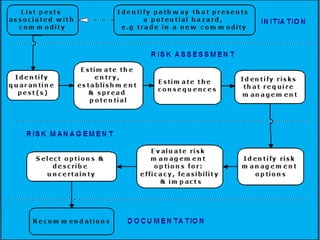
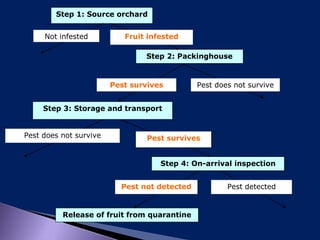
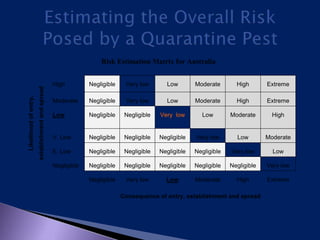
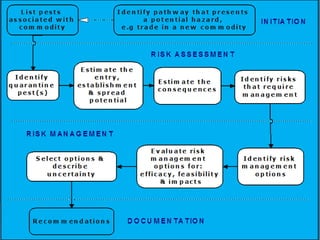
This document discusses pest risk analysis (PRA), which is the process of evaluating biological evidence to determine if a pest should be regulated and what measures should be taken. It involves three main steps: initiation, risk assessment, and risk management. The risk assessment estimates the likelihood of entry, establishment, and spread of a pest, as well as the potential economic consequences. It considers factors like pest biology and distribution, host availability, and climate. Based on these factors, pests are categorized and their risks are estimated on a matrix. Risk management then identifies potential measures to reduce risks to an acceptable level. PRA is mandatory for importing plants and plant materials according to Indian regulations.