Embed presentation
Downloaded 748 times











1. The document discusses various factors that can lead to language change over time, including sociolinguistic, psycholinguistic, and therapeutic factors. 2. Sociolinguistic factors include random fluctuations in pronunciation, the influence of fashion, foreign influence through borrowing or substratum effects, and social needs leading to changes like coinage of new words. 3. Psycholinguistic factors relate to natural tendencies in pronunciation and linking sounds, such as consonants being dropped or sounds assimilating, which can eventually lead to permanent changes in a language.












Examines origins of languages, key questions on language change, independent and dependent variables.
Discusses independent (sociolinguistic, psycholinguistic, therapeutic, chain reaction) and dependent variables.
Explores sociolinguistic changes such as random fluctuations, fashion, and foreign influences.
Details fashion in pronunciation, substratum theory, overcorrection, multilingualism and borrowing.
Discusses language coining, emphasis, and politeness as functional responses to societal needs.
Covers consonant dropping, assimilation, elision, and the natural tendencies in sound patterns.
Describes natural development in syntax and therapeutic changes for memory efficiency.
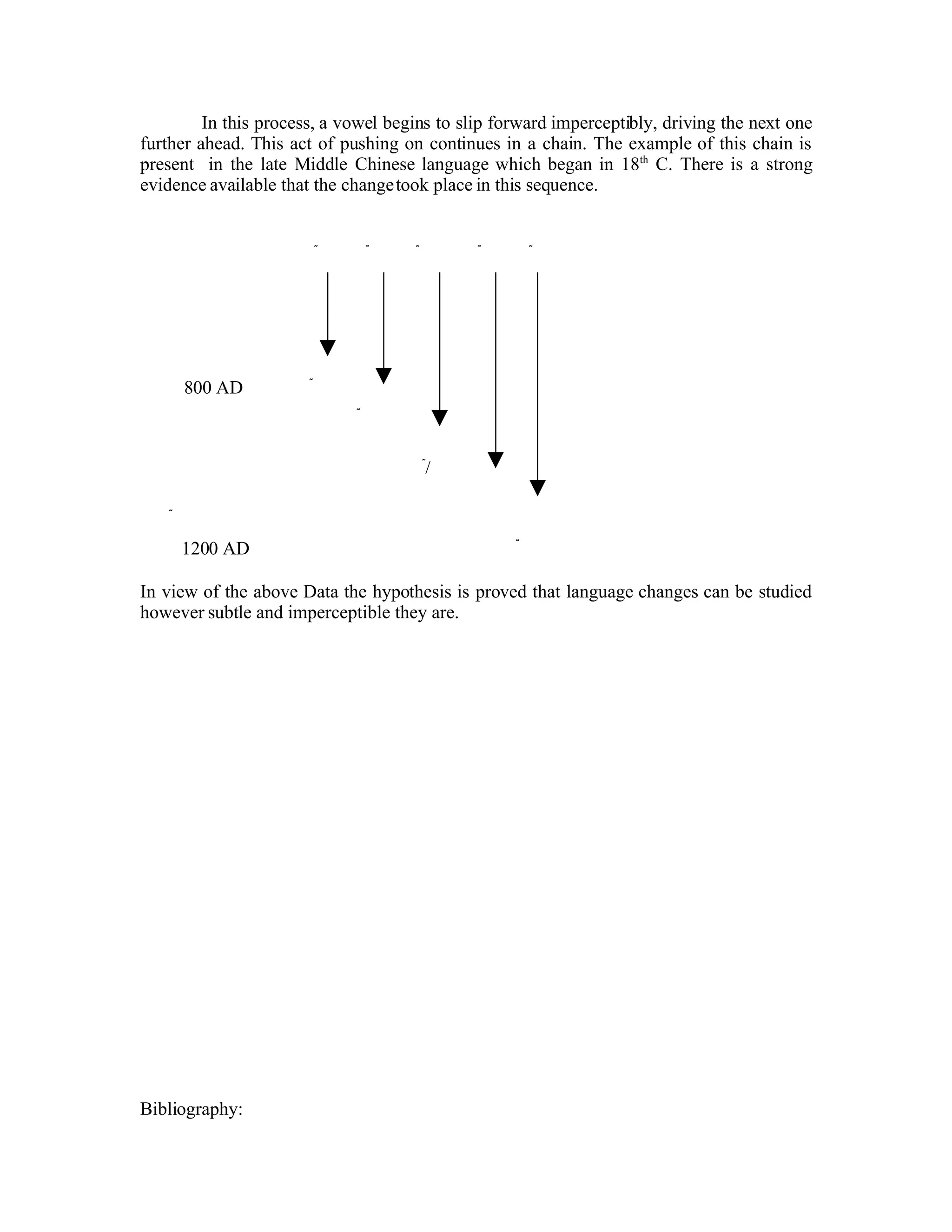
Explains therapeutic changes that lead to larger shifts, referencing Grim's law and vowel shifts.
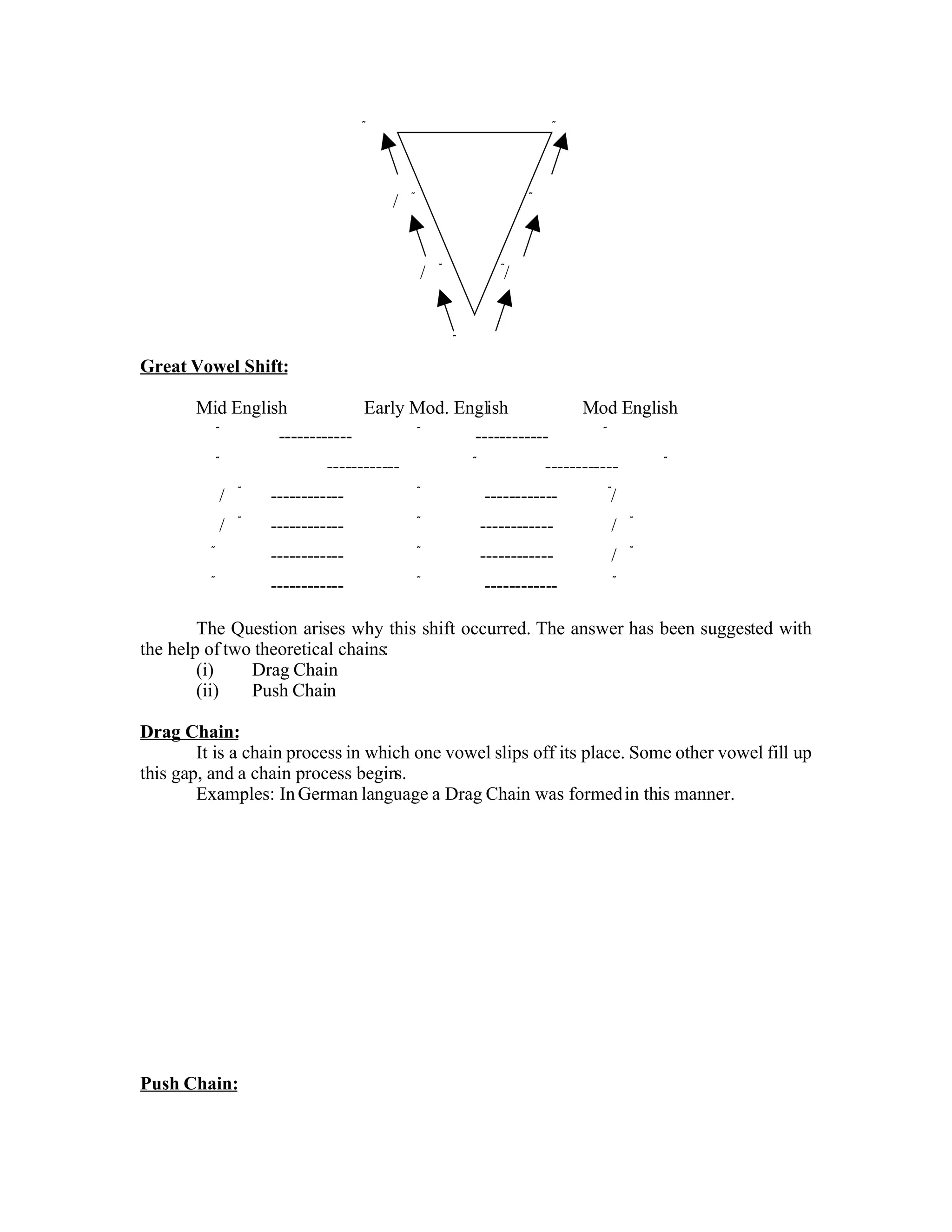
Analyzes the Great Vowel Shift and its chains, such as Drag Chain and Push Chain processes.
Reiterates the hypothesis that subtle changes in language can be studied and understood.
Lists sources referenced in the study of language change and its factors.