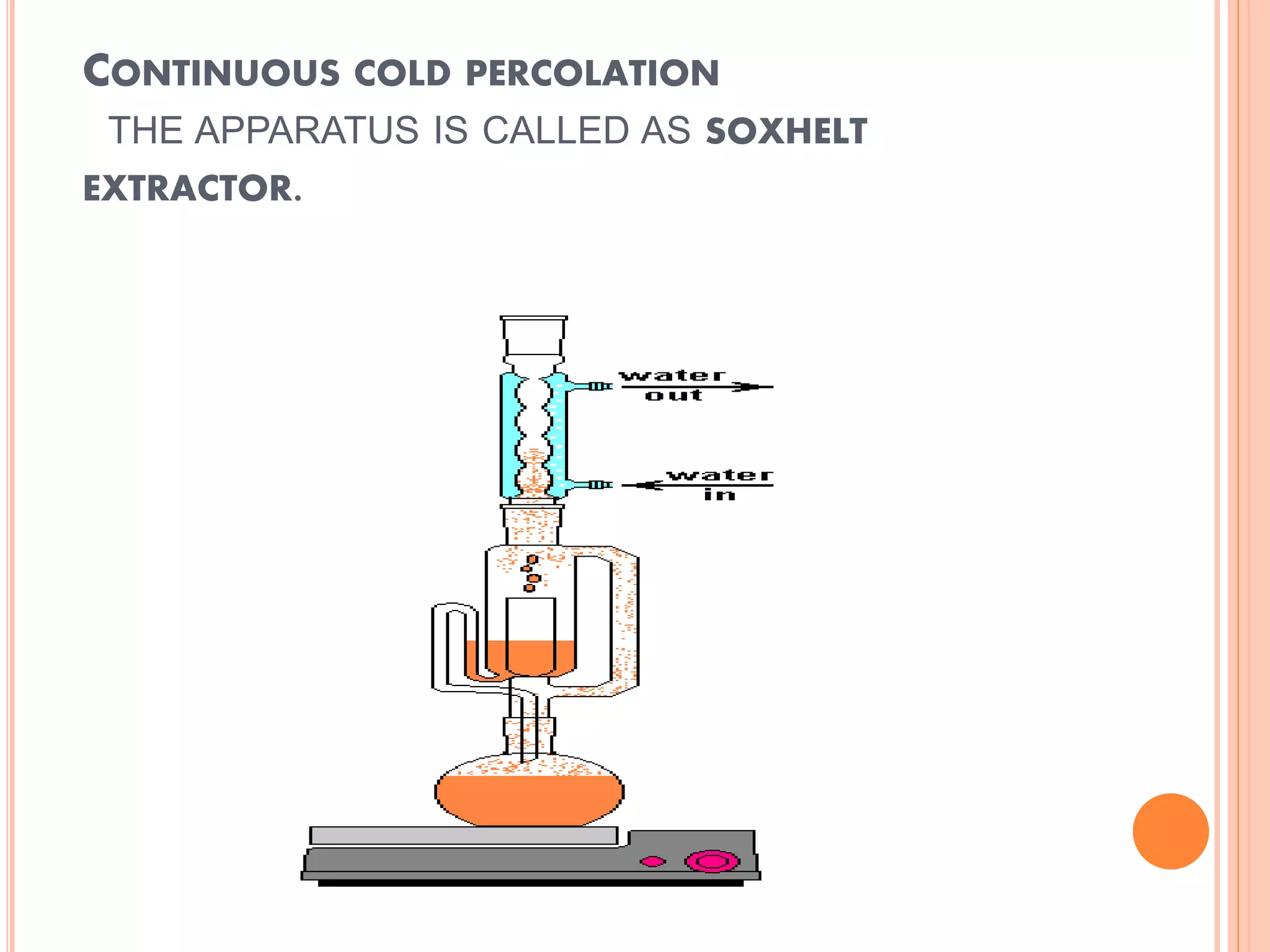
This document discusses percolation, which is the process of extracting soluble constituents from a drug by slowly passing a solvent through the drug. It provides examples of percolation like extracting soluble compounds from coffee. The process of percolation involves comminution, imbibition, packing, maceration, and percolation. It also discusses modified percolation methods like reserved, continuous hot, and continuous cold percolation. Different types of percolators are used depending on factors like the drug properties and desired extraction method.