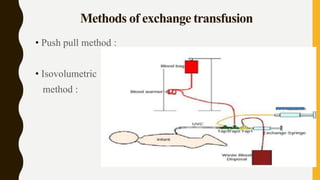
An exchange transfusion involves slowly removing a patient's blood and replacing it with donor blood in order to remove abnormal components and toxins while maintaining blood volume. It is indicated for hyperbilirubinemia, Rhesus/ABO incompatibility, severe anemia, and other conditions. The procedure requires specialized equipment and staffing in a NICU. Blood is warmed and infused using either a push-pull or isovolumetric method while carefully monitoring the infant. Potential complications include blood clots, changes in blood chemistry, heart/lung problems, and low risk of infection.