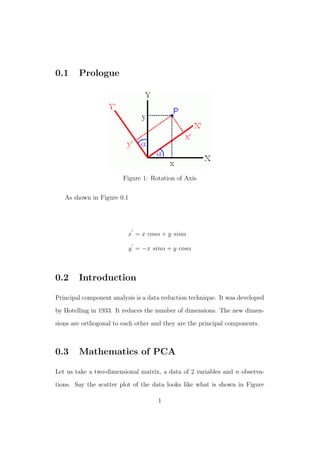
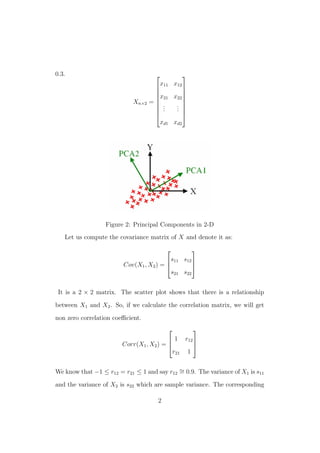
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a technique used to reduce the dimensionality of data by transforming correlated variables into a smaller number of uncorrelated variables called principal components. The first principal component accounts for as much of the variability in the data as possible, and each succeeding component accounts for as much of the remaining variability as possible. PCA involves computing the covariance matrix of the data and then determining the eigenvectors with the highest eigenvalues, which become the principal components.






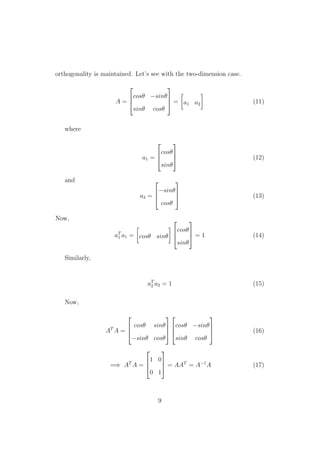
![or
Z = AT
X (5)
where,
Z =
z1
z2
(6)
A =
cosθ −sinθ
sinθ cosθ
(7)
and
X =
x1
x2
(8)
Now, if instead of p = 2 we have p = p, we will get:
Z =
z1
z2
...
zp
=
a11 a12 . . . a1p
a21 a22 . . . a2p
...
...
...
...
ap1 ap2 . . . app
x1
x2
...
xp
(9)
In terms of dimensions:
Zp×1 = [Ap×p]T
× Xp×1 (10)
We say that it is an orthogonal transformation. Let’s see now, how this
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pca-180223100530/85/Principal-Component-Analysis-9-320.jpg)

![already explained by the first principal component) and so on and so forth.
Now, the next step is, how to extract the principal components given the
data matrix X.
The jth
principal component, Zj is equal to at
jx. So,
V ar(Zj) = V ar(at
jx) = at
jV ar(x)aj (27)
as aj is a constant vector.
V ar(X) = Cov(X) = Σ =
σ11 σ12 . . . σ1p
σ21 σ22 . . . σ2p
...
...
...
...
σp1 σp2 . . . σpp
(28)
as X is multivariate data.
=⇒ V ar(Zj) = at
jΣaj (29)
Now,
E[Zj] = E[aT
j x] = aT
j E[x] = aT
j µ (30)
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pca-180223100530/85/Principal-Component-Analysis-12-320.jpg)
![aT
j x ∼ (aT
j µ, at
jΣaj) (31)
If it is Normally distributed, then,
aT
j x ∼ N(aT
j µ, at
jΣaj) (32)
Σ and µ are population parameters. If they are known, then it is pop-
ulation principal component analysis. But, it is usually unknown. In such
a case X is used as the best estimate of µ and S, the sample covariance
matrix, is used as the estimate for σ. And, in that case the PCA is known
as sample principal component analysis. Since population parameters are
rarely known, we will be going ahead with sample PCA. In sample PCA:
E[zj] = E[aT
j X] = aT
j E[X] = aT
j X (33)
V ar(zj) = V ar(aT
j X) = aT
j Cov(X)aj = aT
j Saj (34)
If it is normally distributed then,
aT
j ∼ (aT
j X, aT
j Saj) (35)
Now, we will look at the principles followed to extract the PCs. Principles
of Principals:
• Each PC is a linear combination of X, a p×1 variable vector, i.e., aT
j X
• First PC is aT
1 X, subjected to aT
1 a1 = 1 that maximizes V ar(aT
1 X)
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pca-180223100530/85/Principal-Component-Analysis-13-320.jpg)

