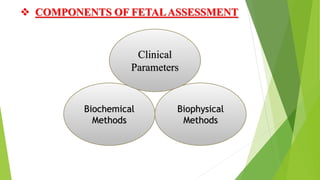
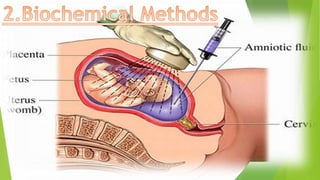
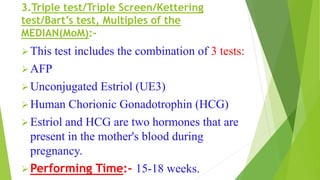
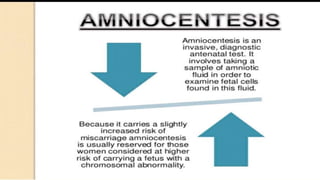
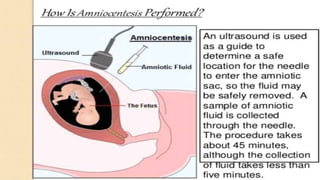
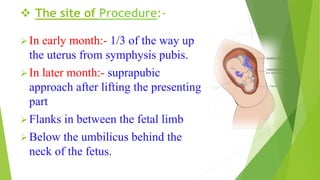
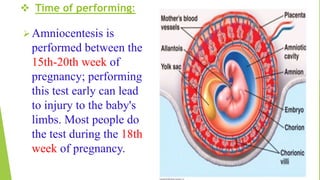
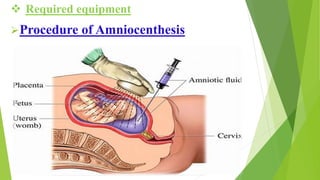
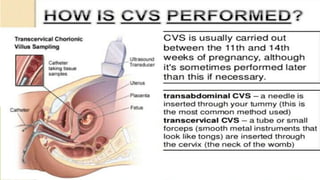
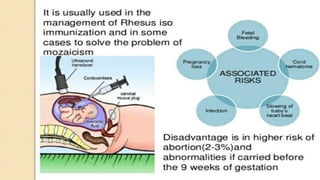
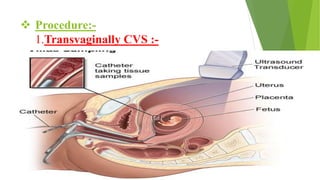
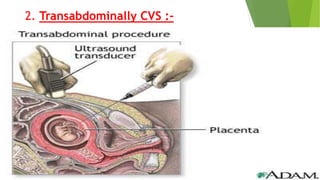
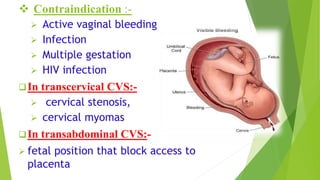
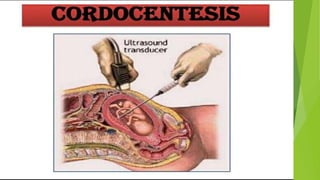
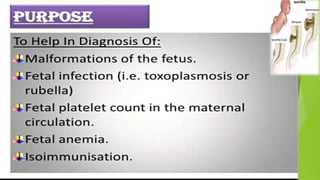
Fetal monitoring aims to ensure fetal well-being and growth throughout pregnancy. It screens for high-risk factors and assesses fetal status using clinical parameters, biochemical methods, and biophysical methods. Common indicators for monitoring include pregnancies with obstetric or medical complications. Biochemical methods include tests of maternal serum, amniotic fluid, and umbilical cord blood to check for conditions like neural tube defects or chromosomal abnormalities. Biophysical methods involve ultrasound imaging and tests of fetal movement, heart rate, and stress response.