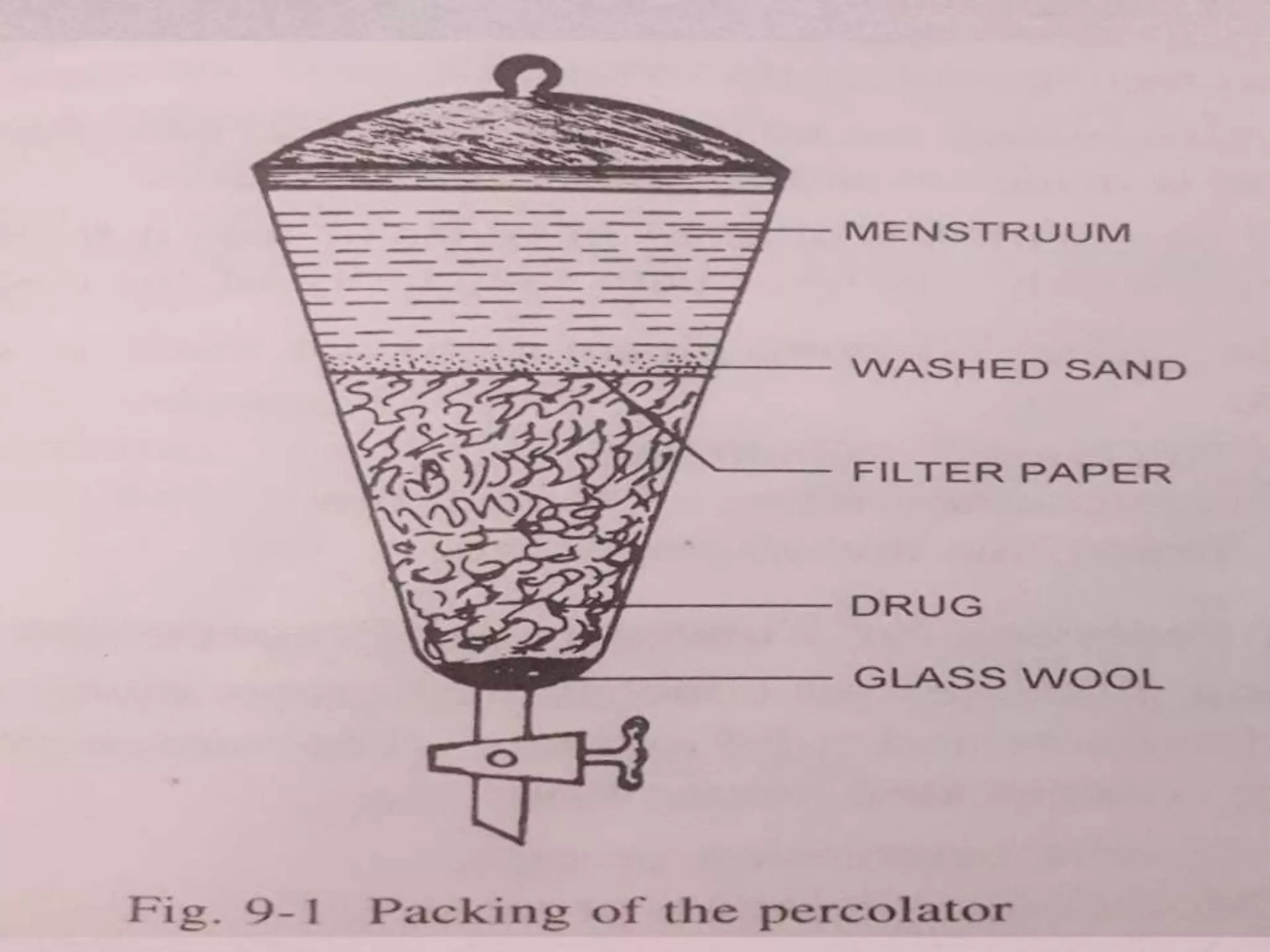
The document discusses various extraction methods used in pharmaceutics including infusion, decoction, maceration, percolation, and digestion. It describes the process, equipment, and examples for each method. Water and alcohol are discussed as common solvents used in extraction due to their ability to dissolve different active pharmaceutical ingredients. The summary focuses on the key extraction techniques and solvents covered.