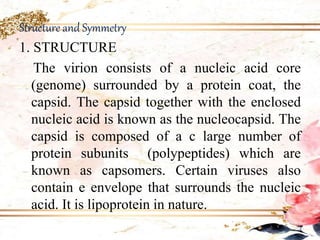
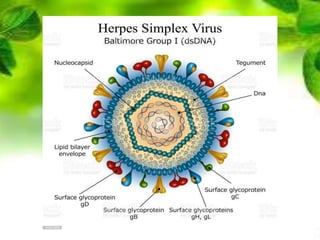
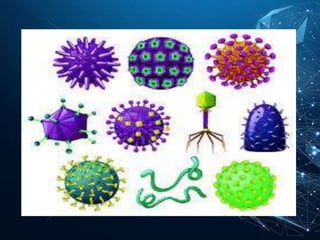
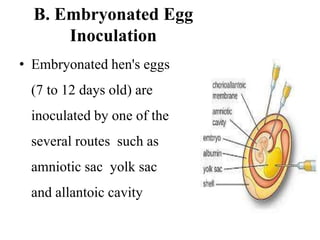
Viruses are the smallest infectious agents that can only replicate inside host cells. They contain either DNA or RNA, but lack the cellular machinery to reproduce. Viruses come in a variety of shapes and sizes, with capsids composed of protein subunits that surround the viral genome. They are cultivated by infecting animals, eggs, or cell cultures. Laboratory diagnosis of viral infections involves directly observing viruses, isolating them in culture, or detecting antibodies produced in response to infection. Viruses are classified based on their nucleic acids and other properties.