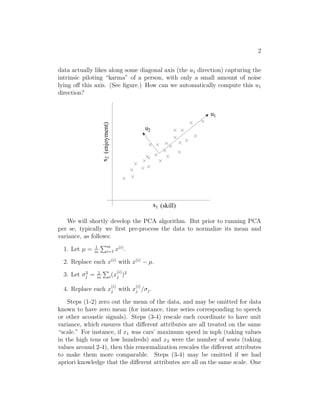
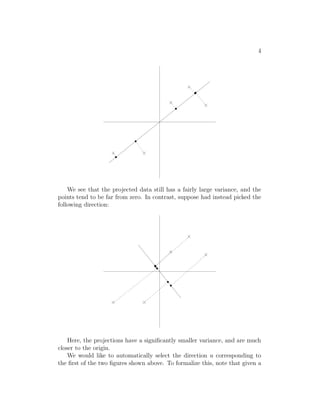
Principal components analysis (PCA) is an algorithm that identifies the subspace where data approximately lies in a way that requires only an eigenvector calculation. PCA works by finding the directions, called principal components, that maximize the variance of the projected data points. It does this by computing the eigenvectors of the covariance matrix of the data, with the top eigenvectors providing the principal components that best explain the variability in the data using a reduced dimensional space. PCA has applications in data compression, dimensionality reduction, noise reduction, and data visualization.