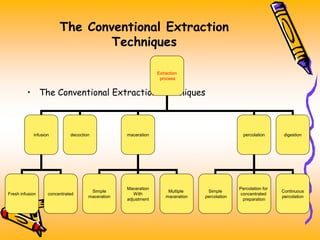
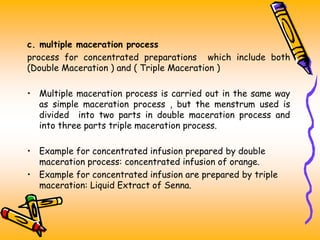
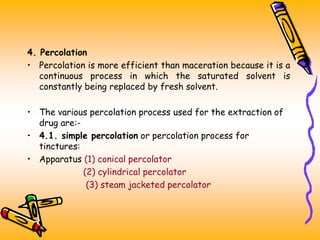
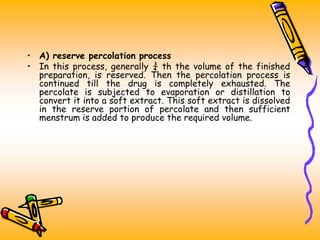
The document discusses various extraction methods used to separate desired components from raw materials. It defines extraction and describes common terms like marc and menstrum. The objectives of extraction are to obtain therapeutic components while removing inert materials. Extraction types include liquid-liquid and solid-liquid extraction. Key factors that affect extraction are also outlined. Common extraction techniques are infusion, decoction, maceration, and percolation. Specific details are provided on how each technique is performed.