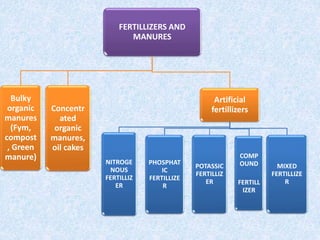
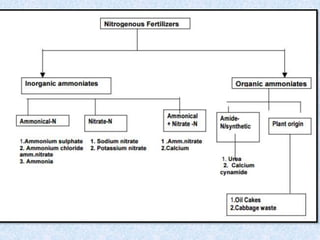
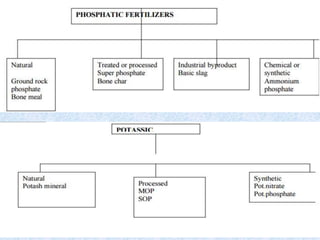
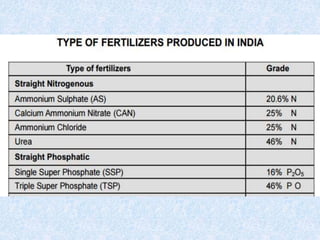
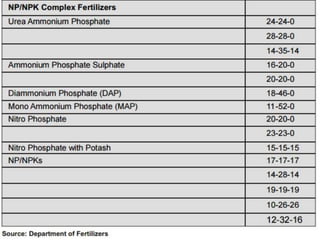
Fertilizers are substances added to soil to provide elements necessary for plant growth. They can be inorganic, organic, or synthetic and are classified based on composition, physical form, and effect on soil pH. Fertilizers are categorized as straight, complex, or mixed based on nutrient composition and as solid, liquid, or gas based on physical form. They are also classified as acid-forming, base, or neutral based on their effect on soil acidity. Micronutrient fertilizers provide essential trace elements needed by plants such as iron, manganese, zinc, and copper.