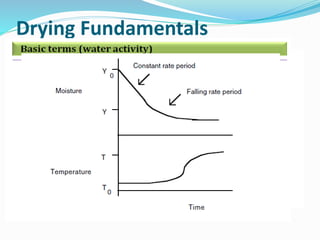
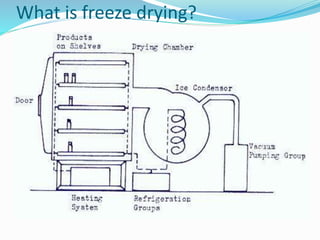
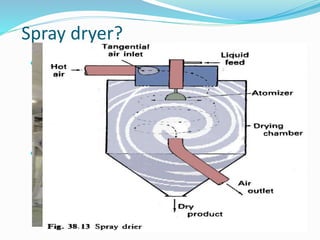
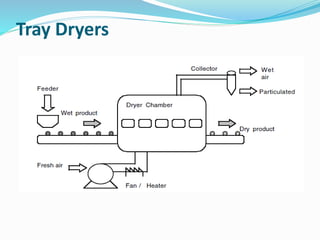
The document discusses various types of machinery used in tea production, including withering troughs, rolling machines, CTC machines, CTC rollers, and dryers. It provides details on the principles and design of withering troughs, which are used to control the withering of fresh tea leaves by managing temperature, humidity, and air flow. Tea rolling machines and CTC machines apply different processes to further prepare the leaves for drying. The document also examines freeze dryers and spray dryers as two common types of industrial dryers used in tea processing.