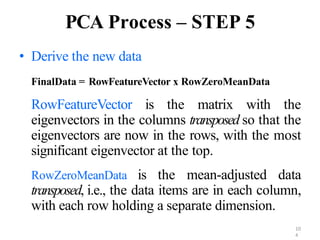
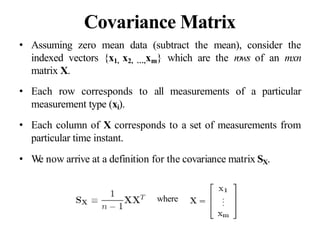
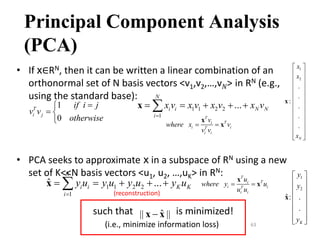
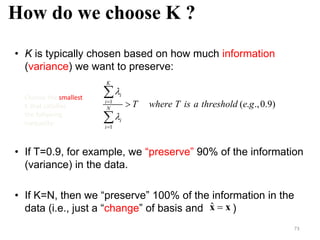
PCA is a dimensionality reduction technique that uses linear transformations to project high-dimensional data onto a lower-dimensional space while retaining as much information as possible. It works by identifying patterns in data and expressing the data in such a way as to highlight their similarities and differences. Specifically, PCA uses linear combinations of the original variables to extract the most important patterns from the data in the form of principal components. The first principal component accounts for as much of the variability in the data as possible, and each succeeding component accounts for as much of the remaining variability as possible.



















![Linear algebra
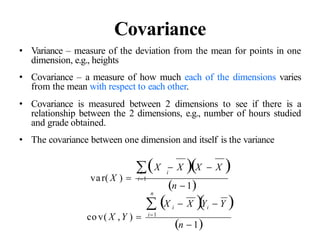
• MatrixA:
• Matrix Transpose
• Vector a
a1
mn
...
...
a ... a
... ... ...
a a ... a
ij mn
A [a ]
m2
m1
2n
22
21
a1n
a11 a12
a
1 i n,1 j m
B [b ] AT
b a ;
ij nm ij ji
[a1,...,an ]
aT
an
a ...;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aimlmodule6lecture4142dimensionreductionintroductionpca-221029062222-36fd678d/85/Dimension-Reduction-Introduction-PCA-pptx-23-320.jpg)
![Matrix and vector multiplication
• Matrix multiplication
A [aij ]mp ; B [bij ]pn ;
AB C [cij ]mn ,where cij rowi (A)colj (B)
• Outer vector product
a A [a ] ; bT
B [b ] ;
ij m1 ij 1n
c ab AB,an mn matrix
• Vector-matrix product
A [aij ]mn ; b B [bij ]n1;
C Ab an m1matrix vector of length m](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aimlmodule6lecture4142dimensionreductionintroductionpca-221029062222-36fd678d/85/Dimension-Reduction-Introduction-PCA-pptx-24-320.jpg)
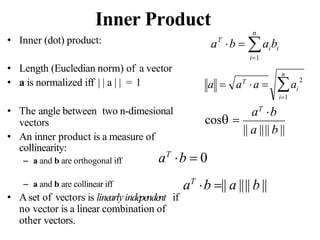
![Determinant and Trace
• Determinant
• Trace
n
j1
A (1)i j
det(M )
ij ij
det(AB)= det(A)det(B)
i 1,....n;
A [aij ]nn ;
det(A) aij Aij ;
n
A [aij ]nn; tr[A] ajj
j1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aimlmodule6lecture4142dimensionreductionintroductionpca-221029062222-36fd678d/85/Dimension-Reduction-Introduction-PCA-pptx-26-320.jpg)
![Matrix Inversion
• A(n x n) is nonsingular if there exists B such that:
AB BA I ; B A1
n
• A=[2 3; 2 2], B=[-1 3/2; 1 -1]
• Ais nonsingular iff
• Pseudo-inverse for a non square matrix, provided
AT
A is not singular
A#
[AT
A]1
AT
A#
A I
|| A|| 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aimlmodule6lecture4142dimensionreductionintroductionpca-221029062222-36fd678d/85/Dimension-Reduction-Introduction-PCA-pptx-27-320.jpg)








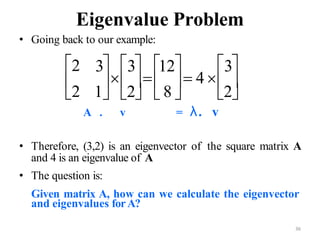
















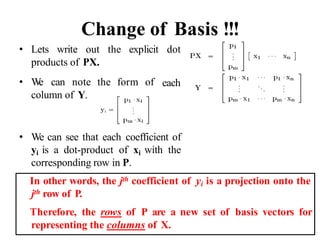




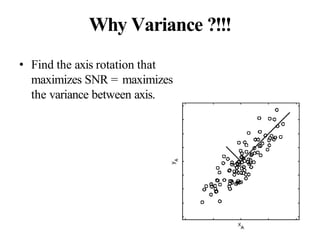




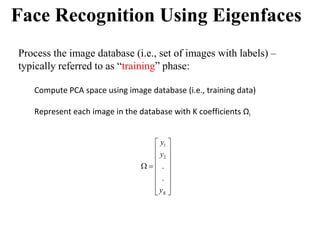
![Suppose we are given x1, x2, ..., xM (N x 1) vectors
Step 1: compute sample mean
Step 2: subtract sample mean (i.e., center data at zero)
Step 3: compute the sample covariance matrix Σx
65
PCA - Steps
N: # of features
M: # data
1
1 M
i
i
M
x x
Φi i
x x
i i
1 1
1 1
( )( )
M M
T T
i i
i i
M M
x x x x x
1 T
AA
M
where A=[Φ1 Φ2 ... ΦΜ]
i.e., the columns of A are the Φi
(N x M matrix)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aimlmodule6lecture4142dimensionreductionintroductionpca-221029062222-36fd678d/85/Dimension-Reduction-Introduction-PCA-pptx-65-320.jpg)


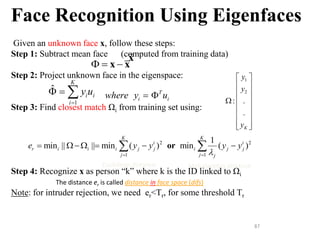
![68
What is the Linear Transformation
implied by PCA?
• The linear transformation y = Tx which performs the
dimensionality reduction in PCA is:
1
2
ˆ
( )
.
.
T
K
y
y
U
y
x x i.e., the rows of T are the first K
eigenvectors of Σx
1
2
ˆ
( ) .
.
K
y
y
U
y
x x
T = UT
1 2
[ ... ] matrix
K
where U u u u N x K
i.e., the columns of U are the
the first K eigenvectors of Σx
1 1 2 2
1
ˆ ...
K
i i K K
i
y u y u y u y u
x x
K x N matrix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aimlmodule6lecture4142dimensionreductionintroductionpca-221029062222-36fd678d/85/Dimension-Reduction-Introduction-PCA-pptx-68-320.jpg)







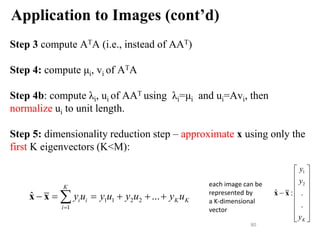
![Application to Images (cont’d)
The key challenge is that the covariance matrix Σx is now very
large (i.e., N2 x N2) – see Step 3:
Step 3: compute the covariance matrix Σx
Σx is now an N2 x N2 matrix – computationally expensive to
compute its eigenvalues/eigenvectors λi, ui
(AAT)ui= λiui
77
1
1 1
M
T T
i
i
AA
M M
x i
where A=[Φ1 Φ2 ... ΦΜ]
(N2 x M matrix)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aimlmodule6lecture4142dimensionreductionintroductionpca-221029062222-36fd678d/85/Dimension-Reduction-Introduction-PCA-pptx-77-320.jpg)
![Application to Images (cont’d)
We will use a simple “trick” to get around this by relating the
eigenvalues/eigenvectors of AAT to those of ATA.
Let us consider the matrix ATA instead (i.e., M x M matrix)
Suppose its eigenvalues/eigenvectors are μi, vi
(ATA)vi= μivi
Multiply both sides by A:
A(ATA)vi=Aμivi or (AAT)(Avi)= μi(Avi)
Assuming (AAT)ui= λiui
λi=μi and ui=Avi
78
A=[Φ1 Φ2 ... ΦΜ]
(N2 x M matrix)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aimlmodule6lecture4142dimensionreductionintroductionpca-221029062222-36fd678d/85/Dimension-Reduction-Introduction-PCA-pptx-78-320.jpg)



![83
Example (cont’d)
y=(int)255(x - fmin)/(fmax - fmin)
• How can you visualize the eigenvectors (eigenfaces) as an
image?
− Their values must be first mapped to integer values in the
interval [0, 255] (required by PGM format).
− Suppose fmin and fmax are the min/max values of a given
eigenface (could be negative).
− If xϵ[fmin, fmax] is the original value, then the new value
yϵ[0,255] can be computed as follows:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aimlmodule6lecture4142dimensionreductionintroductionpca-221029062222-36fd678d/85/Dimension-Reduction-Introduction-PCA-pptx-83-320.jpg)