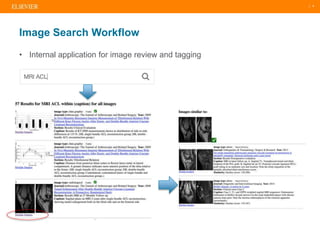
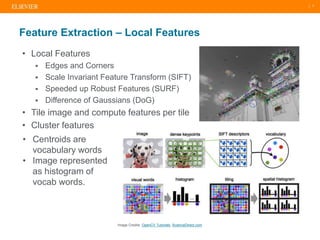
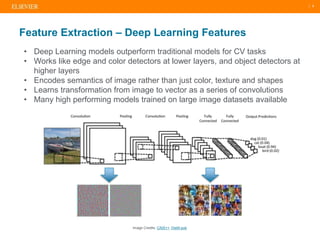
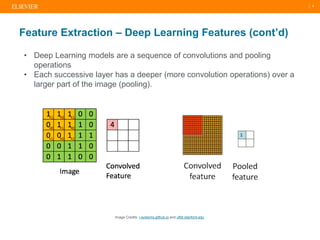
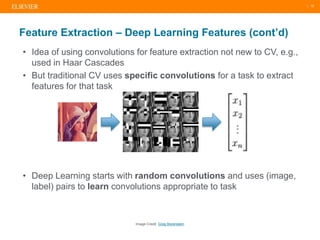
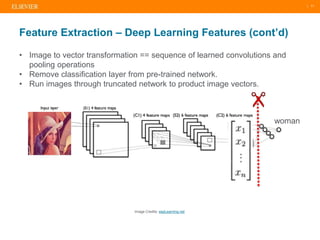
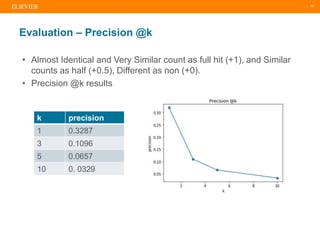
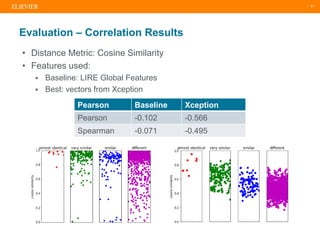
The document presents a comprehensive overview of evolving medical image similarity search techniques, emphasizing the use of feature extraction methods including global, local, and deep learning approaches. Key indexing strategies discussed include locality sensitive hashing, bag of visual words, and novel hybrid indexing techniques integrated with machine learning tools. Future work focuses on improving search accuracy through caption integration, dimensionality reduction, and advanced indexing approaches.