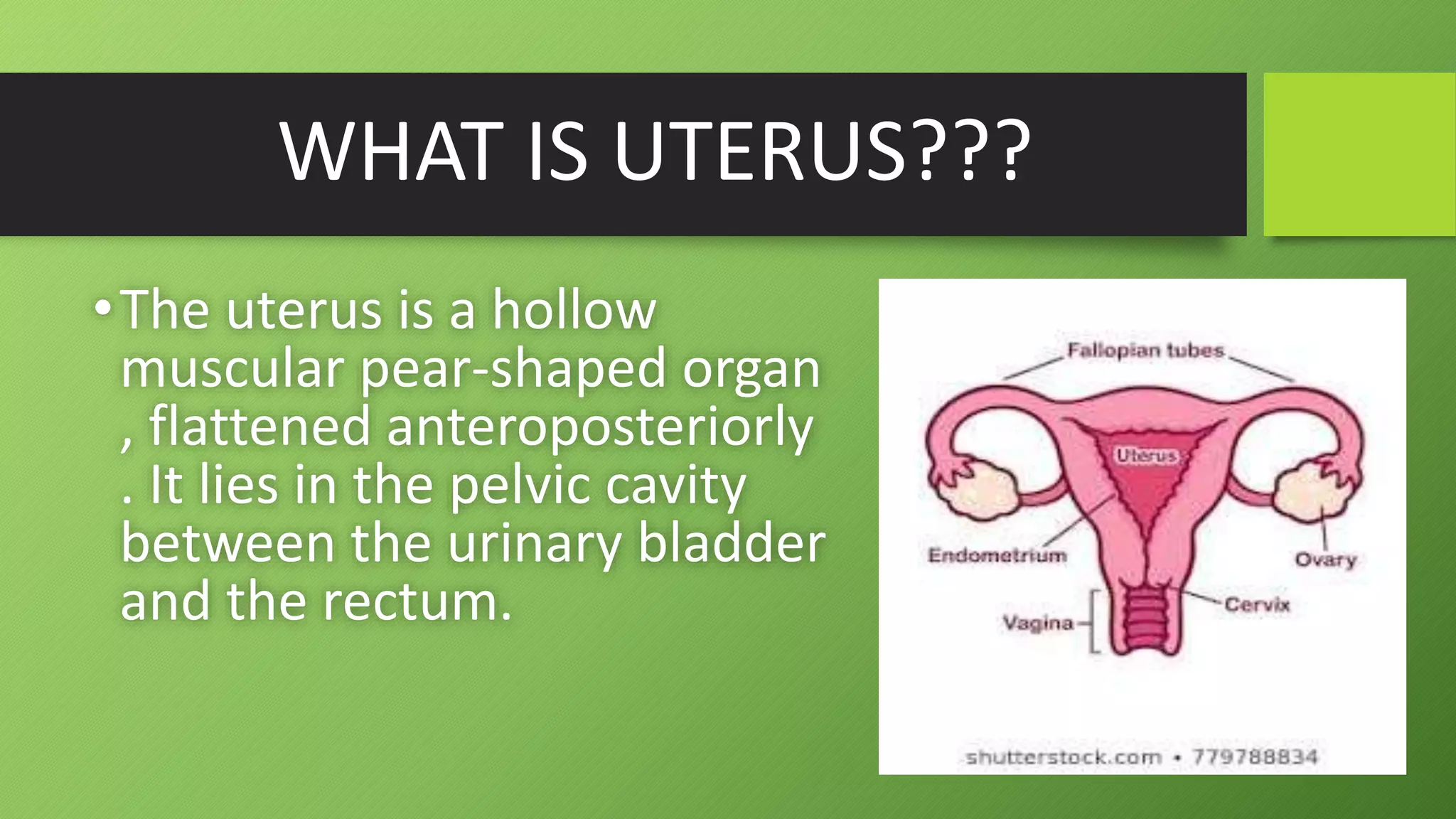
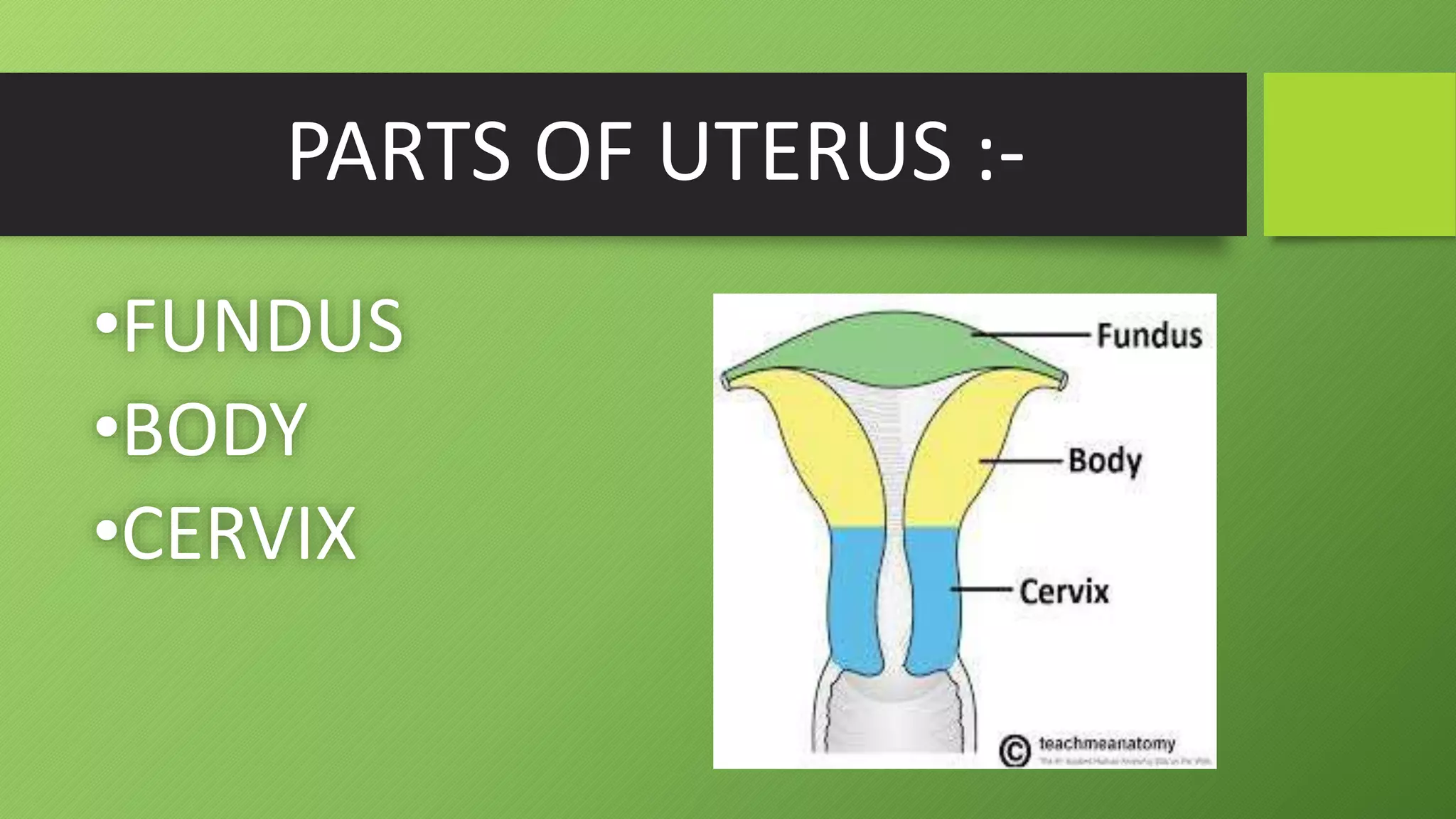
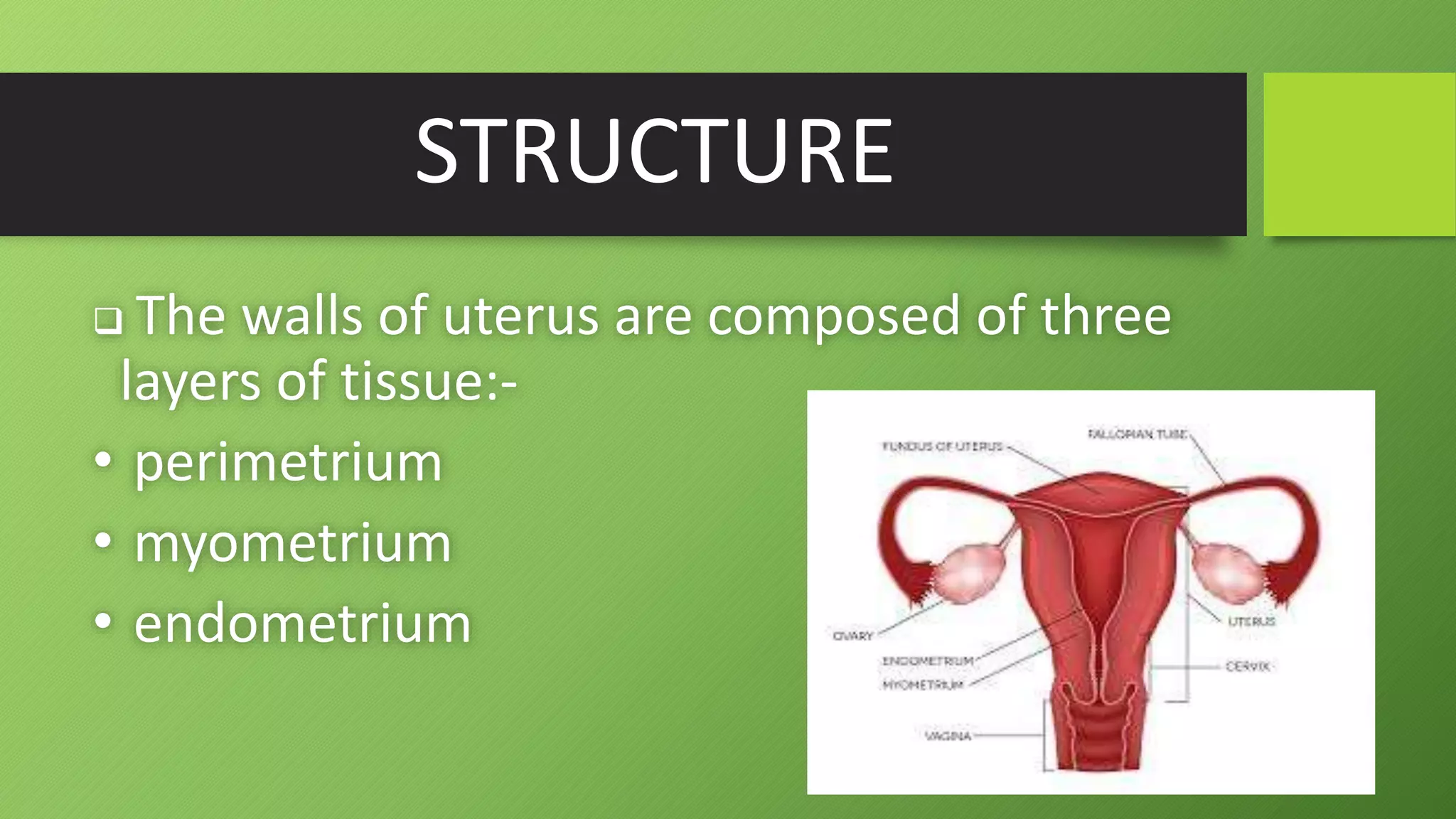
The uterus is a pear-shaped, hollow muscular organ located in the pelvic cavity between the bladder and rectum. It is about 7.5cm long and 5cm wide. The uterus has three layers - an outer layer called the perimetrium, a thick middle muscular layer called the myometrium, and an inner mucus membrane layer called the endometrium. The uterus houses and nourishes a fertilized egg until childbirth. Problems with the uterus may cause abnormal bleeding.