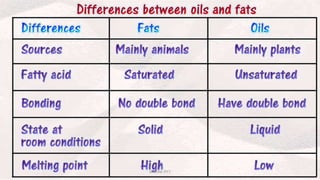
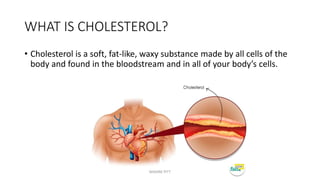
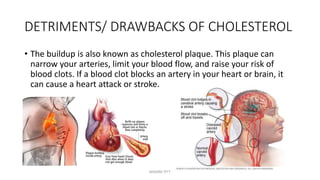
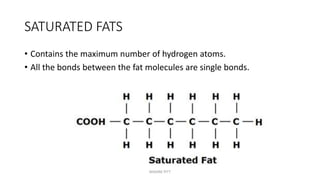
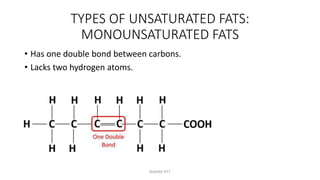
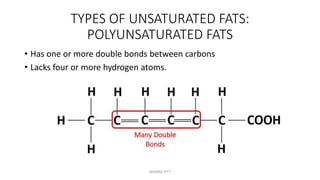
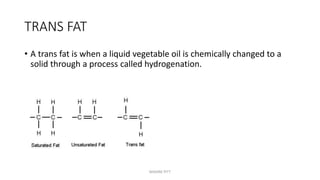
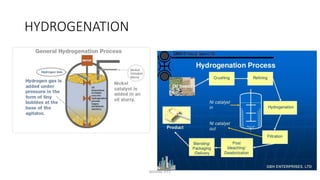
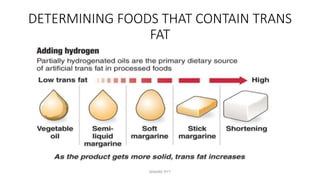
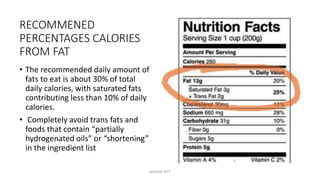
Triglycerides are the main type of lipid and are composed of glycerol bonded to three fatty acids. Triglycerides serve as energy stores and insulation. Phospholipids are another type of lipid and are the main component of cell membranes. Cholesterol is an important steroid and is either carried by HDL (good cholesterol) or LDL (bad cholesterol). Fats are classified as saturated, monounsaturated, or polyunsaturated depending on the structure of their fatty acids. Unsaturated fats are preferable to saturated fats as they may help improve cholesterol levels.