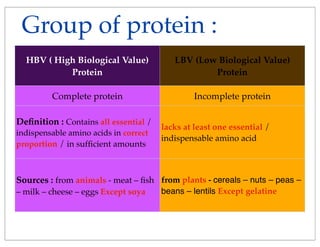
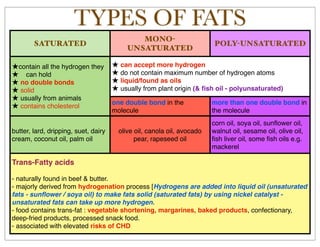
Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and fatty acids are the main macronutrients. Carbohydrate and protein deficiencies can cause weakness, hypoglycemia, and delayed healing. Excess protein is removed by the liver and kidneys. There are different types of fats including saturated, monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, and trans fats. Fats provide energy, cushion organs, aid vitamin absorption, and carry flavor, but high saturated fat intake increases disease risk. Essential fatty acids must be obtained through diet for brain and heart health. Ways to reduce fat intake include limiting red meat and fried foods in favor of plant oils, and choosing low-fat dairy and spreads.