The document summarizes the key stages of fertilization and embryonic development in humans. It describes:
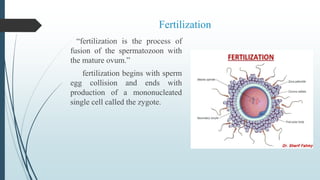
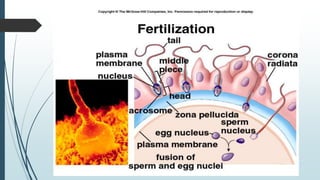
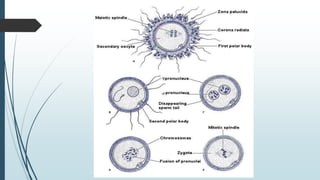
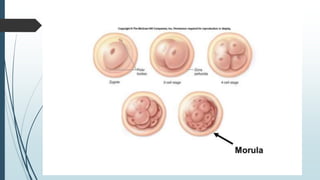
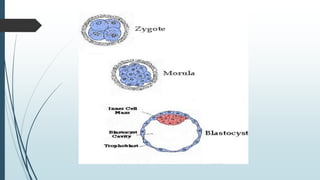
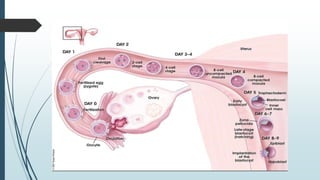
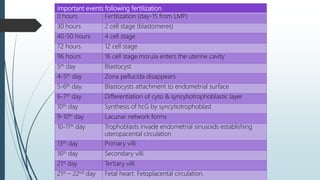
1) Fertilization occurring when the sperm fuses with the ovum in the fallopian tube to form a zygote, which undergoes cell division over several days to become a morula and then a blastocyst.
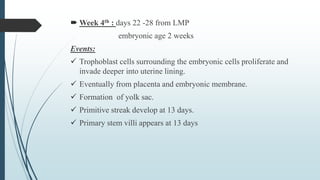
2) The blastocyst implants in the uterine wall and the trophoblast develops to form the placenta, while the inner cell mass forms the embryo and its structures.
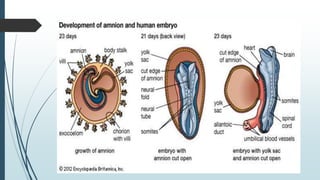
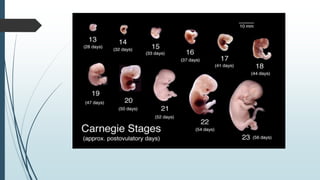
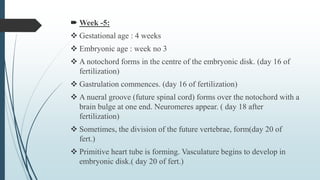
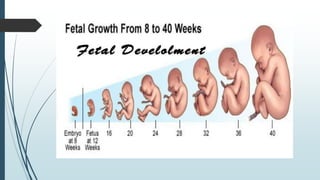
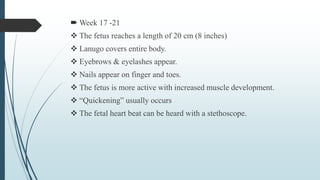
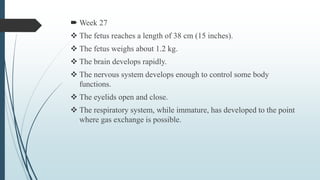
3) It outlines the major developmental milestones from weeks 3-31, including organ formation, growth of limbs and senses, and increasing activity of the fetus.