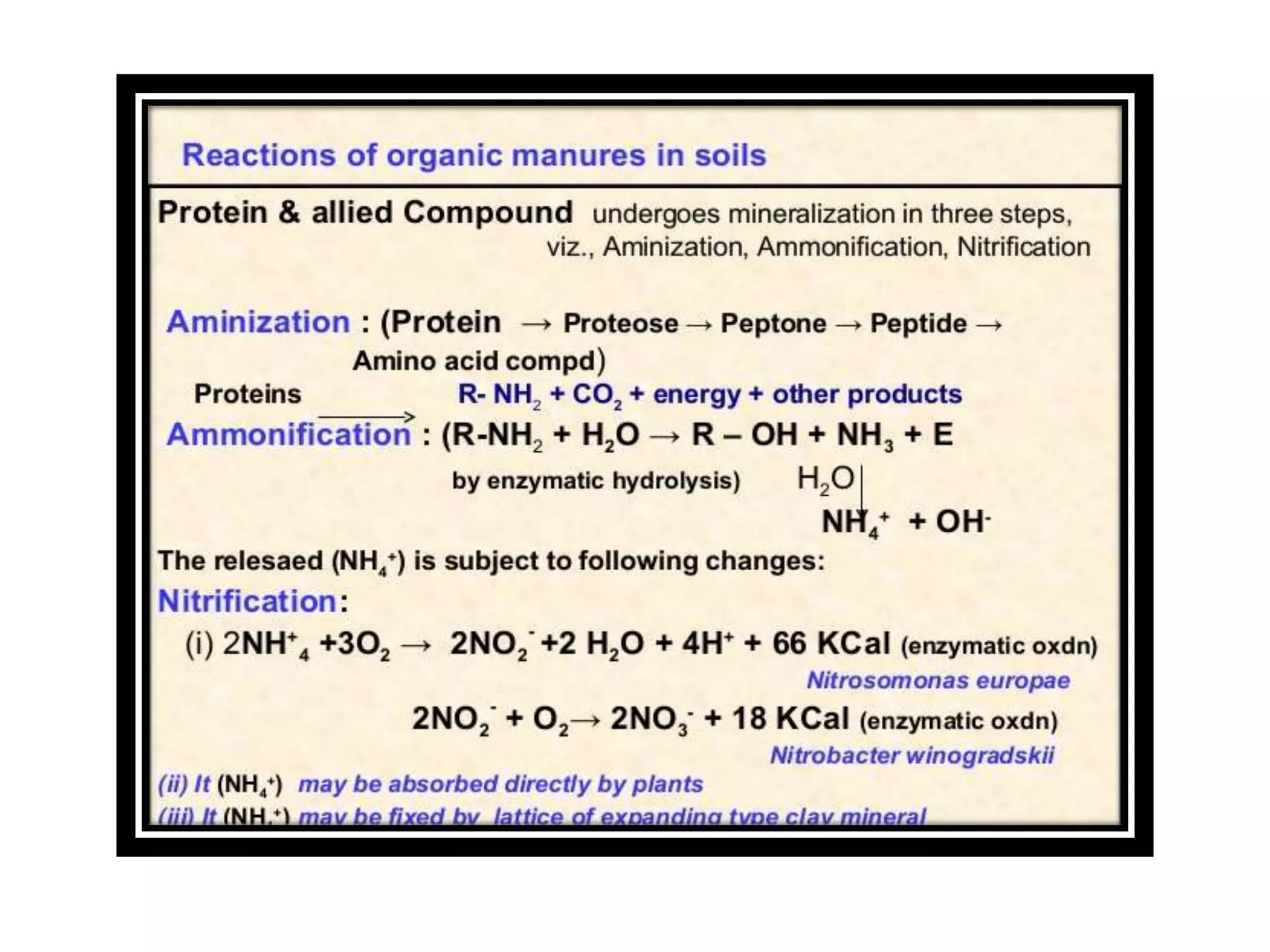
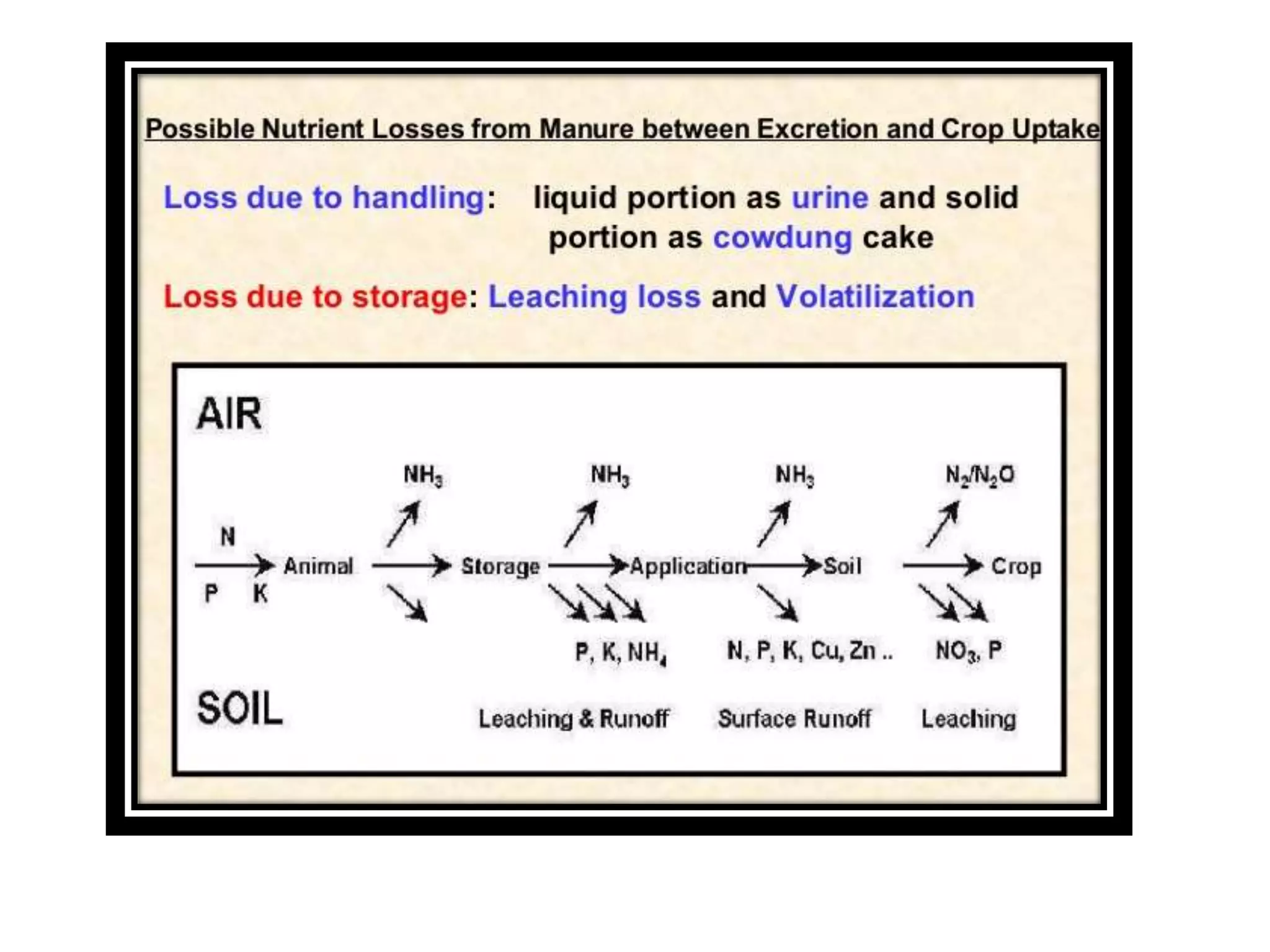
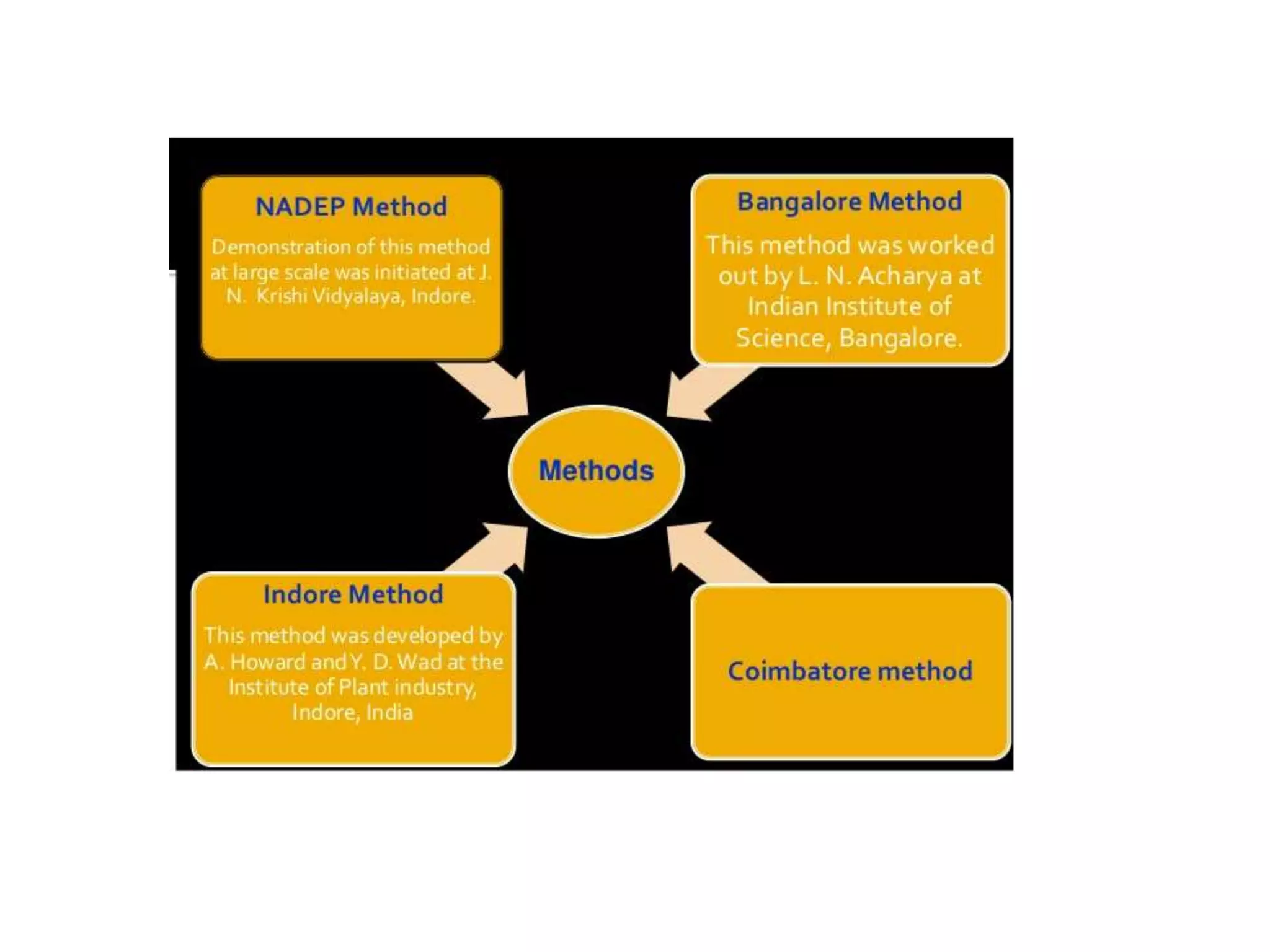
The document discusses the classification, properties, and nutrient availability of bulky and concentrated organic manures, including their preparation and composting processes. It outlines differences between organic and inorganic manures, the intricacies of composting (both aerobic and anaerobic), and factors that affect decomposition like aeration, moisture, and temperature. Additionally, it details the composition of farm yard manure (FYM) and the influences on its quality.