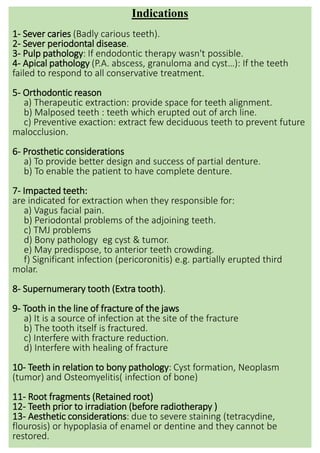
Tooth extraction, also called exodontia, is the removal of teeth from their socket in the jawbone. There are two main methods: intra-alveolar extraction using forceps to remove the tooth through the socket, and trans-alveolar extraction which requires raising a bone flap and removing bone around the roots before extracting. Tooth extraction is indicated for severe dental caries, periodontal disease, pulp or bone pathology, orthodontic reasons like crowding, prosthetic needs, impacted teeth causing issues, supernumerary teeth, teeth fractured with jaw fractures, or aesthetic reasons. Contraindications include uncontrolled local or systemic infections, previous radiation therapy, or uncontrolled medical conditions.