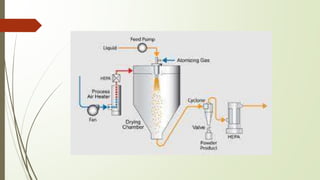
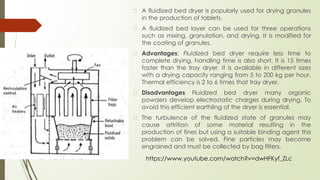
Drying is a process that removes solvent from a substance, leaving a solid end product. There are two main drying methods: thermal and non-thermal. Spray drying is a thermal drying method that uses atomization to produce liquid droplets that are dried into individual particles by hot gas. It is commonly used for drying heat-sensitive materials and can control particle properties. The spray drying process involves atomizing the liquid feed, drying the droplets in a chamber using hot air, and separating the dried product particles from the exit air.