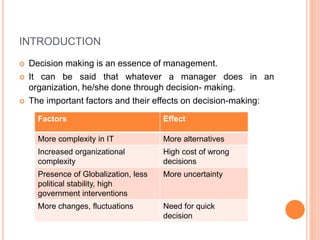
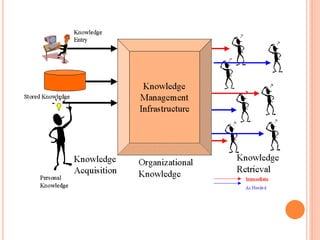
Decision making is essential for management. A decision support system is an interactive IT system that helps managers make decisions, especially in semi-structured or unstructured situations. It has three main components: a database, model base, and dialogue box for the user interface. Business intelligence systems are data-driven decision support systems that help improve business decision making through technologies for collecting, integrating, analyzing and presenting business information. Knowledge management systems aim to help organizations create, capture, analyze, apply and reuse knowledge to improve performance and gain a competitive advantage.