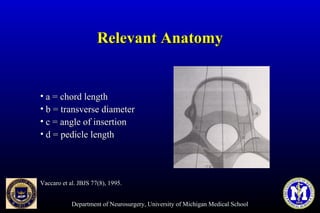
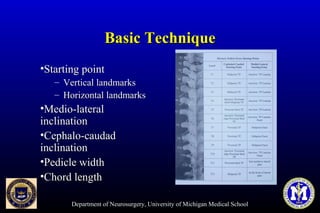
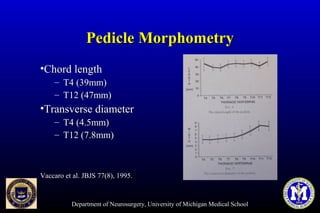
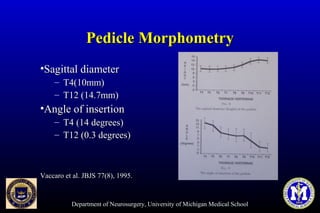
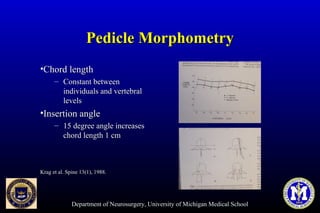
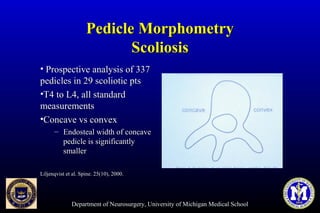
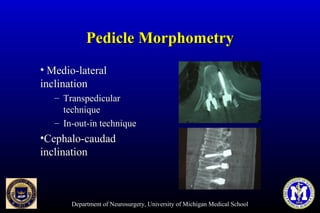
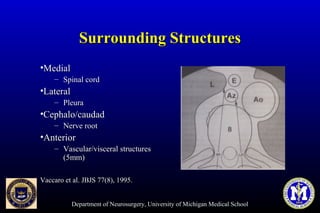
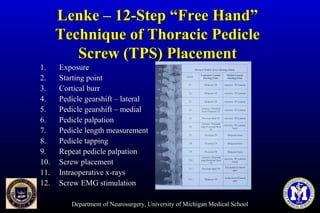
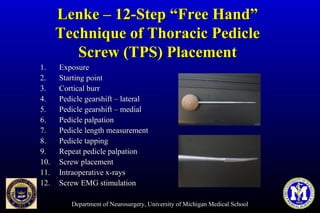
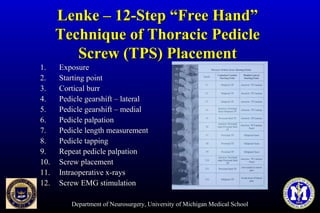
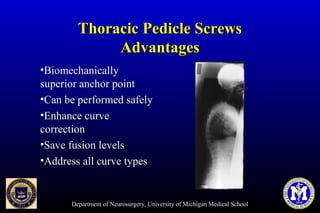
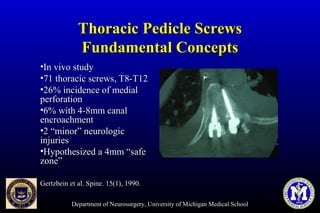
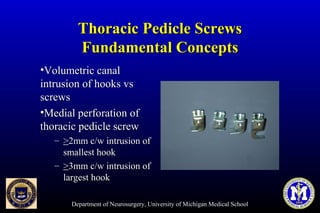
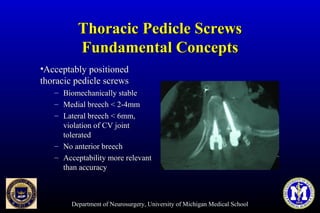
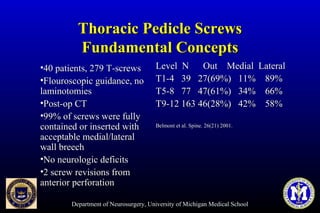
This document discusses thoracic pedicle screws for spinal fixation. It provides details on relevant anatomy, techniques for placement including free-hand and fluoroscopy-guided methods, and pedicle screw electromyography. While pedicle screws provide biomechanical advantages, the thoracic pedicles are small, requiring careful technique to minimize neurologic risks. With experience, free-hand techniques can achieve acceptable placement in most cases without breaching safety thresholds.