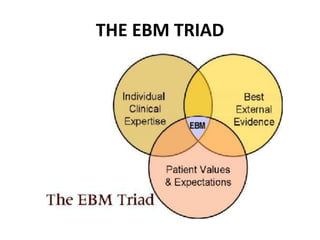
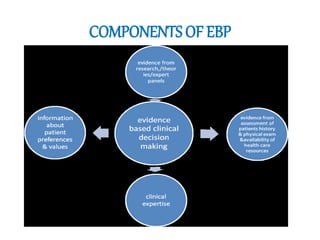
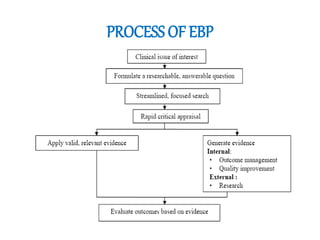
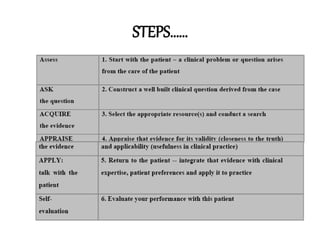
This document discusses evidence-based practice (EBP) in nursing. It defines EBP as integrating the best research evidence, clinical expertise, and patient values. The aims of EBP include providing high-quality, cost-effective care and advancing nursing practice through a focus on evidence rather than habits. EBP follows steps including formulating questions, finding evidence, critically appraising evidence, and integrating it with clinical expertise and patient preferences. Nurses play an important role in EBP through leadership, applying evidence, sharing knowledge, and participating in EBP projects and research.