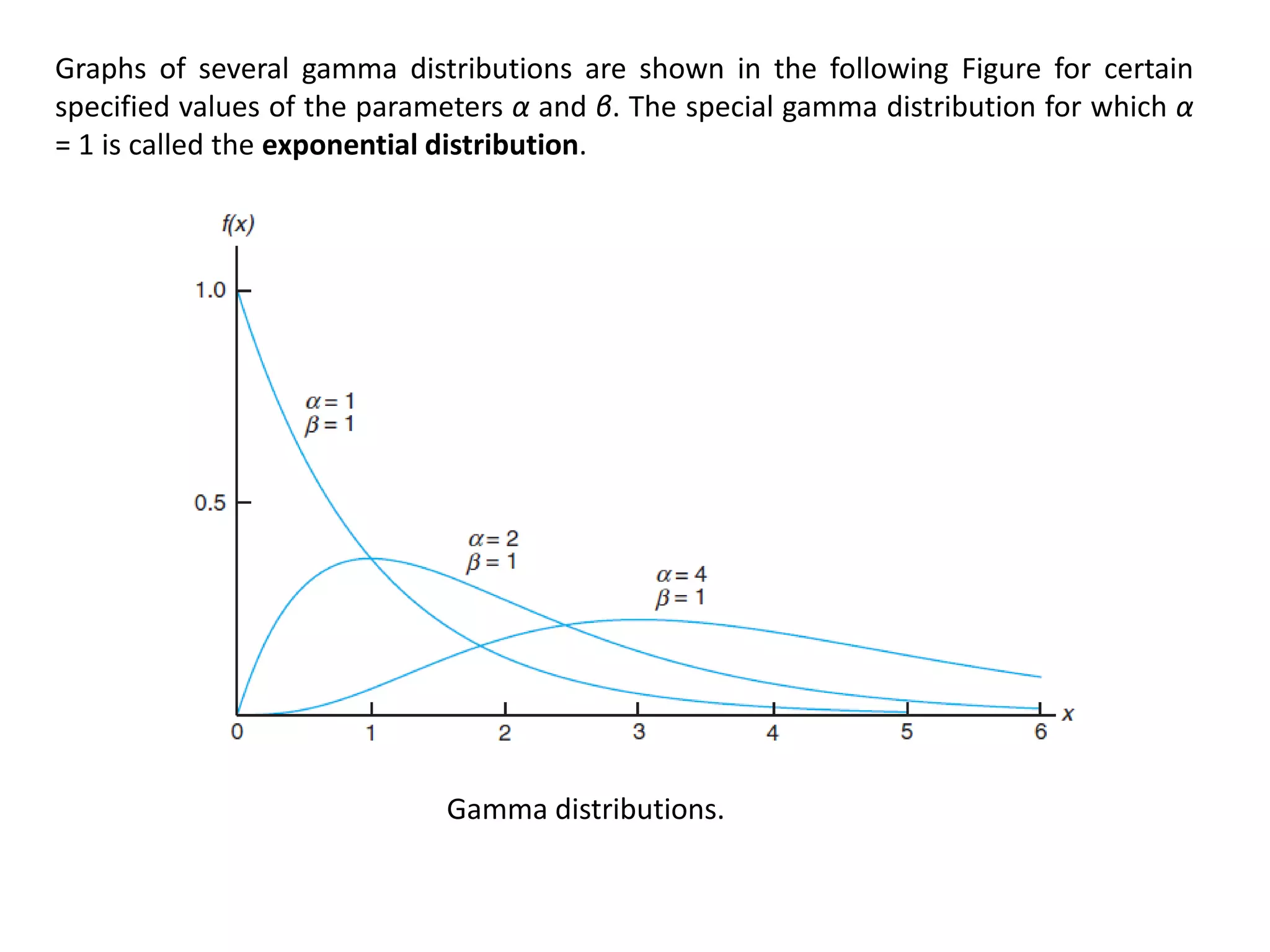
The document discusses the gamma and exponential distributions. It states that the exponential distribution is a special case of the gamma distribution and that both are useful for modeling things like time between arrivals and time to failure. It provides definitions and graphs of gamma distributions and explains that the gamma distribution's mean and variance are functions of its parameters. It then gives an example of using the exponential distribution to calculate the probability of components failing and an example of using the gamma distribution to calculate survival time probabilities.