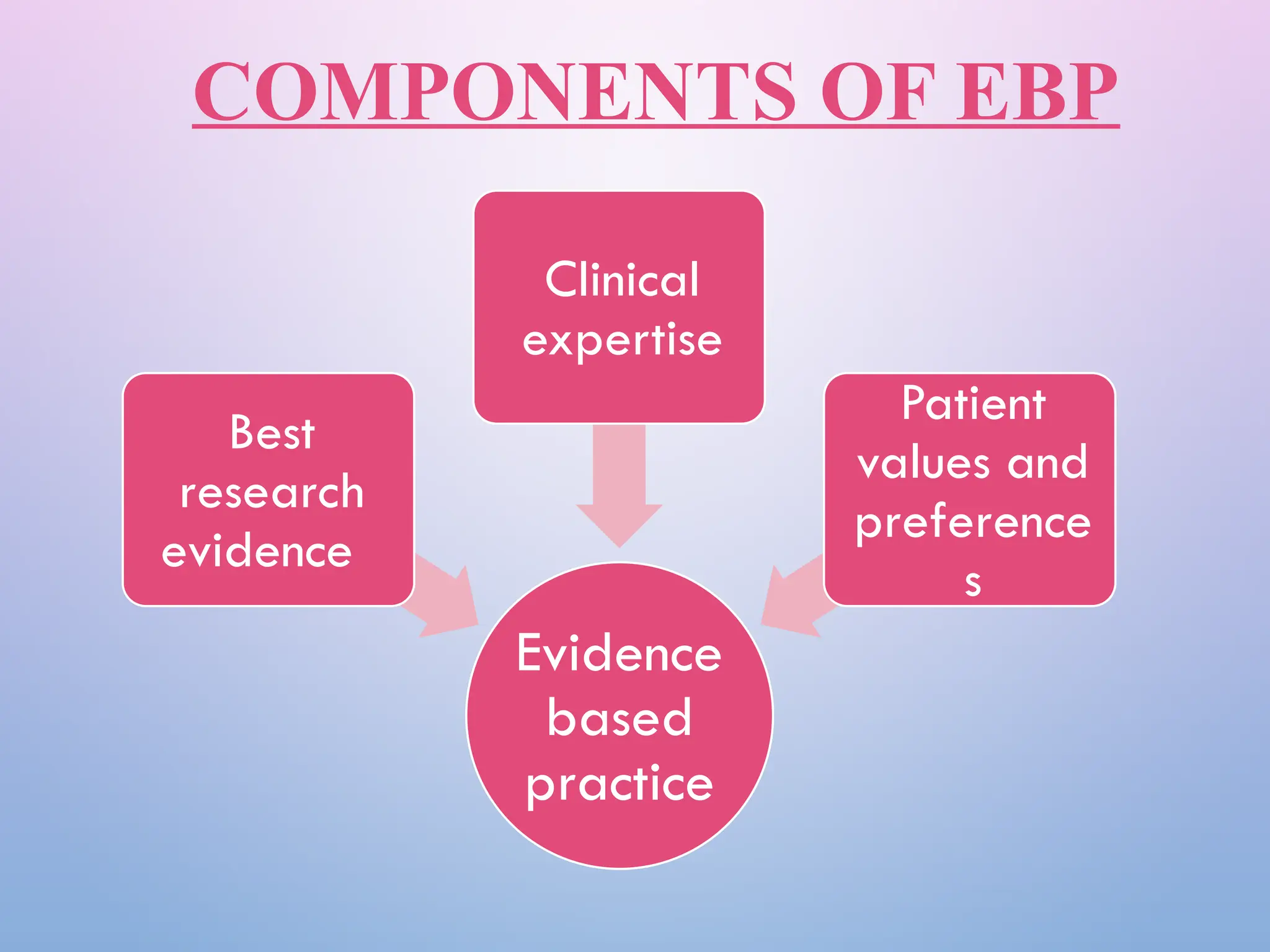
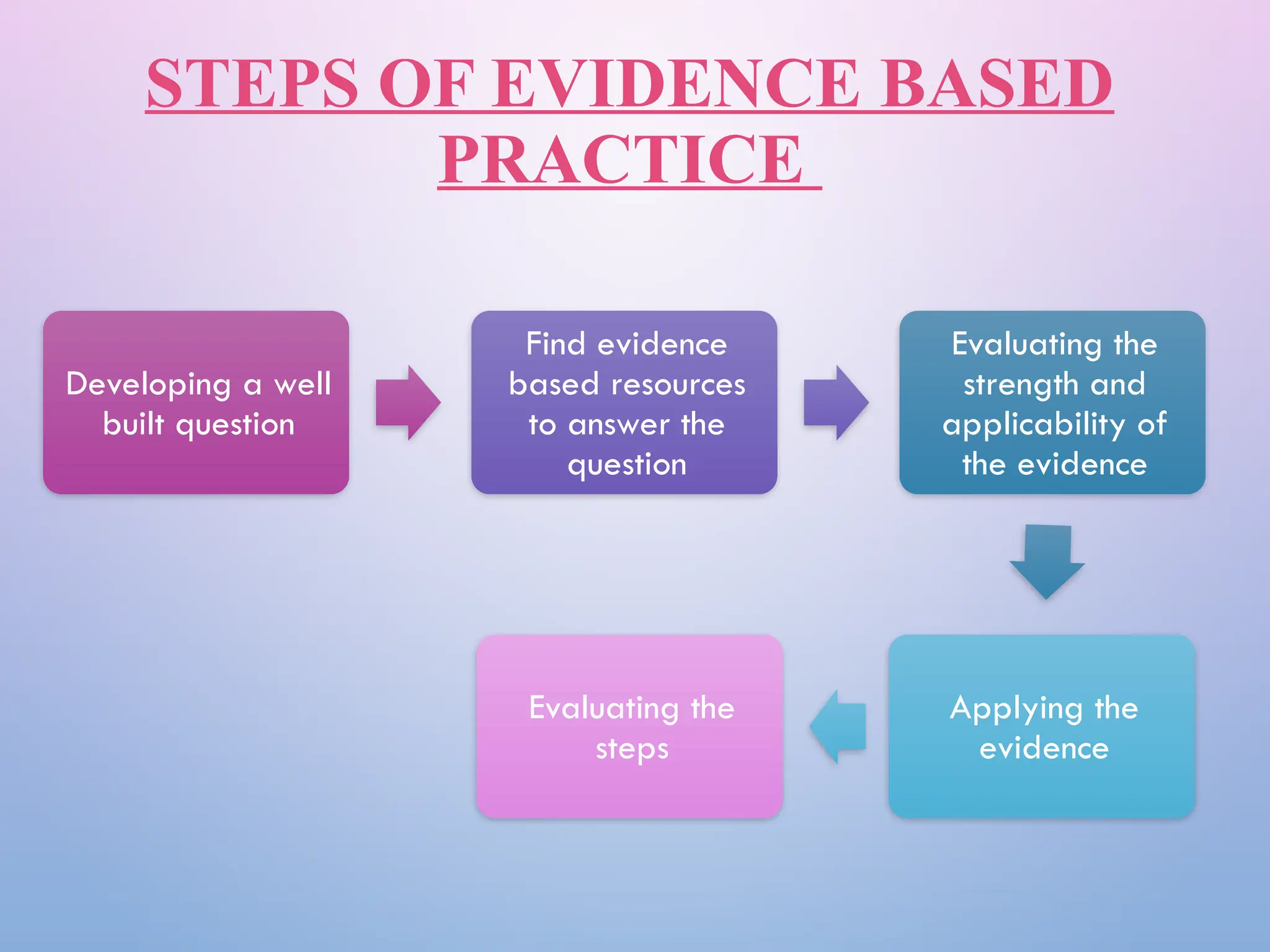
The document discusses evidence-based practice (EBP) in nursing, emphasizing its role in providing high-quality, cost-effective care based on clinical evidence and patient preferences. It outlines the components, aims, objectives, steps, resources, and barriers associated with EBP, highlighting its benefits in improving patient outcomes and nursing efficiency. The conclusion asserts that EBP is essential for transforming health care and enhancing clinical decision-making.