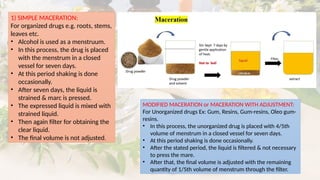
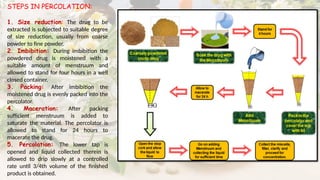
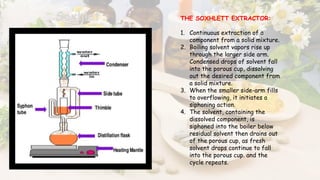
What is Galenicals?
Galenicals are herbal medicines prepared according to formulas developed by Galen, a Greek physician. They are extracted from crude plant materials using solvents like water or alcohol.
TYPES OF EXTRACTS:
1)Dry extract (Tab, cap.) Ex: belladonna extract
2)Soft (Ointment, suppository) Ex: glycerrhiza extract.
3)Liquid: As tincture
Solvent used for Extraction