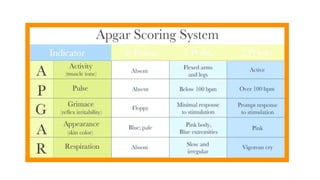
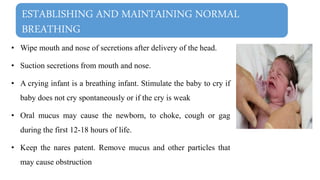
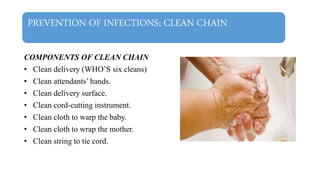
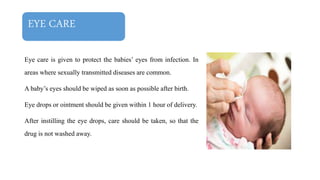
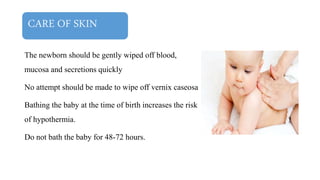
This document discusses essential newborn care, including assessments, importance, and steps. It outlines that essential newborn care should be provided immediately after birth and continue for the first 7 days. Key assessments include a head-to-toe examination, APGAR scoring, maturity assessment, and transitional assessment. Essential care includes establishing breathing, ensuring warmth, initiating breastfeeding, preventing infection through clean delivery practices, eye care, and more. The document provides details on each assessment and the steps of newborn care at birth.