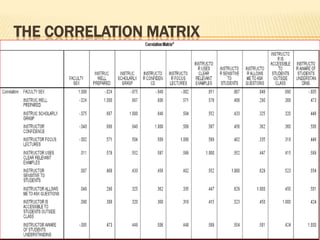
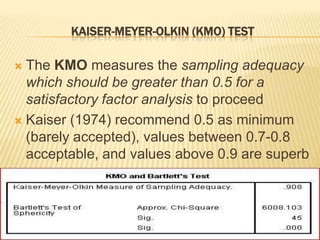
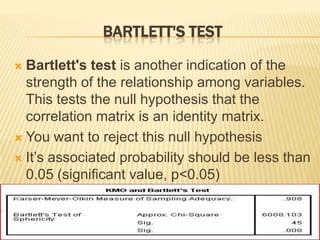
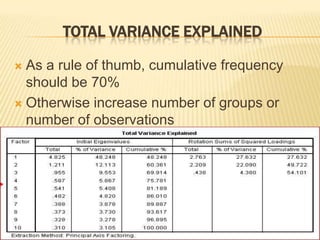
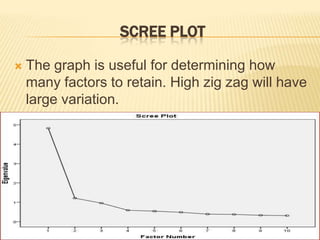
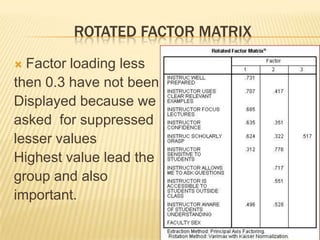
Factor analysis is a statistical method used to reduce the number of variables in a dataset by grouping correlated variables together into factors. It requires a minimum sample size of 10 observations per variable to avoid computational issues, and the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin test and Bartlett's test are used to assess the factorability of the correlation matrix. The rotated factor matrix displays the factor loadings and shows which variables group together under each factor.