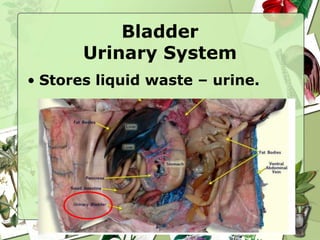
This document provides an overview of frog anatomy and the major organ systems. It describes the skin, heart, lungs, liver, gallbladder, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, spleen, fatty bodies, mesentary, bladder, and esophagus. The presentation is intended to help students complete a frog dissection lab booklet by identifying each organ's location and basic function within the respiratory, circulatory, digestive, urinary, integumentary, and reproductive systems.