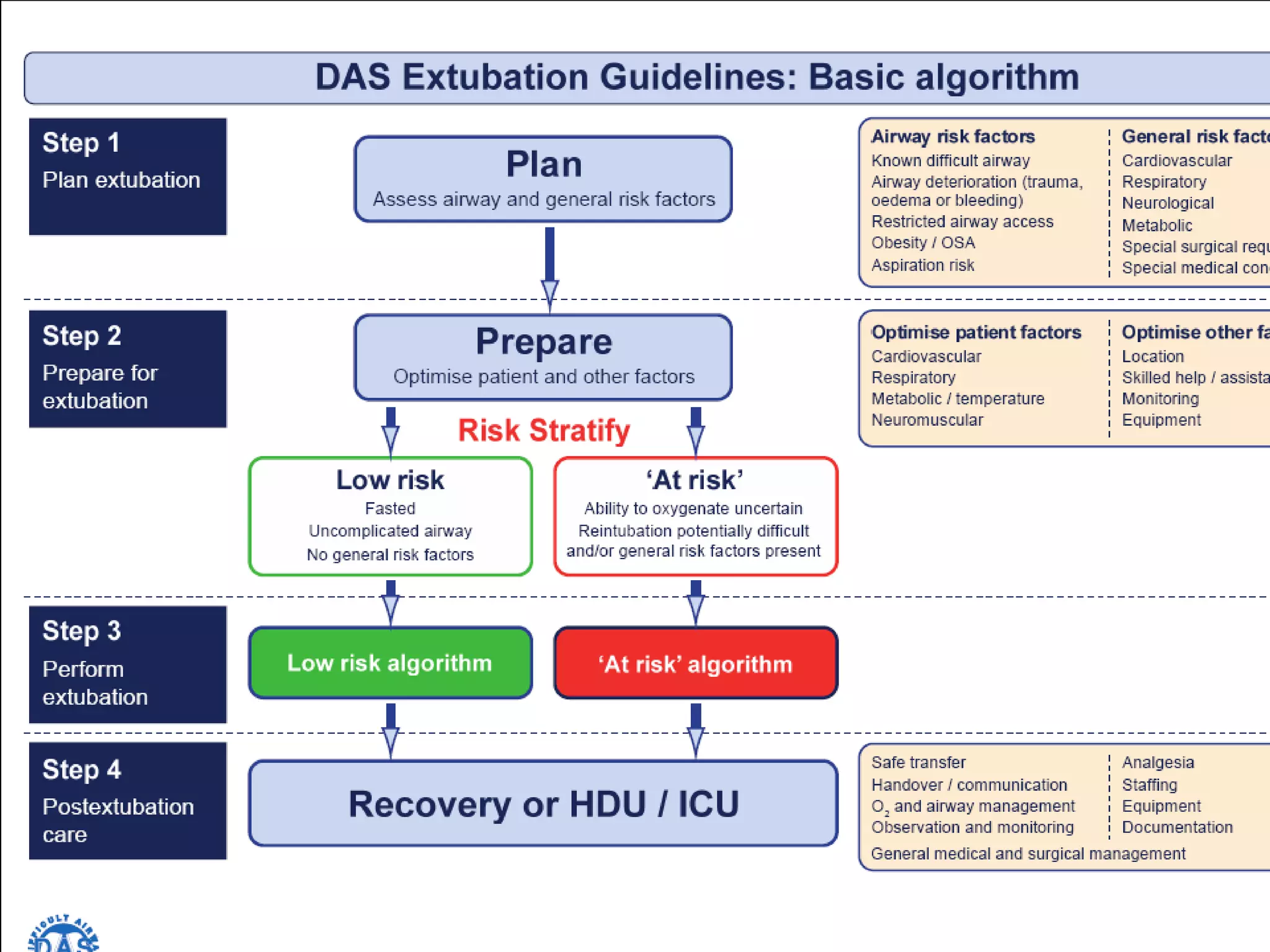
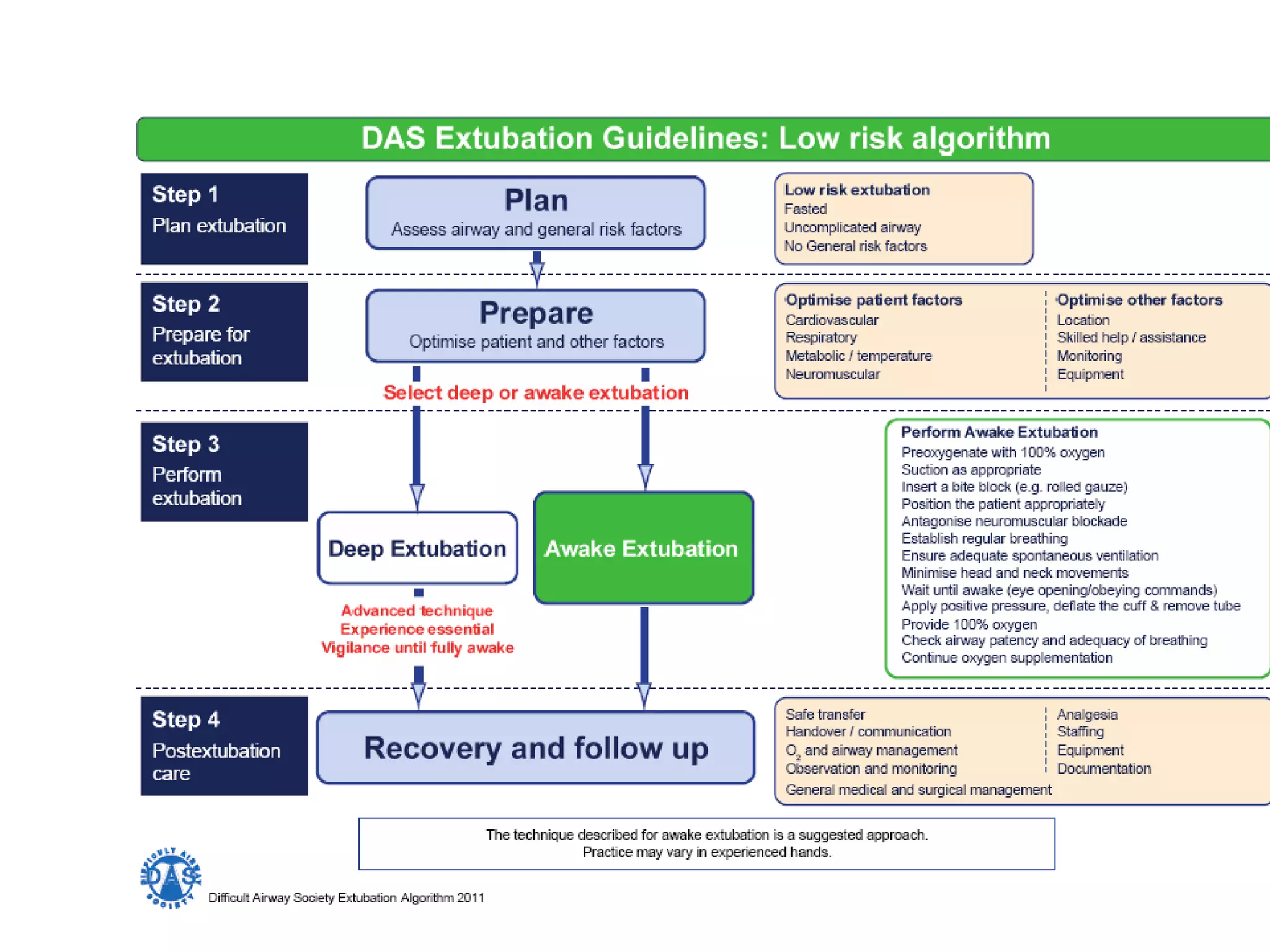
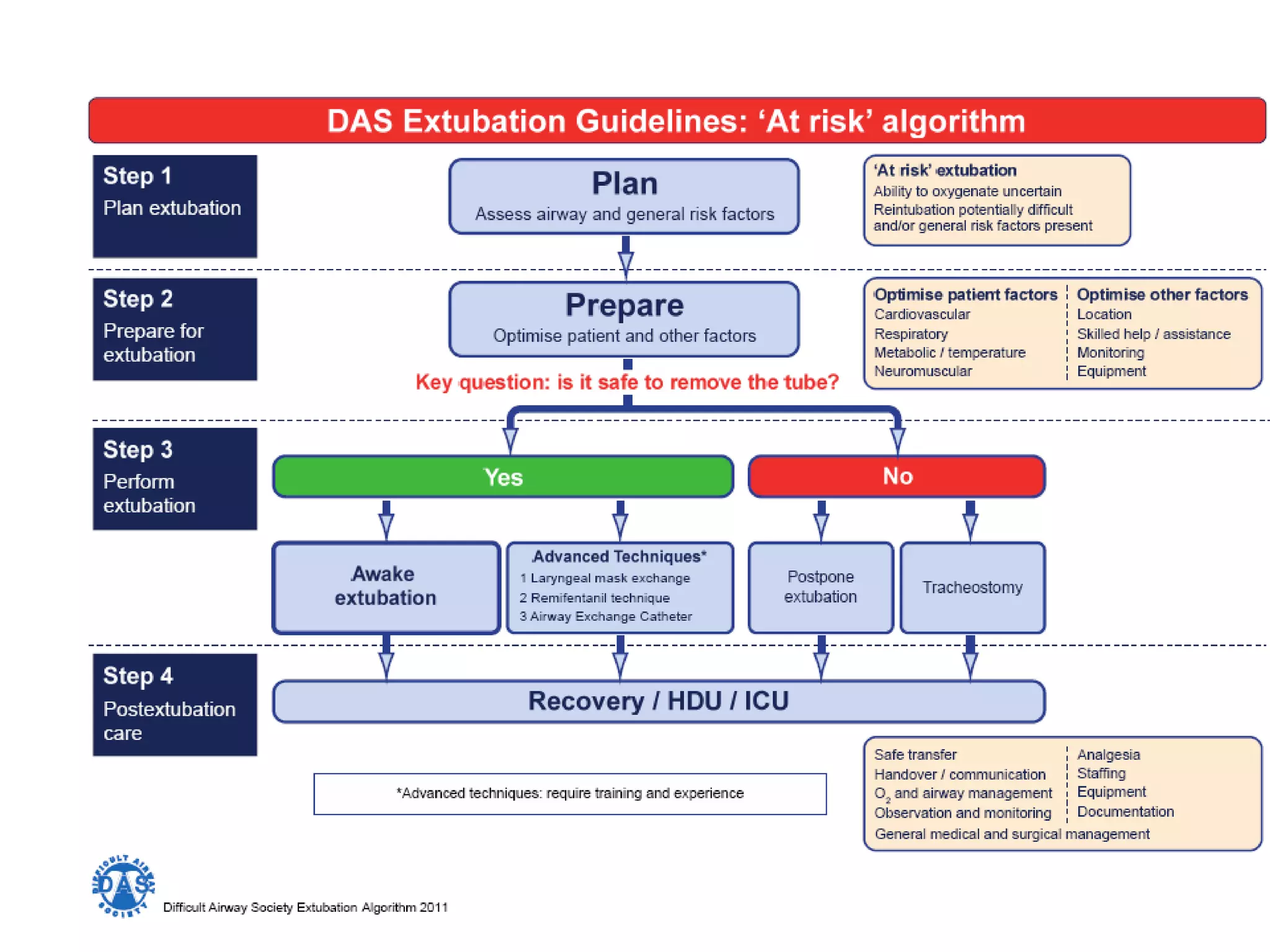
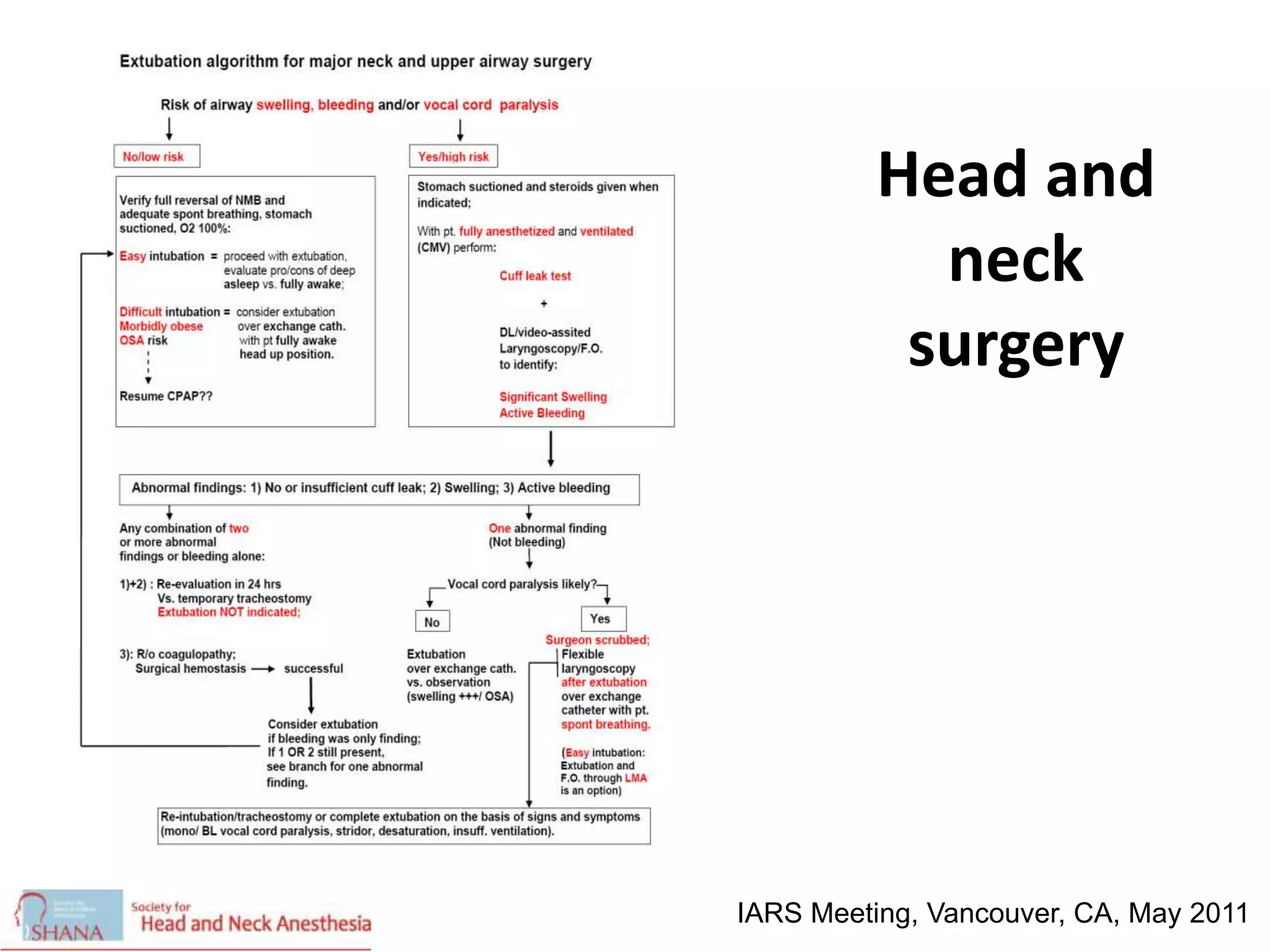
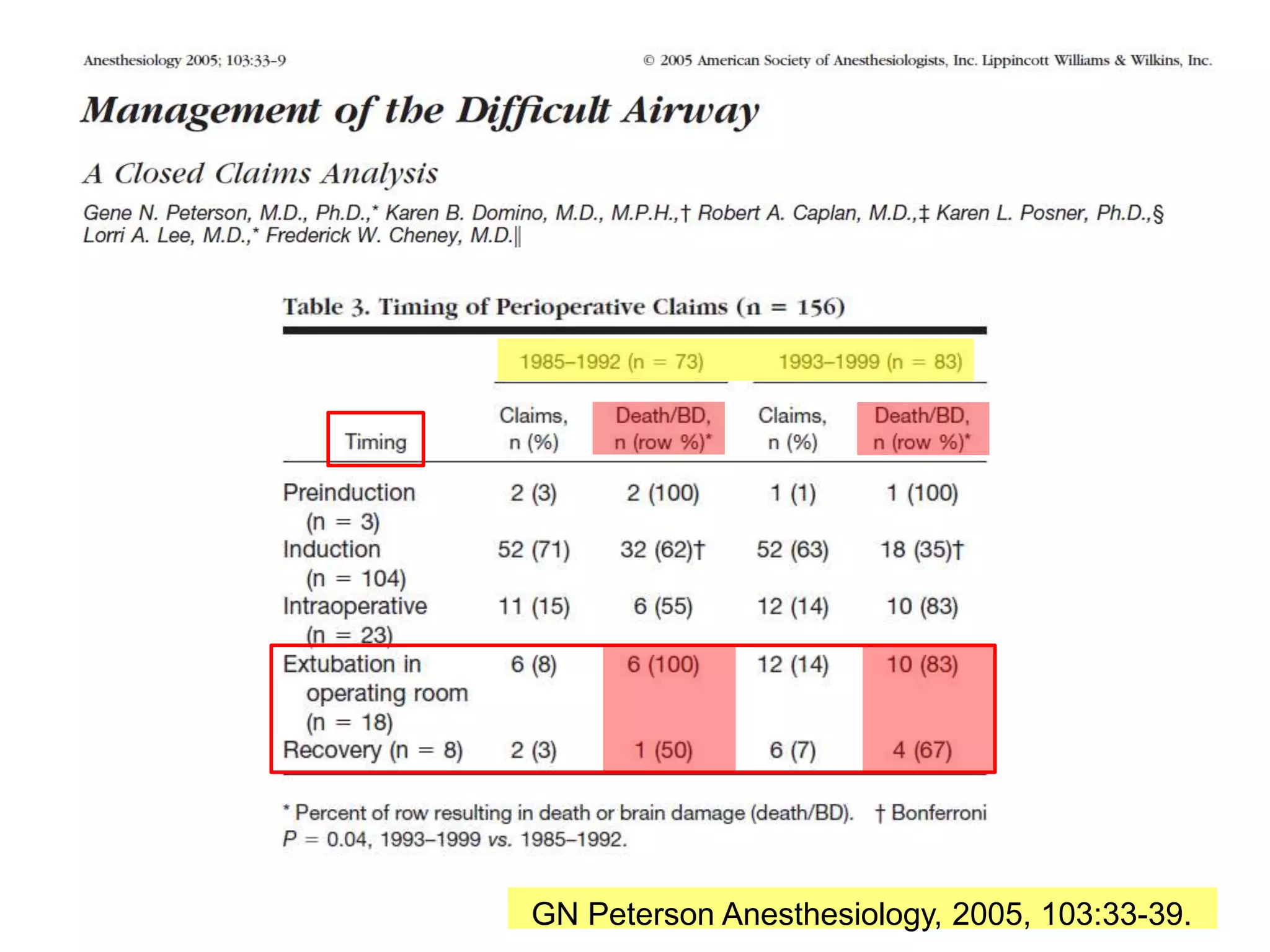
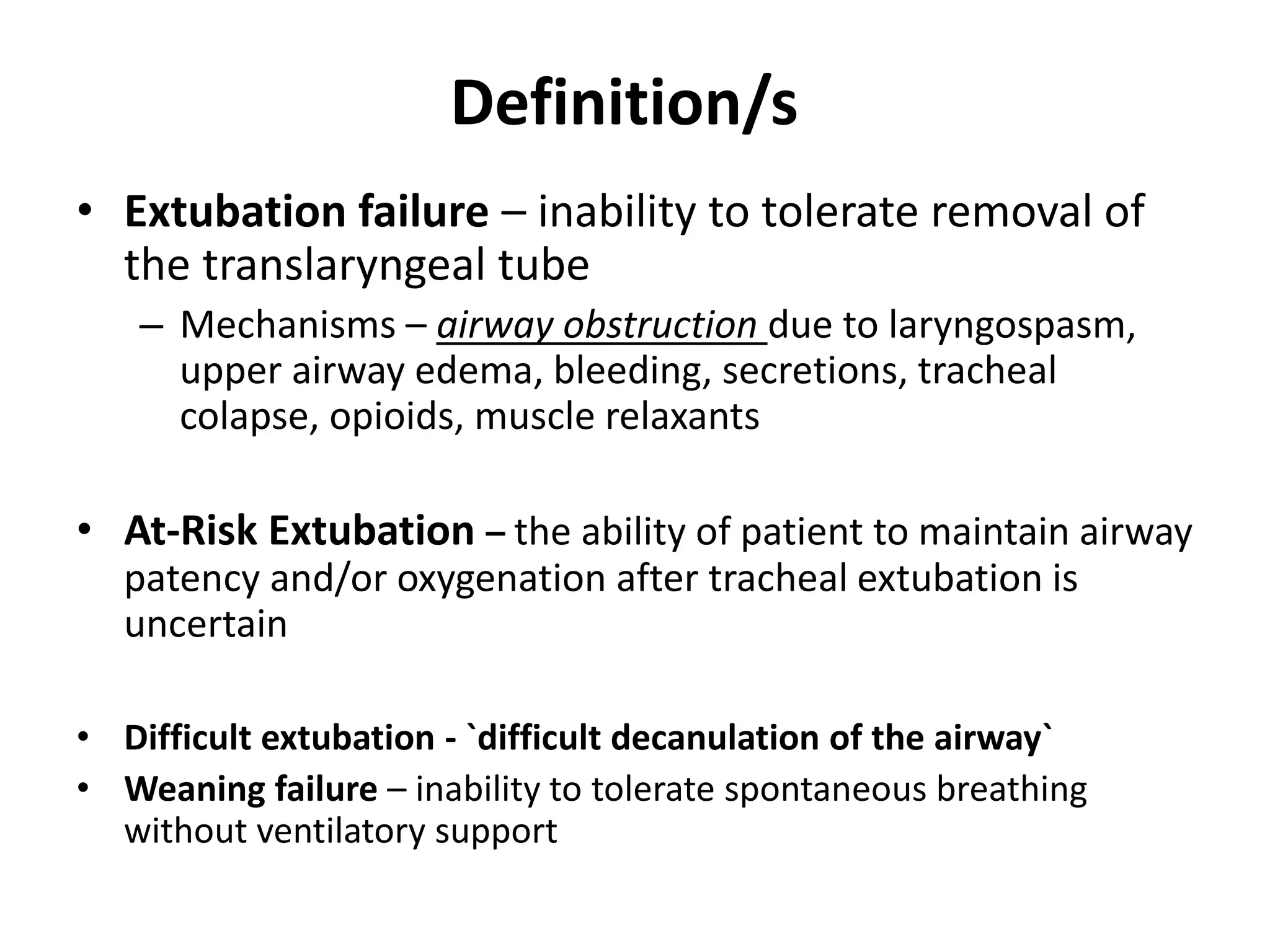
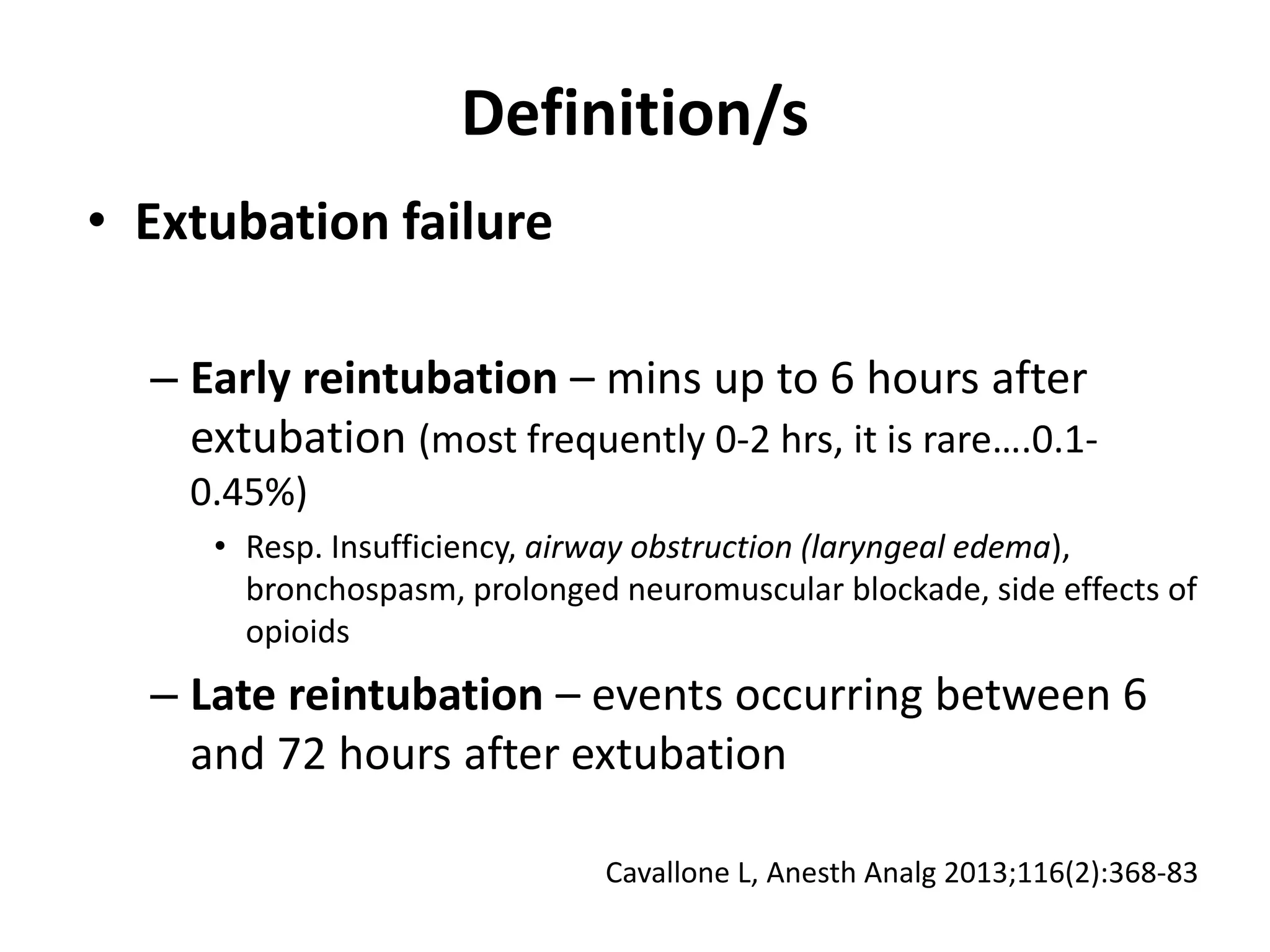
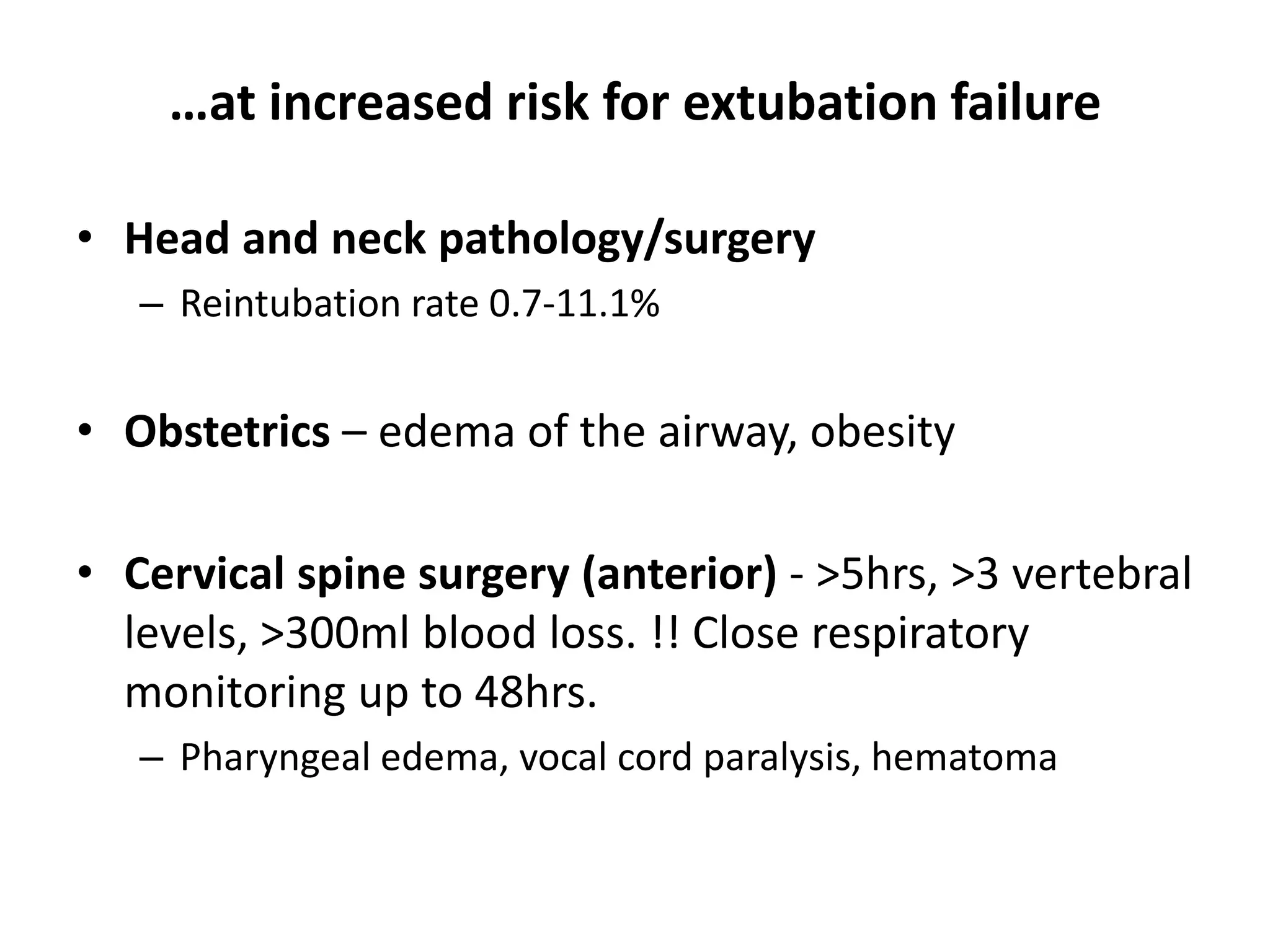
The document discusses extubation of difficult airways. It notes that while respiratory adverse events at induction of anesthesia have decreased, rates of death or brain damage during tracheal extubation have remained unchanged, suggesting more education is needed. Among failed extubation claims since 2000, 94% resulted in death or permanent brain damage. The document provides definitions for extubation failure and at-risk extubation. It discusses patient risk factors and causes of extubation failure, and reviews guidelines from the American Society of Anesthesiologists and Difficult Airway Society for developing an extubation strategy.








![The preformulated extubation strategy should include:
1. A consideration of the relative merits of awake extubation versus extubation
before the return of consciousness.
2. An evaluation for general clinical factors that may produce an adverse
impact on ventilation after the patient has been extubated.
3. The formulation of an airway management plan that can be implemented if the
patient is not able to maintain adequate ventilation after extubation.
4. A consideration of the short-term use of a device that can serve as a guide for
expedited reintubation. This type of device can be a stylet (intubating bougie) or
conduit.
- Stylets or intubating bougies are usually inserted through the lumen of the tracheal tube and into the
trachea before the tracheal tube is removed. […] Conduits are usually inserted through the mouth and
can be used for supraglottic ventilation and intubation The ILMA and LMA are examples of conduit.
ASA guidelines 2013.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/extubationofthedifficultairway-210826035917/75/Extubation-of-the-difficult-airway-14-2048.jpg)



![The preformulated extubation strategy should include:
1. A consideration of the relative merits of awake extubation versus extubation
before the return of consciousness.
2. An evaluation for general clinical factors that may produce an adverse
impact on ventilation after the patient has been extubated.
3. The formulation of an airway management plan that can be implemented if the
patient is not able to maintain adequate ventilation after extubation.
4. A consideration of the short-term use of a device that can serve as a guide for
expedited reintubation. This type of device can be a stylet (intubating bougie) or
conduit.
- Stylets or intubating bougies are usually inserted through the lumen of the tracheal tube and into the
trachea before the tracheal tube is removed. […] Conduits are usually inserted through the mouth and
can be used for supraglottic ventilation and intubation The ILMA and LMA are examples of conduit.
ASA guidelines 2013.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/extubationofthedifficultairway-210826035917/75/Extubation-of-the-difficult-airway-18-2048.jpg)



![The preformulated extubation strategy should include:
1. A consideration of the relative merits of awake extubation versus extubation
before the return of consciousness.
2. An evaluation for general clinical factors that may produce an adverse
impact on ventilation after the patient has been extubated.
3. The formulation of an airway management plan that can be implemented if the
patient is not able to maintain adequate ventilation after extubation.
4. A consideration of the short-term use of a device that can serve as a guide for
expedited reintubation. This type of device can be a stylet (intubating bougie) or
conduit.
- Stylets or intubating bougies are usually inserted through the lumen of the tracheal tube and into the
trachea before the tracheal tube is removed. […] Conduits are usually inserted through the mouth and
can be used for supraglottic ventilation and intubation The ILMA and LMA are examples of conduit.
ASA guidelines 2013.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/extubationofthedifficultairway-210826035917/75/Extubation-of-the-difficult-airway-22-2048.jpg)

![The preformulated extubation strategy should include:
1. A consideration of the relative merits of awake extubation versus extubation
before the return of consciousness.
2. An evaluation for general clinical factors that may produce an adverse
impact on ventilation after the patient has been extubated.
3. The formulation of an airway management plan that can be implemented if the
patient is not able to maintain adequate ventilation after extubation.
4. A consideration of the short-term use of a device that can serve as a guide for
expedited reintubation. This type of device can be a stylet (intubating bougie) or
conduit.
- Stylets or intubating bougies are usually inserted through the lumen of the tracheal tube and into the
trachea before the tracheal tube is removed. […] Conduits are usually inserted through the mouth and
can be used for supraglottic ventilation and intubation The ILMA and LMA are examples of conduit.
ASA guidelines 2013.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/extubationofthedifficultairway-210826035917/75/Extubation-of-the-difficult-airway-24-2048.jpg)

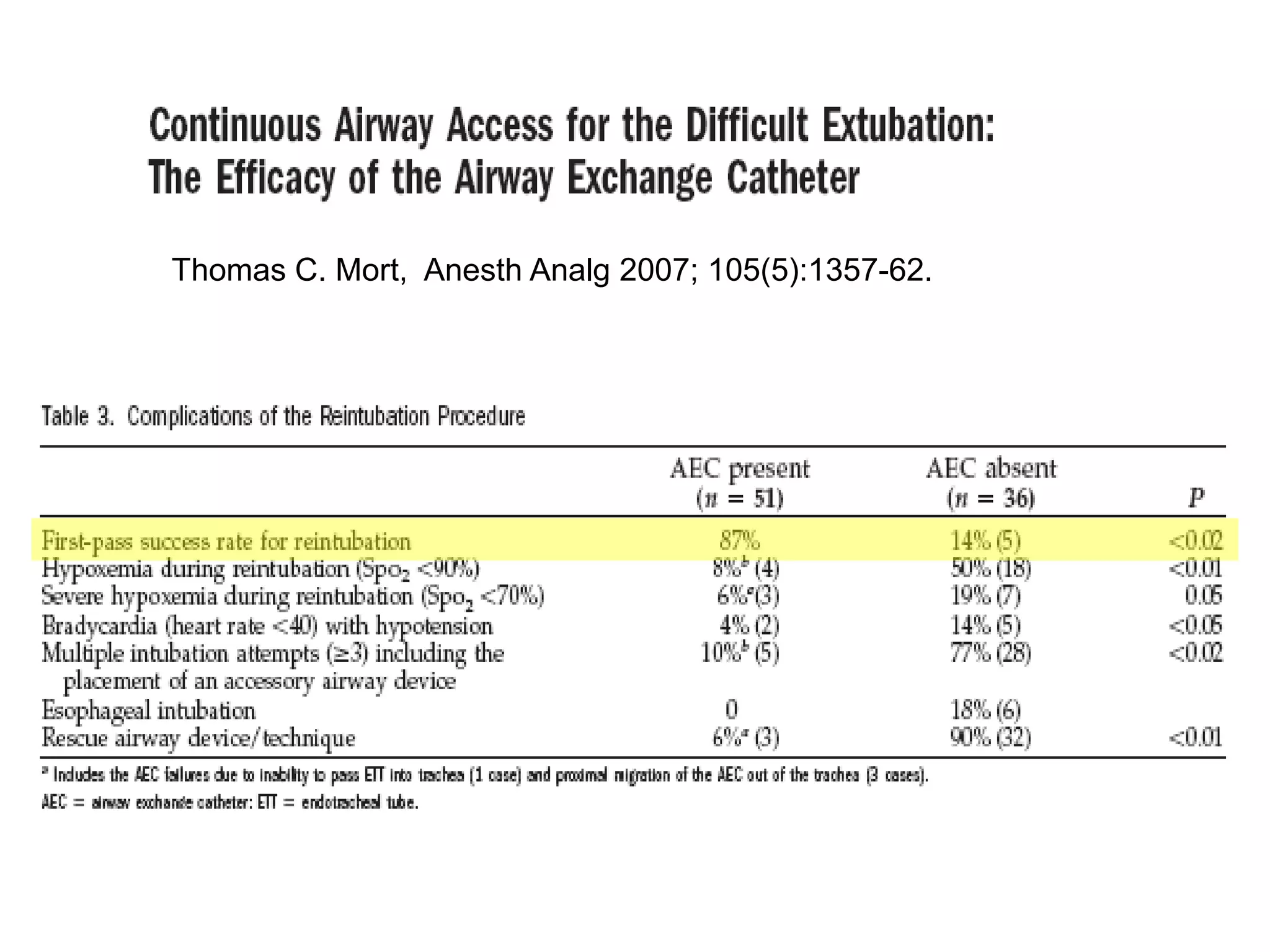
![Should a patient with an AEC in situ decompensate,
tracheal re-intubation is the key management strategy.
Supplemental oxygen can be
provided using standard techniques
prior to intubation.
Oxygen insufflation through an AEC appears to be associated
with a lower risk of volutrauma or barotrauma, but […] it is not
risk-free.
L Duggan, Can J Anesth/J Can Anesth (2011) 58:560–568
Use AEC for re-intubation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/extubationofthedifficultairway-210826035917/75/Extubation-of-the-difficult-airway-27-2048.jpg)