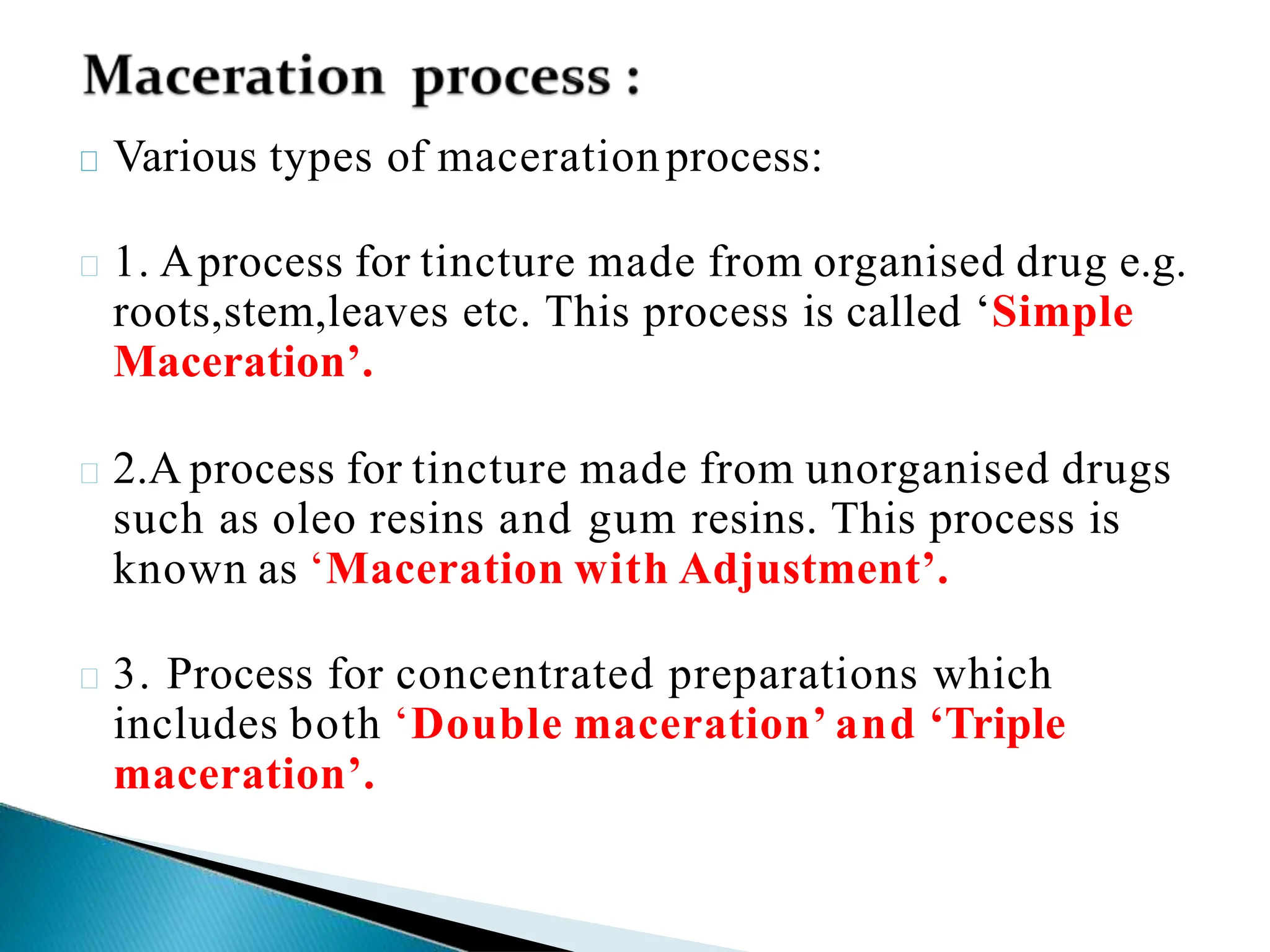
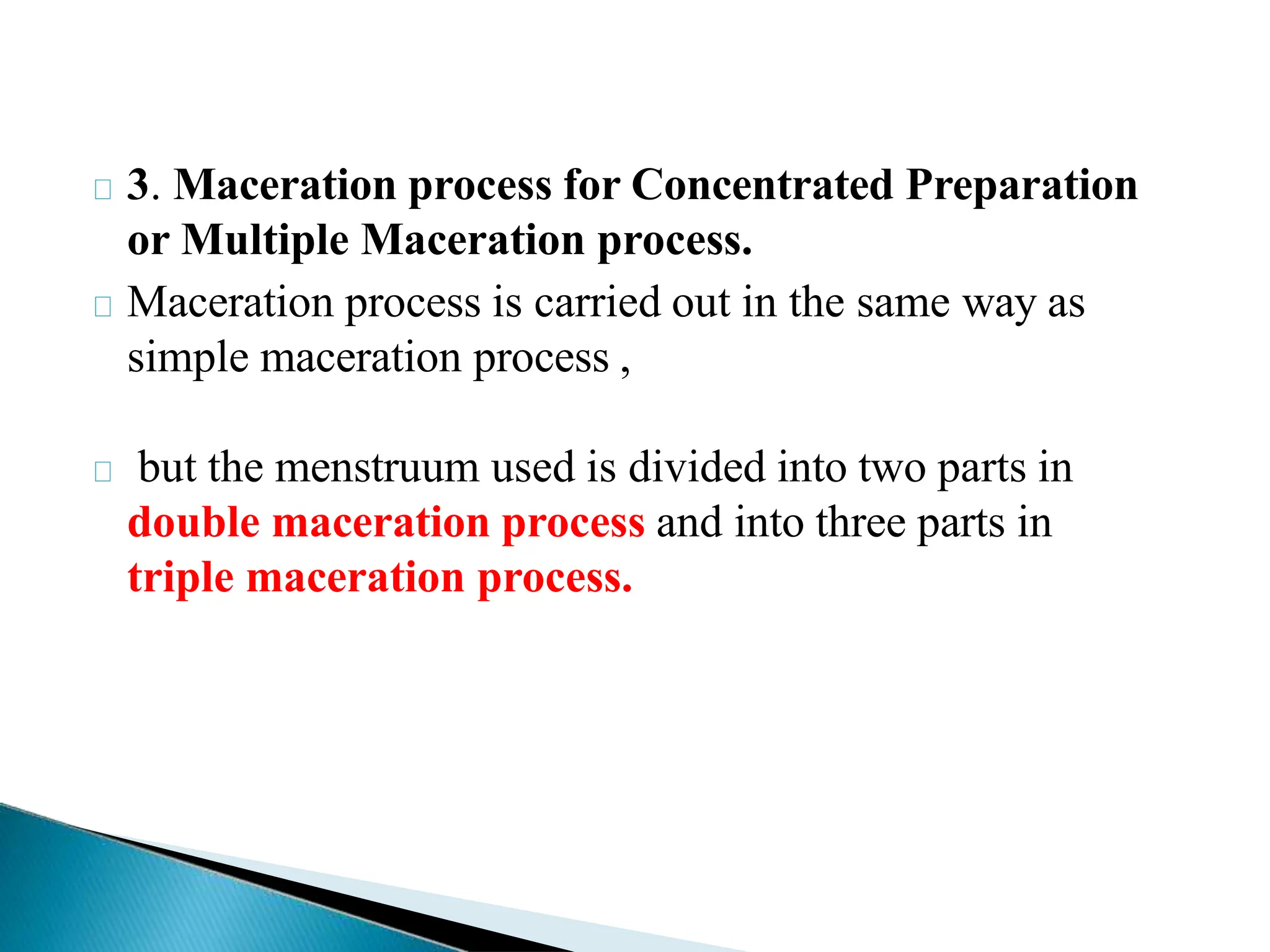
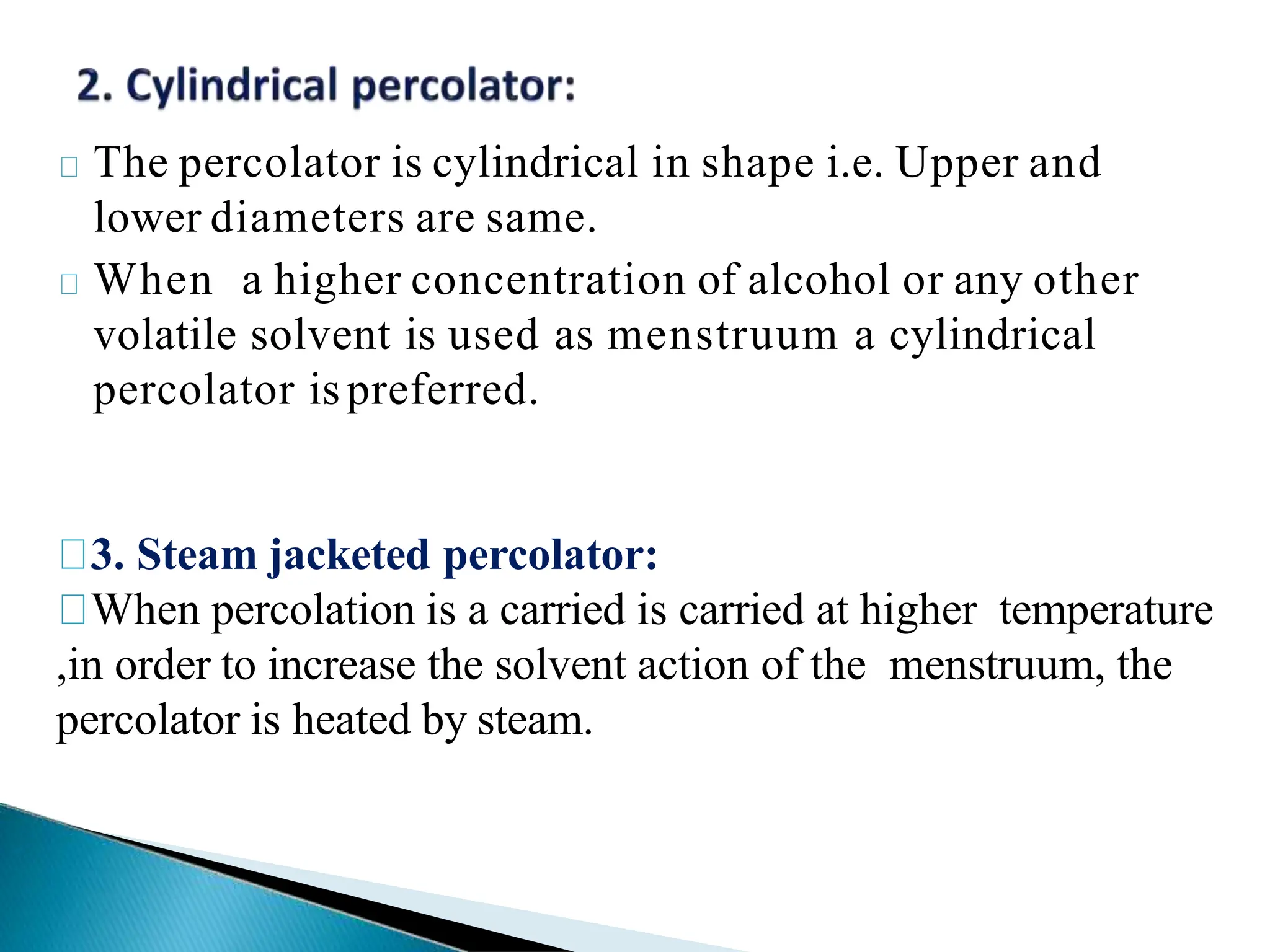
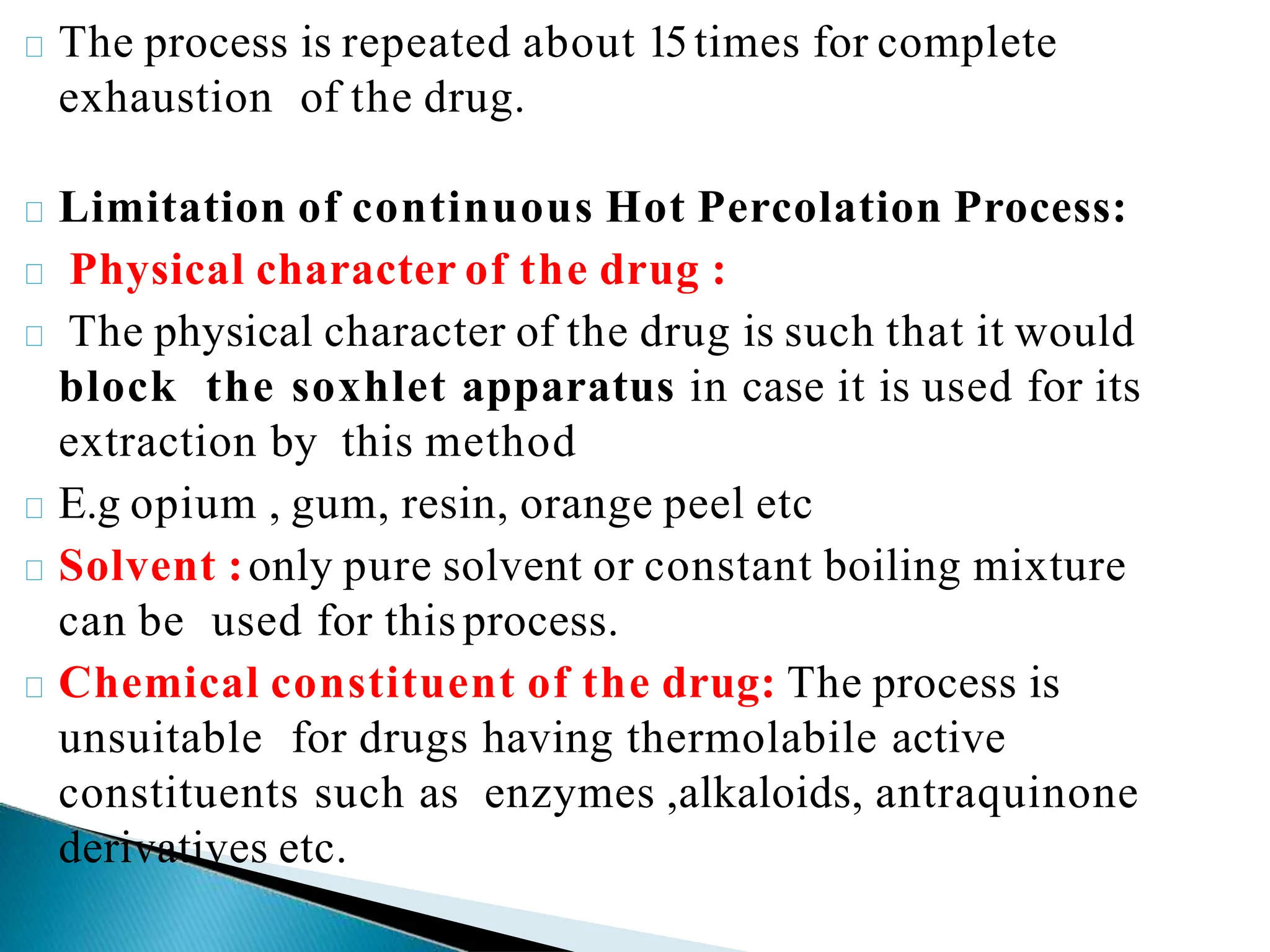
The document elaborates on various extraction processes for medicinal plant and animal tissues, detailing their definitions, methods, and the solvents used, such as water and alcohol. It explains different techniques like infusion, decoction, maceration, percolation, and digestion, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages, along with practical examples. Additionally, the document describes Ayurvedic dosage forms, including anjans, aristas, and ghan, explaining their preparation and applications.