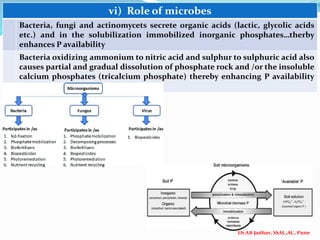
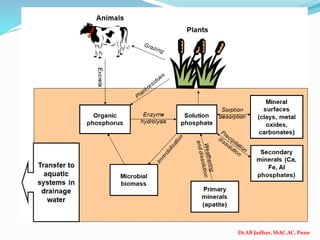
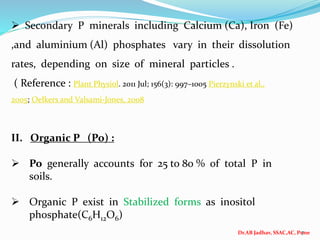
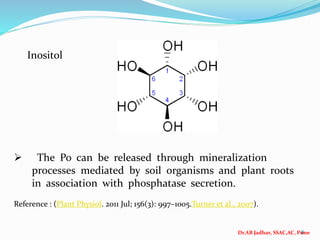
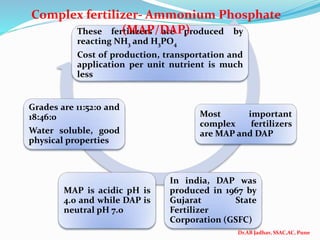
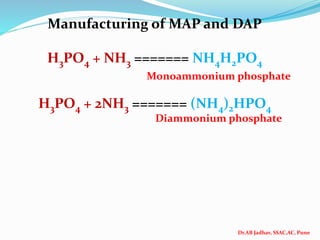
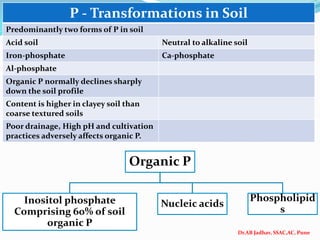
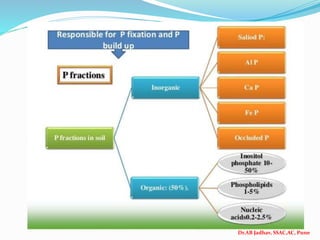
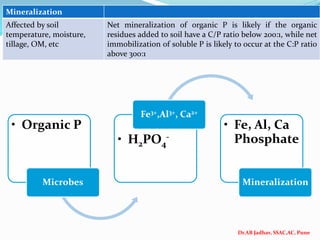
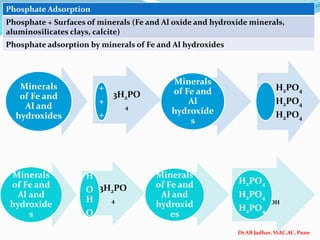
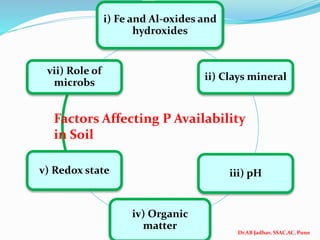
The document discusses phosphorus and phosphatic fertilizers. It begins with an introduction to phosphorus as a macronutrient for plants and describes how it exists in different forms in soils, including inorganic and organic phosphorus. It then discusses the production processes for common phosphatic fertilizers like single super phosphate (SSP), triple super phosphate (TSP), and ammonium phosphates (MAP and DAP). The document outlines the chemical reactions involved in the manufacture of these fertilizers. It also addresses phosphorus transformations in soil, including mineralization, immobilization, adsorption, and the factors that influence phosphorus availability.















![Dr.AB Jadhav, SSAC,AC, Pune
In the early days P-fertilizers
were manufactured from bones.
P-fertilizers are now
manufactured from rock-
phosphate mineral source found
in igneous, sedimentary and
metamorphic
Minerals bearing P are
apatite (Major), quartz,
silicates, carbonates,
sulphates, sesquioxides, etc.
Two imp. Material required
for P-fertilizer production
are rock phosphate (32%
P2O5) and H2SO4
Commercial rock phosphates
types
1) Fluorapatite [Ca10(PO4)6F2)]
2) Hydroxyapatite [Ca10(PO4)6
(OH2)]
3) Chloroapatite [Ca10(PO4)6 (Cl2)]
Now SSP is being replaced by
DAP as high analysis
fertilizers
Phosphatic Fertilizers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soils502lectureno1822phosphorus-210903083616/85/Soils-502-lecture-no-18-22-phosphorus-19-320.jpg)
![Dr.AB Jadhav, SSAC,AC, Pune
Furnace (Thermal)
Process
Apatite is heated to above 14000C in presence of Si and C and
reduced to elemental P in a furnace. It is then oxidized to P2O5 and
dissolved in water to form H3PO3
Heating
Ca10(PO4)6F2)] + 6 SiO2 + 15 C ===== 3 (3CaO.2SiO2) + 1.5 P4 + CaF2 +
15 CO
Apatite 14000C
P4 + 5 O2 ====2 P2O5
P2O5 + 3 H2O ==== 2 H3PO4 (Phosphoric acid)
Phosphoric acid is an important product to produce P
fertilizers
H3PO3 is produced by two processes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soils502lectureno1822phosphorus-210903083616/85/Soils-502-lecture-no-18-22-phosphorus-21-320.jpg)
![Dr.AB Jadhav, SSAC,AC, Pune
Wet Process (Acidulation
route)
Mineral acids like HNO3 or H2SO4 or HCl are reacted with apatite
to produce phosphoric acid. 90.2 % of H3PO4 comes from this
processes.
Cost of production is very less as against furnace processes.
Ca10(PO4)6F2)] + 10 H2SO4 + 20 H2O ==== 6 H3PO4 + 10
CaSO4.2H2O + 2HF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soils502lectureno1822phosphorus-210903083616/85/Soils-502-lecture-no-18-22-phosphorus-22-320.jpg)

![Dr.AB Jadhav, SSAC,AC, Pune
Finely ground rock phosphate is treated with H2SO4 in the
manufacturing of SSP and TSP
SSP
Ca10(PO4)6F2)] + 7 H2SO4 + 17 H2O ==== 3 Ca (H2PO4)2.H2O) + 7 CaSO4.2H2O
+ 2 HF
Monocalium phosphate
TSP
Ca10(PO4)6F2)] + 14 H3PO4 + 10 H2O ==== 10 Ca (H2PO4)2.H2O) +
2 HF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soils502lectureno1822phosphorus-210903083616/85/Soils-502-lecture-no-18-22-phosphorus-25-320.jpg)


![Dr.AB Jadhav, SSAC,AC, Pune
pH Form
dominat
es
Fixation
At low pH H2PO4
- P is fixed as Fe phosphate (strengite): FeIII PO4.H2O and
Al phosphate (vericite): AlPO4.2H2O
At
moderate
soil acidity
Acidic soil
HPO4
2- &
H2PO4-
At neutral
pH to
slightly
alkaline pH
HPO4
2- Soluble P is converted gradually to dicalcium phosphate
(CaHPO4.2H2O), octacalcium phosphate
[(Ca8H2(PO4)6.H2O], Tricalcium phosphate [Ca(PO4)2] and
hydroyl apatite 3[Ca3(PO4)2] which decreases solubility
abd P availability decreases.
Ca-P > Al-P > Fe-P
iii) pH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soils502lectureno1822phosphorus-210903083616/85/Soils-502-lecture-no-18-22-phosphorus-36-320.jpg)