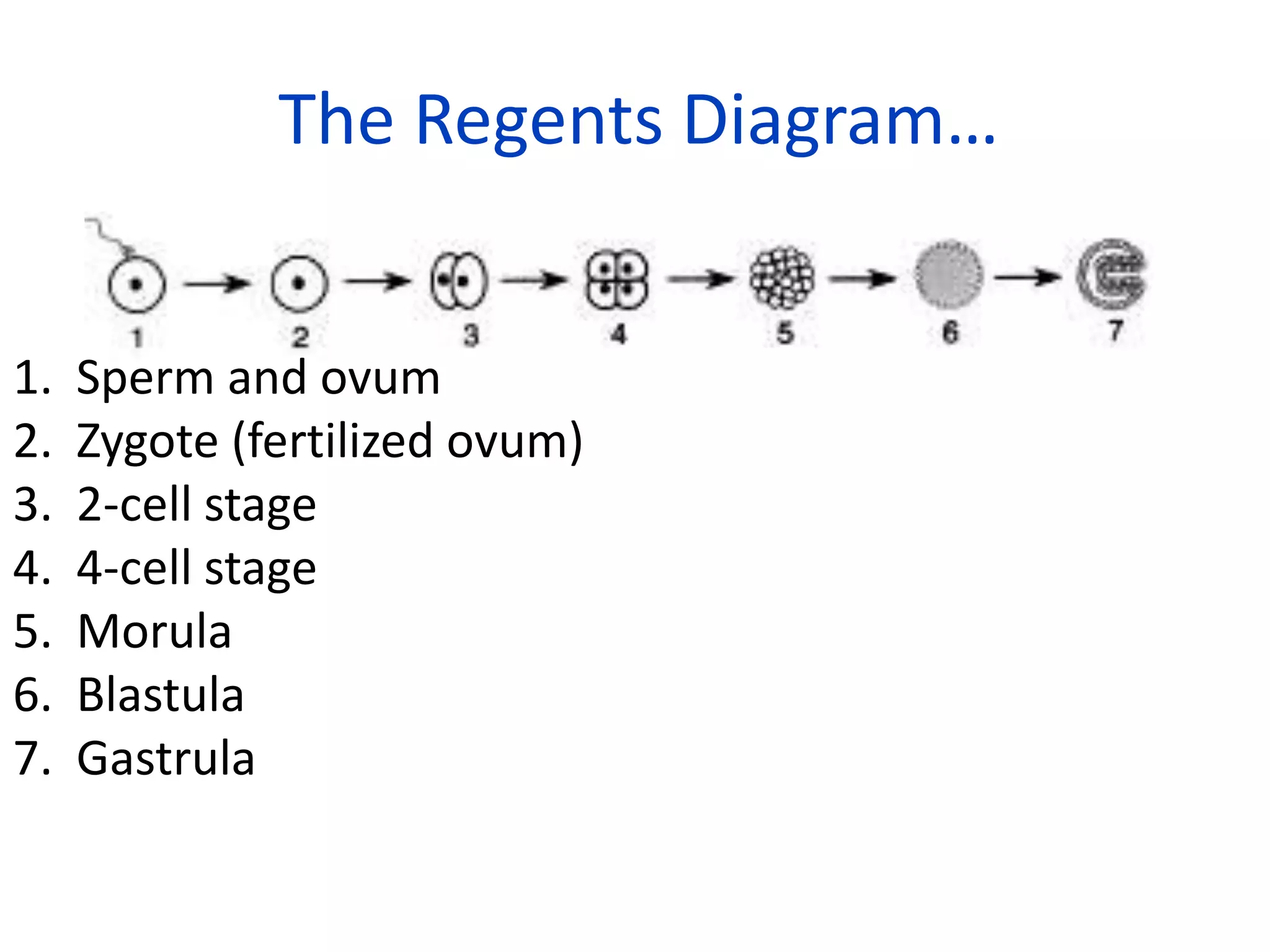
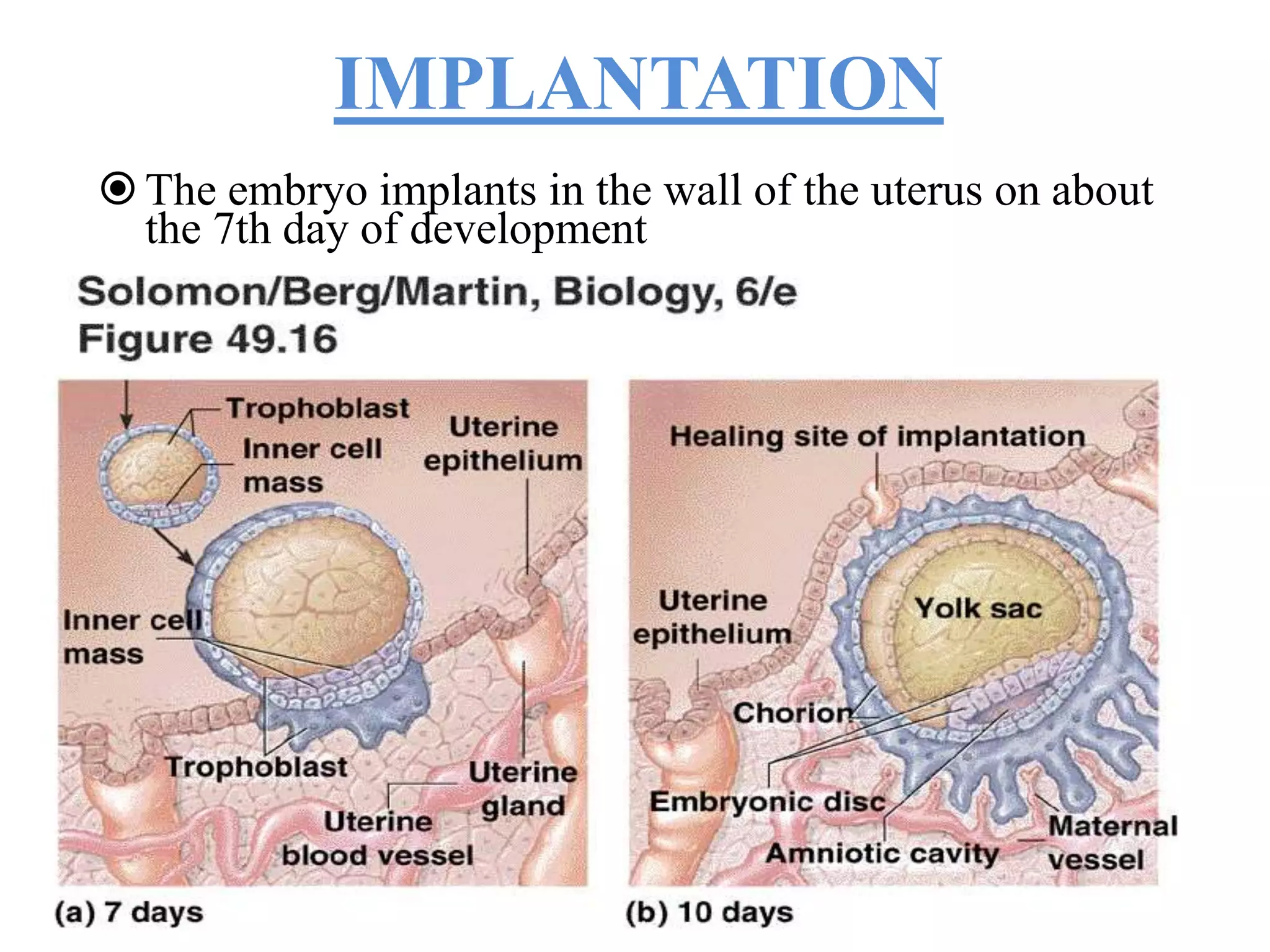
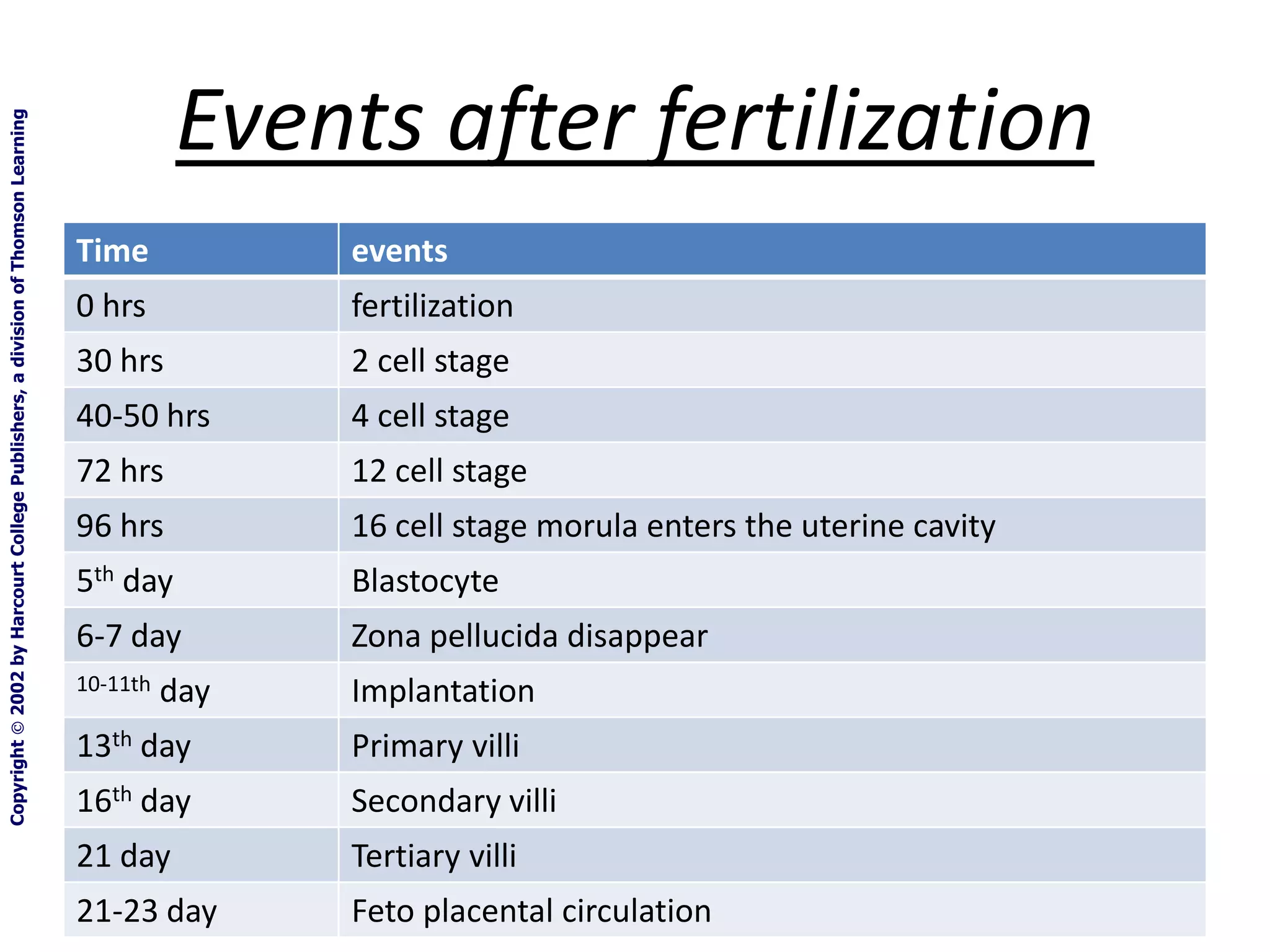
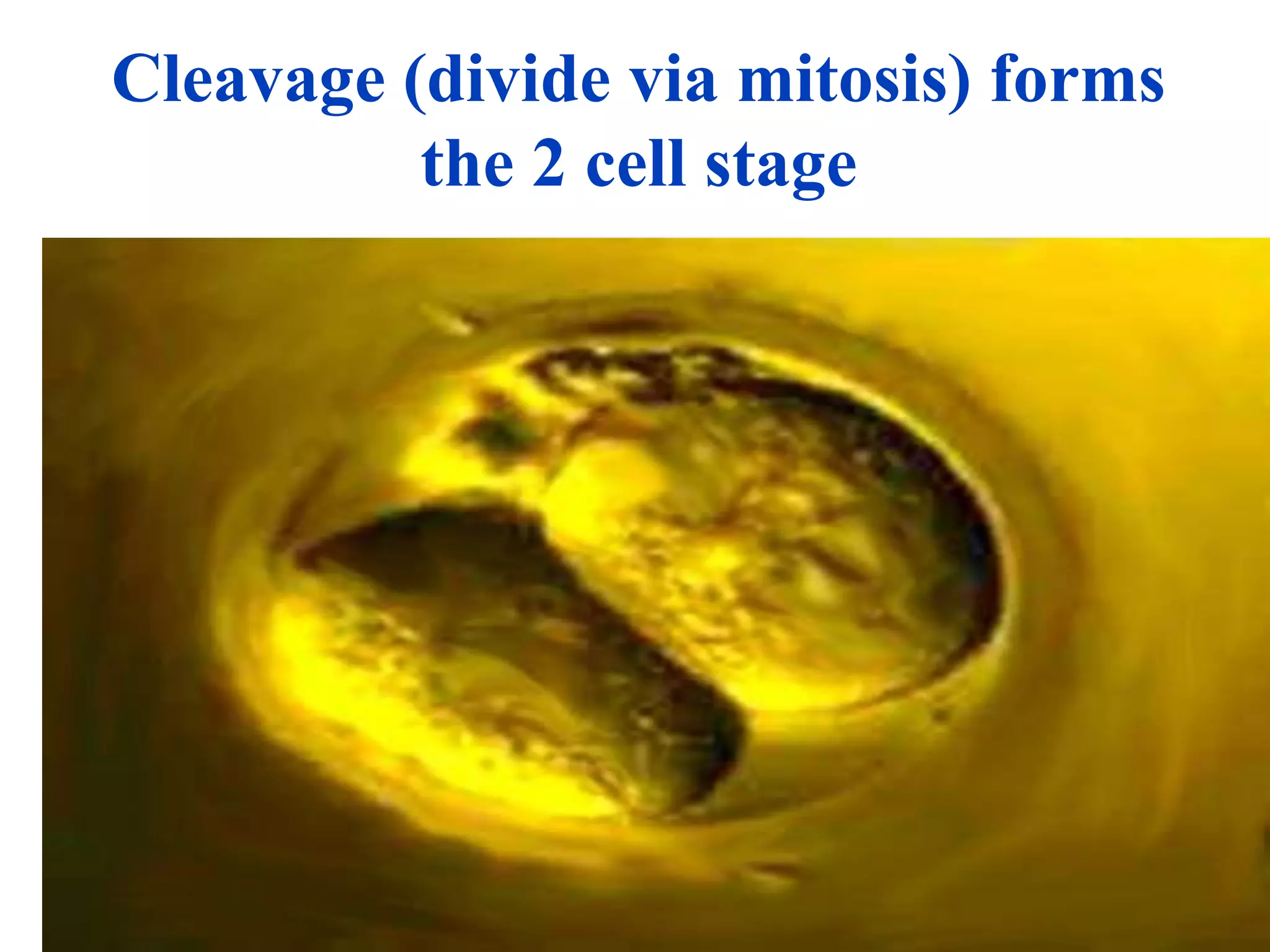
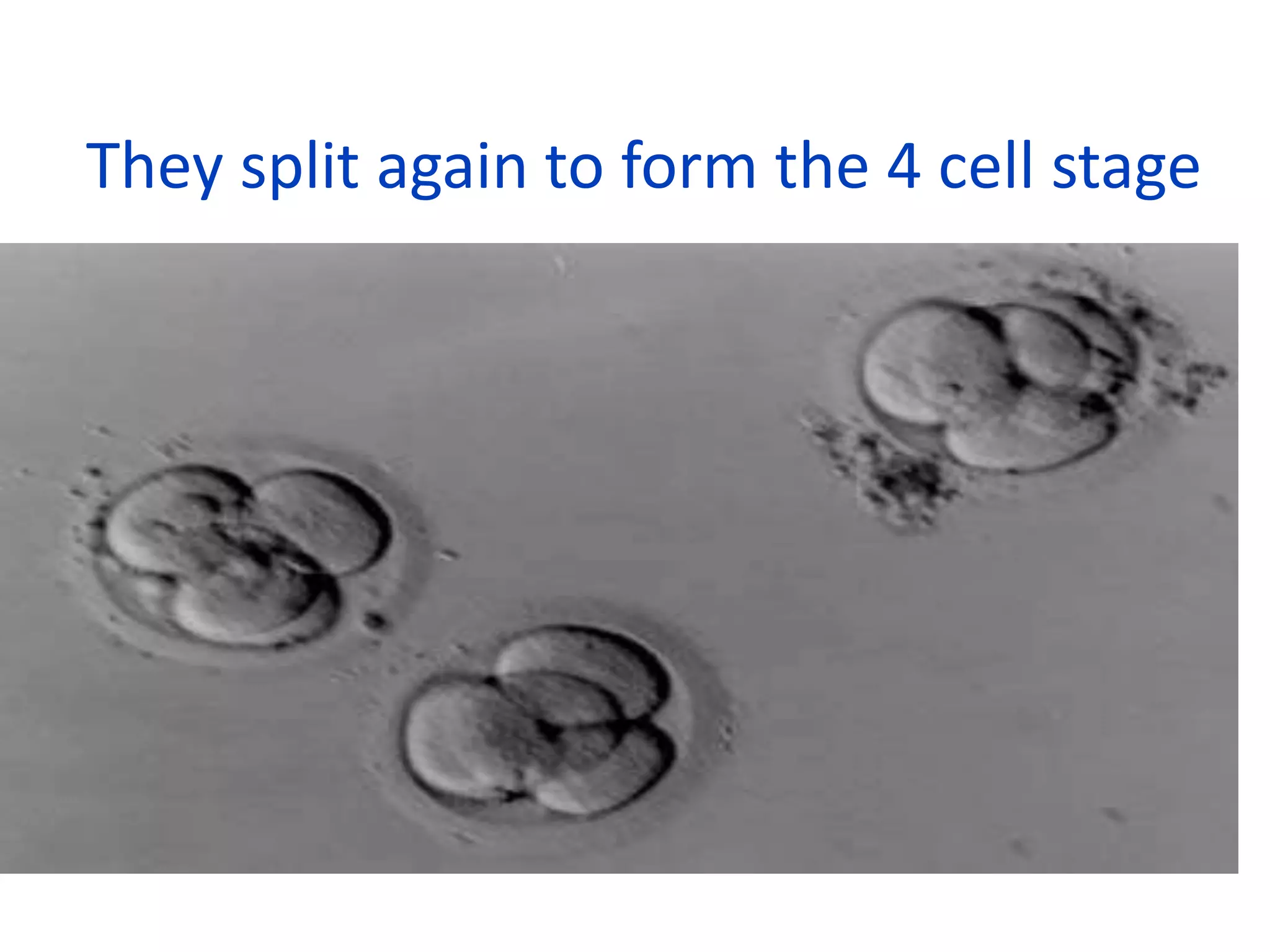
Fertilization occurs when a sperm enters an ovum and their nuclei fuse to form a zygote with 46 chromosomes. This takes place in the fallopian tubes. The zygote then undergoes cell division, forming a morula, blastula, and gastrula. During the gastrula stage, the three germ layers form - ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm - which will give rise to the embryo's organs and tissues. The blastocyst then implants in the uterus, where the placenta develops to support fetal development over the following months.








![STRUCTURE DEVELOP FROM BLASTULA
1. OUTER LAYER-PLACENTA & CHORIon IT
HAVING TWO LAYER
– Syncyti trophoblast[outer]-provide nutrient to
maternal blood
– Cyto trophoblast[inner]-secrete hormone hcg
2. Inner cell mass](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fertilization-200412112709/75/Fertilization-12-2048.jpg)