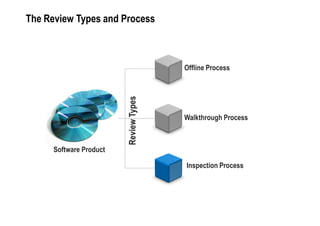
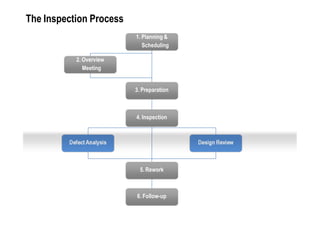
Fagan Inspection is a rigorous quality control technique invented in the 1970s for inspecting software documents to find defects. It involves a team reviewing a document using a structured process with defined roles. The process includes planning, an overview meeting, individual preparation, the inspection meeting, defect analysis, rework, and follow up. When performed properly it is very effective at finding defects early. However, inspections are rarely used due to professional and organizational ignorance, difficulties in implementation, and intangible perceived benefits. Making inspections work requires addressing these challenges.