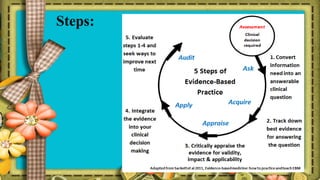
The document discusses the emergence of evidence-based medicine (EBM) and practice (EBP), emphasizing the importance of scientific evidence in nursing for optimal patient care. It outlines the definitions, purposes, and processes of EBP, while identifying barriers to its implementation, such as overwhelming information, lack of critical appraisal skills, and time constraints. The document advocates for nurses to adopt EBP to enhance the credibility and quality of nursing practices.