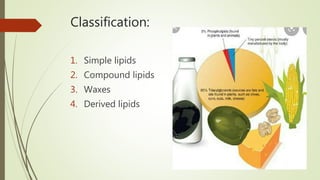
This document discusses lipids (fats) including their composition, classification, functions, sources, and deficiencies. Lipids are comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and provide 9 calories per gram. They are classified as simple lipids, compound lipids, waxes, and derived lipids. The main lipids in diet are triglycerides, phospholipids, and sterols. Triglycerides make up 95% of dietary and body lipids and are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids. Phospholipids are important structures in membranes. Sterols are precursors to bile acids and sex hormones. Fats have many important functions like being an energy source and aiding vitamin absorption. Deficiencies can cause skin disorders like