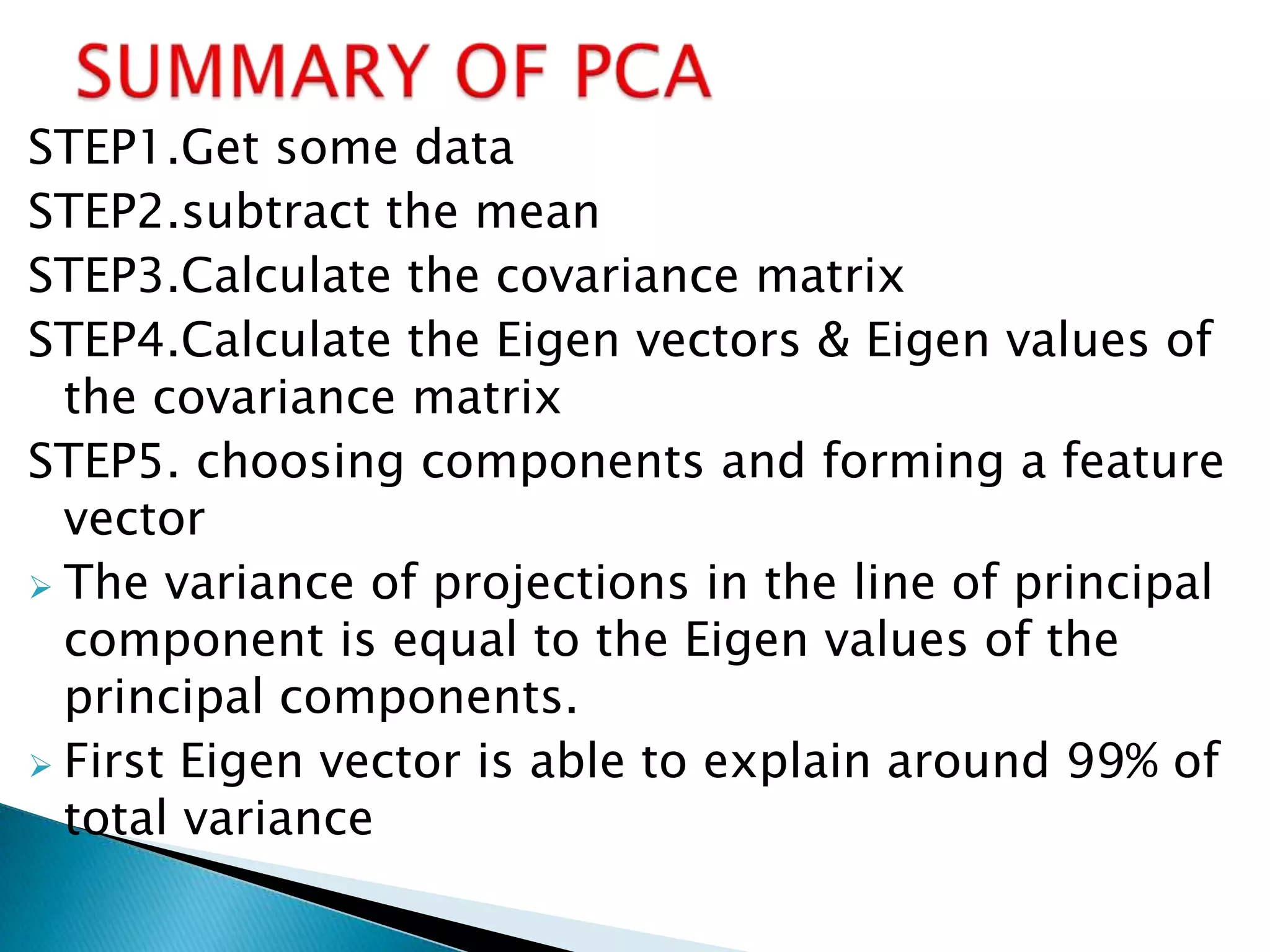
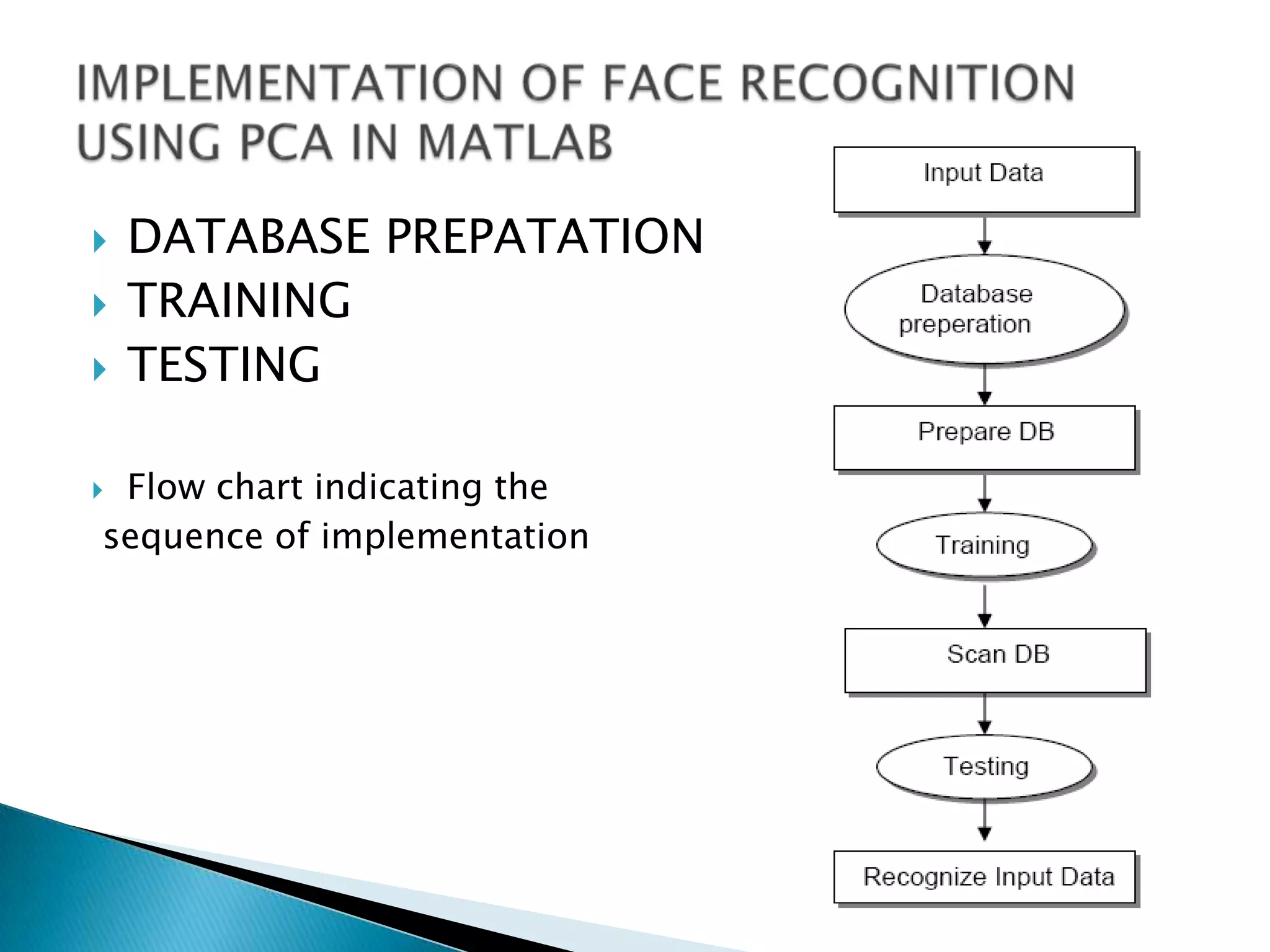
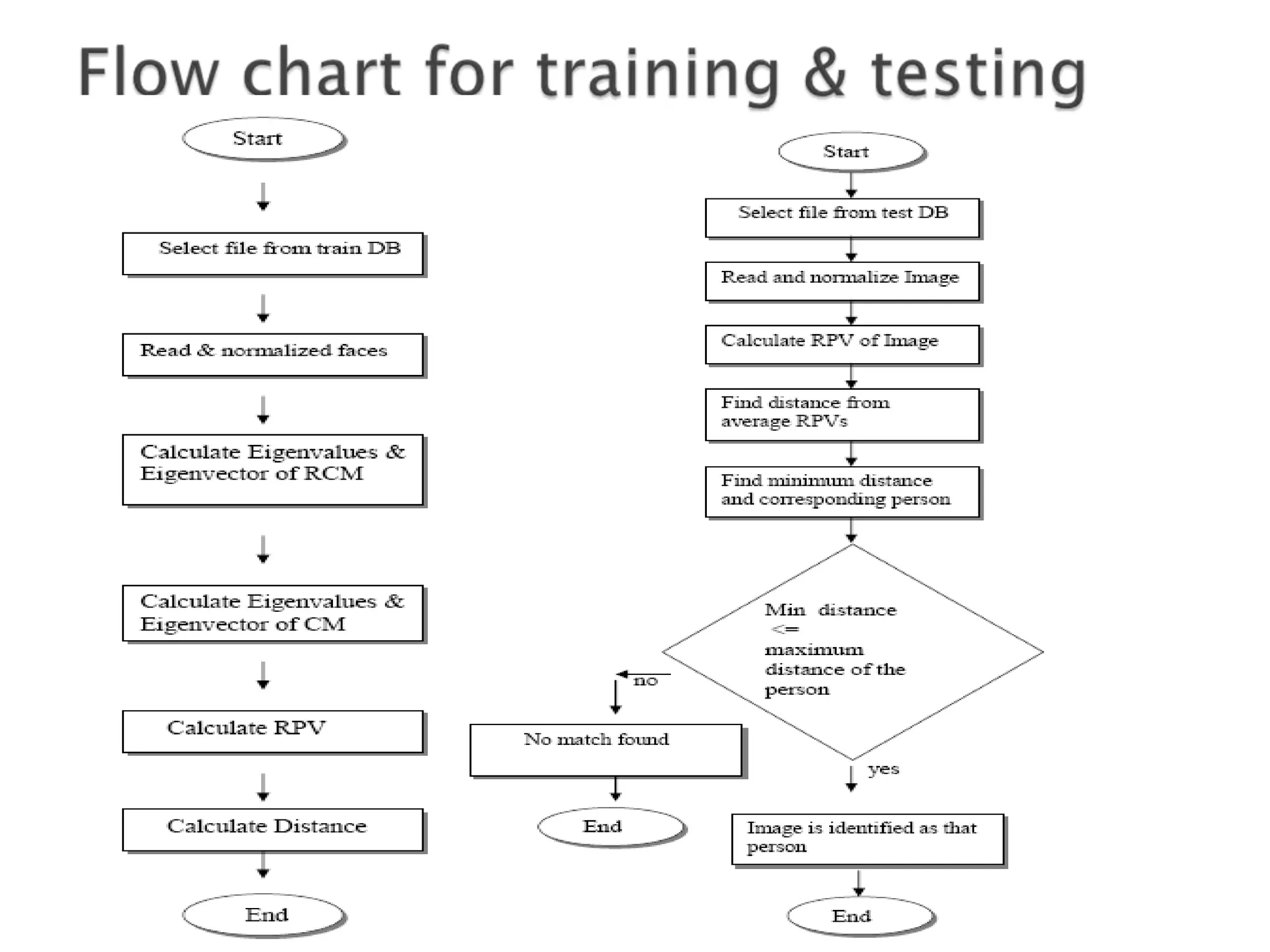
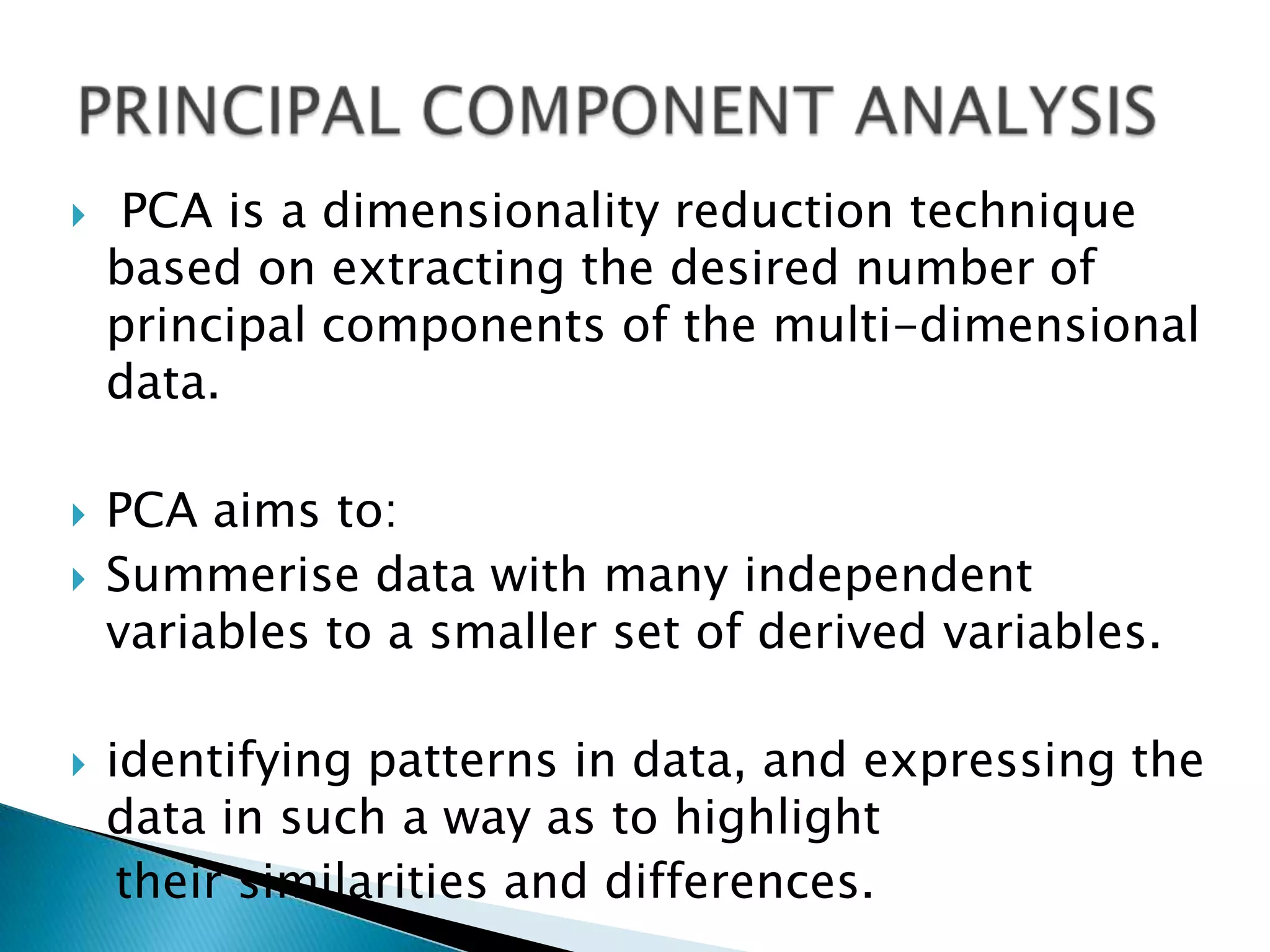
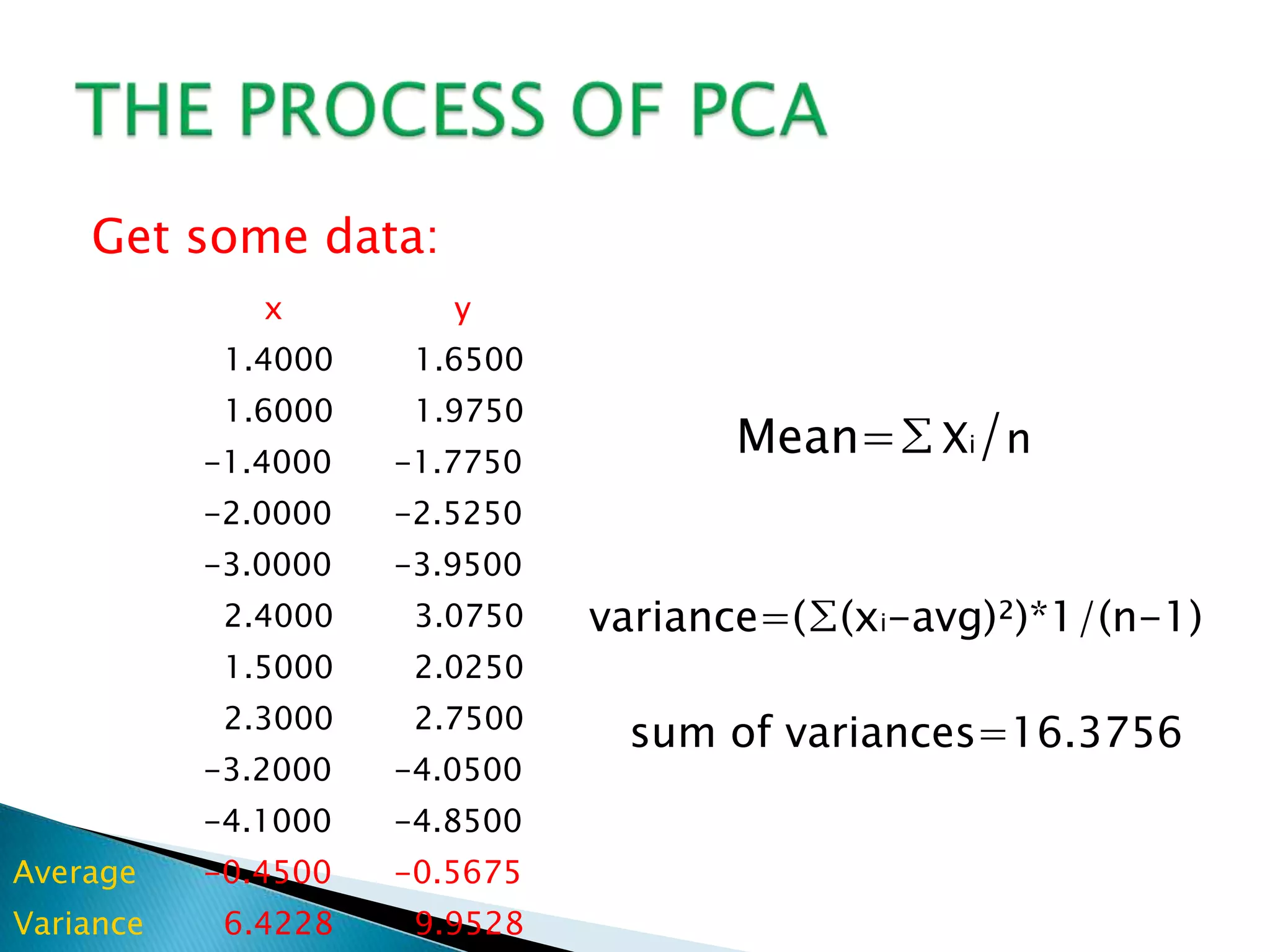
Face recognition uses principal component analysis (PCA) to reduce the dimensionality of face image data and identify patterns to recognize individuals. PCA involves extracting principal components from the data to summarize it with fewer variables while highlighting similarities and differences. The process involves getting sample face image data, subtracting the mean, calculating the covariance matrix, finding eigenvectors and eigenvalues to form a feature vector for projections of the data in the direction of the principal components. This allows for face recognition by training a database and testing unknown images.



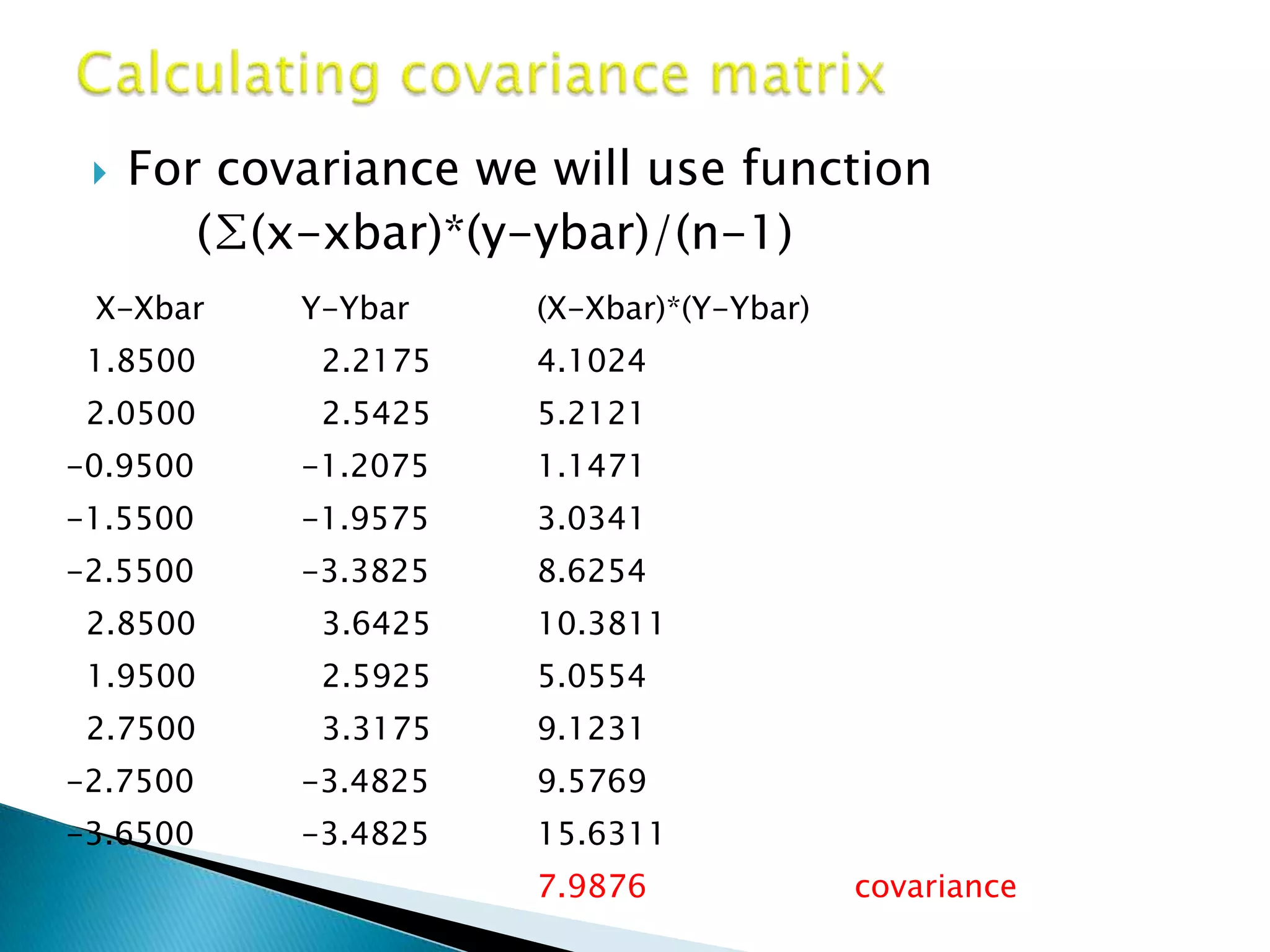
![ In general the covariance matrix is
= [covariance(x,x) covariance(x,y)
covariance(y,x) covariance(y,y)]
= [variance(x) covariance(x,y)
covariance(x,y) variance(y)]
= [6.4228 7.9876
7.9876 9.9528]
To obtain Eigen values by solving function
determinant {A-lamda(I)}=0
Solving equation A, we get the Eigen values are
lamda=16.36809984,0.007462657
Here sum of two eigen values is always equal to
the sum of variances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/miniproectslides-130116091227-phpapp01/75/face-recognition-using-Principle-Componet-Analysis-9-2048.jpg)
![ To obtain Eigen vector by solving for matrix x in
such a way that, {A-lambda(i)}*[X]=[0].
For first Eigen value 16.36809984, we get
[X]=[0.6262
0.7797]
For second Eigen value 0.007462657,we get
[X]=[0.7797
-0.6262]
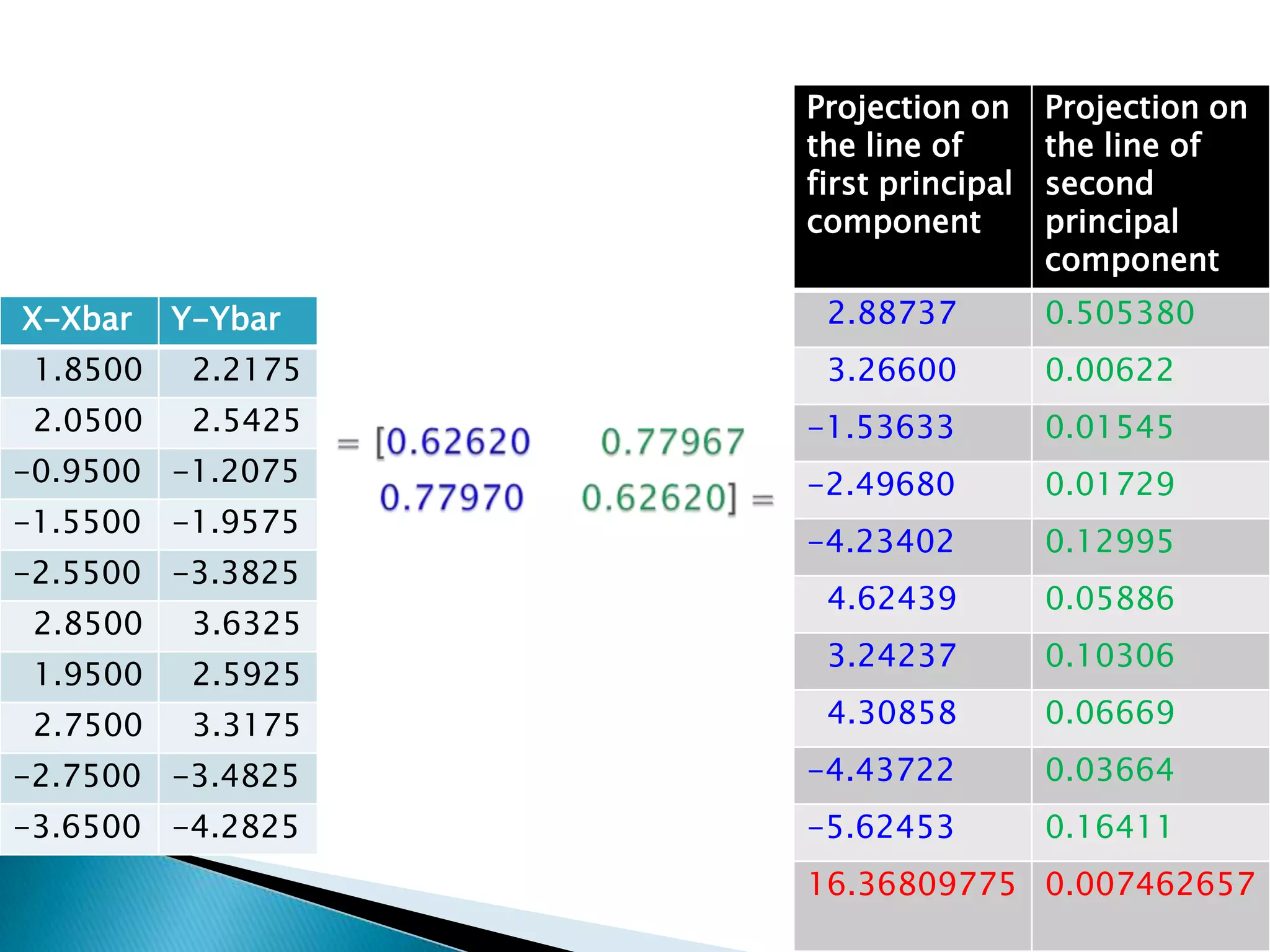
To obtain coordinates of data point in the direction
of Eigen vectors by multiplying the centered data
matrix to the Eigen vector matrix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/miniproectslides-130116091227-phpapp01/75/face-recognition-using-Principle-Componet-Analysis-10-2048.jpg)