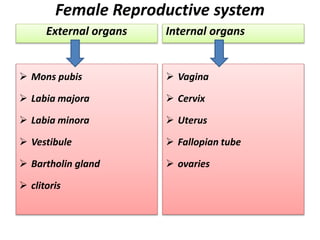
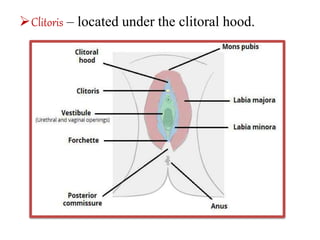
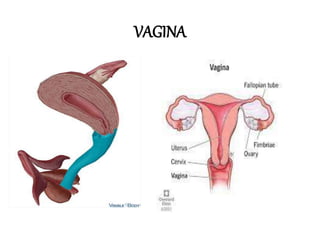
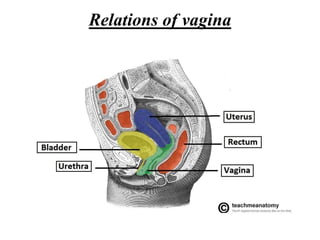
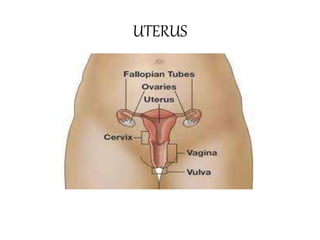
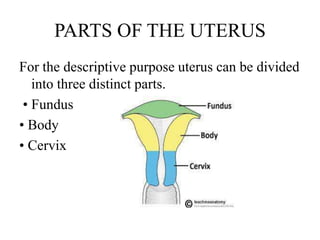
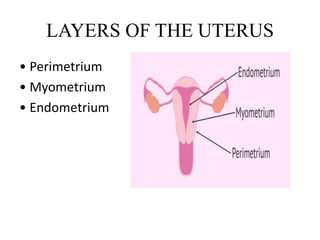
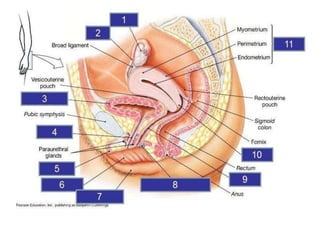
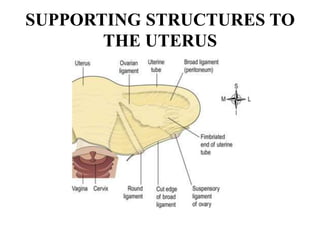
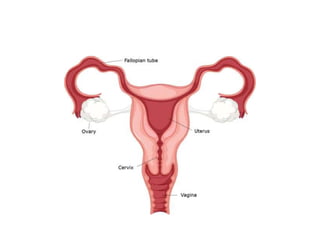
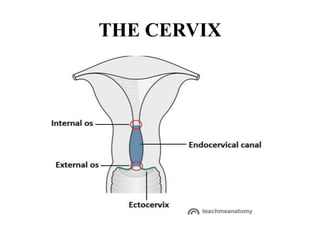
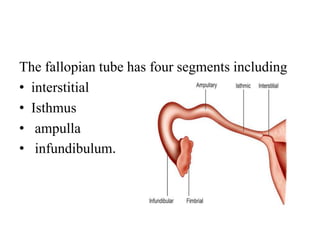
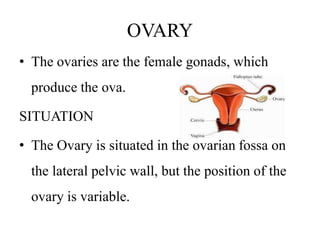
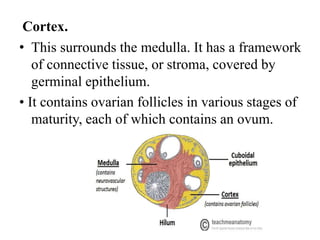
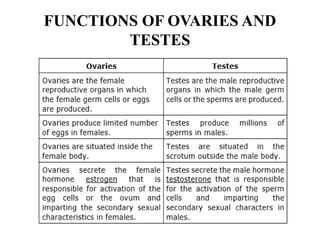
The female reproductive system has both external and internal organs that work together to produce eggs, secrete hormones, provide a site for fertilization and gestation, and enable childbirth. The external organs include the vulva and internal organs include the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. The ovaries produce eggs and female hormones, the fallopian tubes transport eggs to the uterus, and the uterus nourishes a fetus and enables birth. Together these organs allow for reproduction and continuity of the human species.