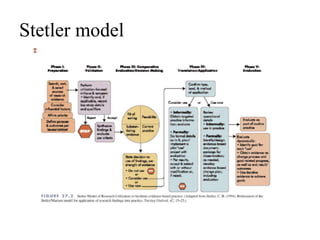
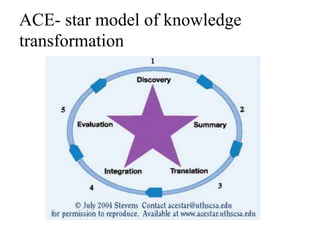
Evidence based practice (EBP) involves integrating the best available research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values. EBP begins with identifying an issue and searching for relevant research evidence, which is then evaluated and applied. Several models describe the EBP process, including the Stetler, Iowa, and ACE Star models. Barriers to EBP include limitations in the available research evidence as well as nurse, organizational, and professional barriers. The key steps in the EBP process are selecting an issue, assembling and evaluating evidence, assessing implementation potential, and developing, implementing, and evaluating guidelines through a pilot study.