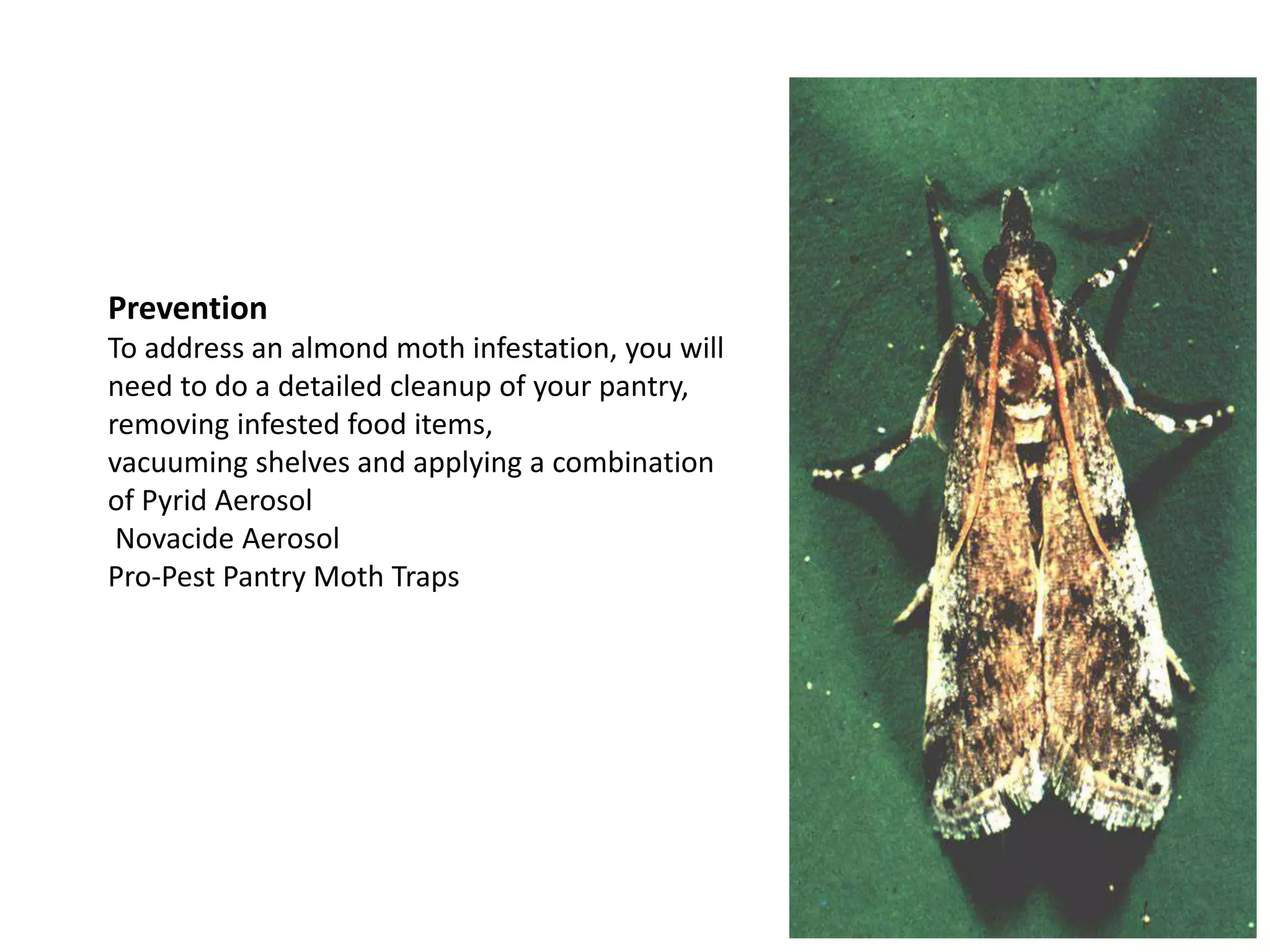
This document provides information on several external feeding pests that infest stored grains and foods. It introduces red flour beetle, Indian meal moth, almond moth, rice moth, and khapra beetle. For each pest, it provides the scientific name, distribution, host range, and brief descriptions of physical characteristics and life cycles. Signs of infestation and prevention methods are also mentioned for some pests. The document aims to educate about common external grain feeders and their identification.