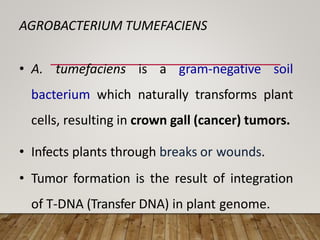
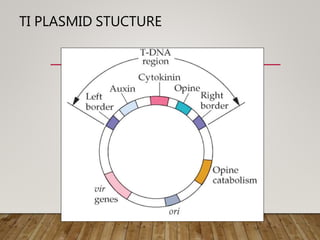
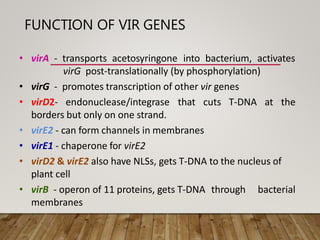
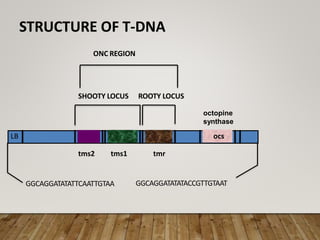
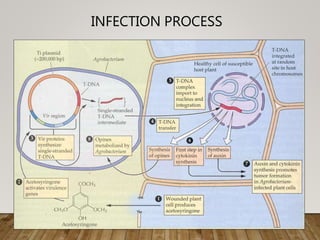
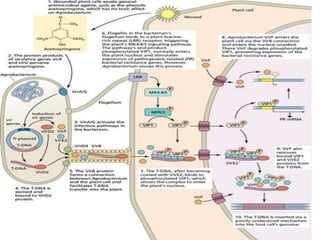
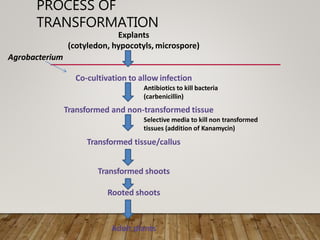
This document summarizes Agrobacterium tumefaciens and its Ti plasmid, which are used in plant genetic engineering. It discusses that A. tumefaciens naturally infects plant cells and transfers T-DNA from its Ti plasmid into the plant genome, causing crown gall tumors. The Ti plasmid contains virulence genes that are activated by plant signals and help transfer T-DNA. Disarmed Ti plasmids, lacking tumor-causing genes, are used as vectors to insert foreign DNA into plant cells via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, involving co-cultivation of plant explants with Agrobacterium and selection of transformed tissues.