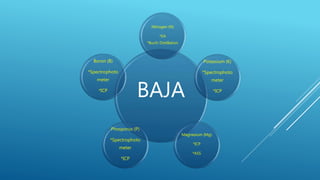
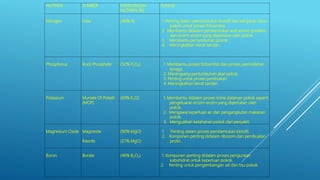
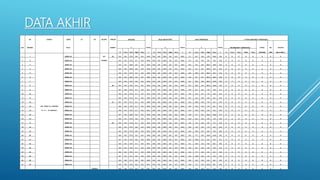
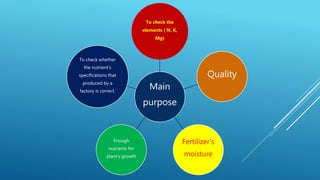
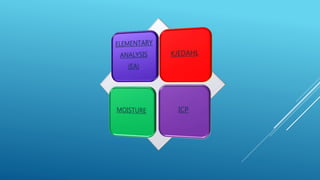
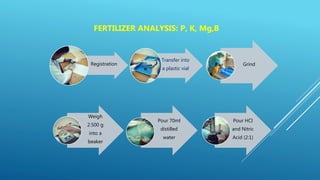
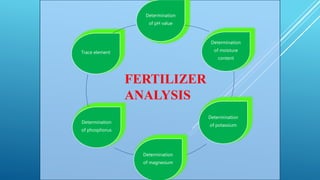
The document discusses fertilizer analysis conducted at a laboratory. Various methods are used to analyze the nutrient content of fertilizer samples, including elemental analysis, particle size analysis, moisture content testing, and inductively coupled plasma analysis. The laboratory aims to ensure fertilizers meet specified nutrient levels to effectively support plant growth and development.