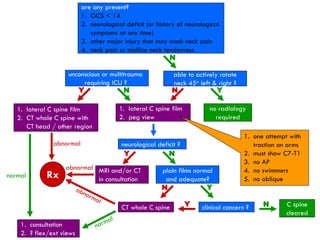
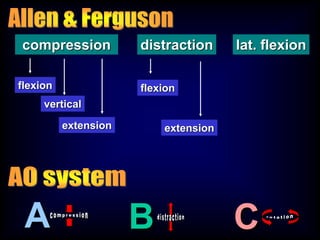
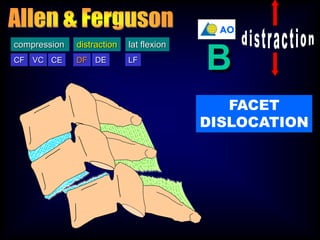
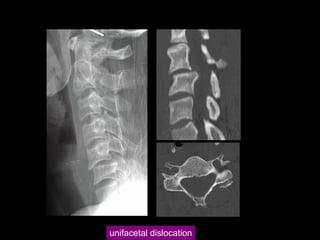
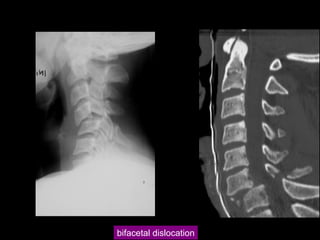
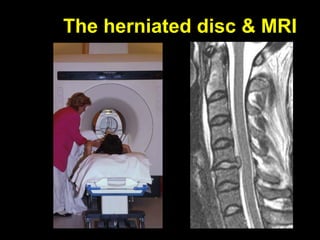
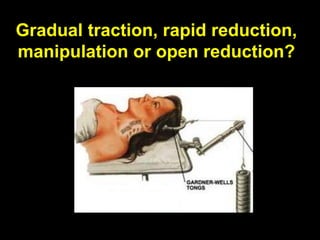
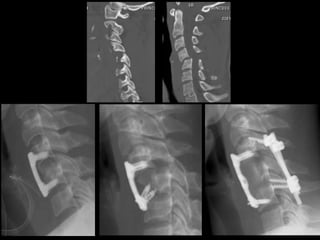
This document discusses the initial management and treatment of cervical spine facet dislocations. It provides guidelines for evaluation including imaging based on neurological status. Reduction techniques discussed include gradual traction, rapid reduction, and manipulation under general anesthesia. The role of MRI is debated, with most recommending MRI for incomplete neurological injuries before reduction. Anterior discectomy and fusion or posterior fusion are discussed as surgical stabilization options after reduction.