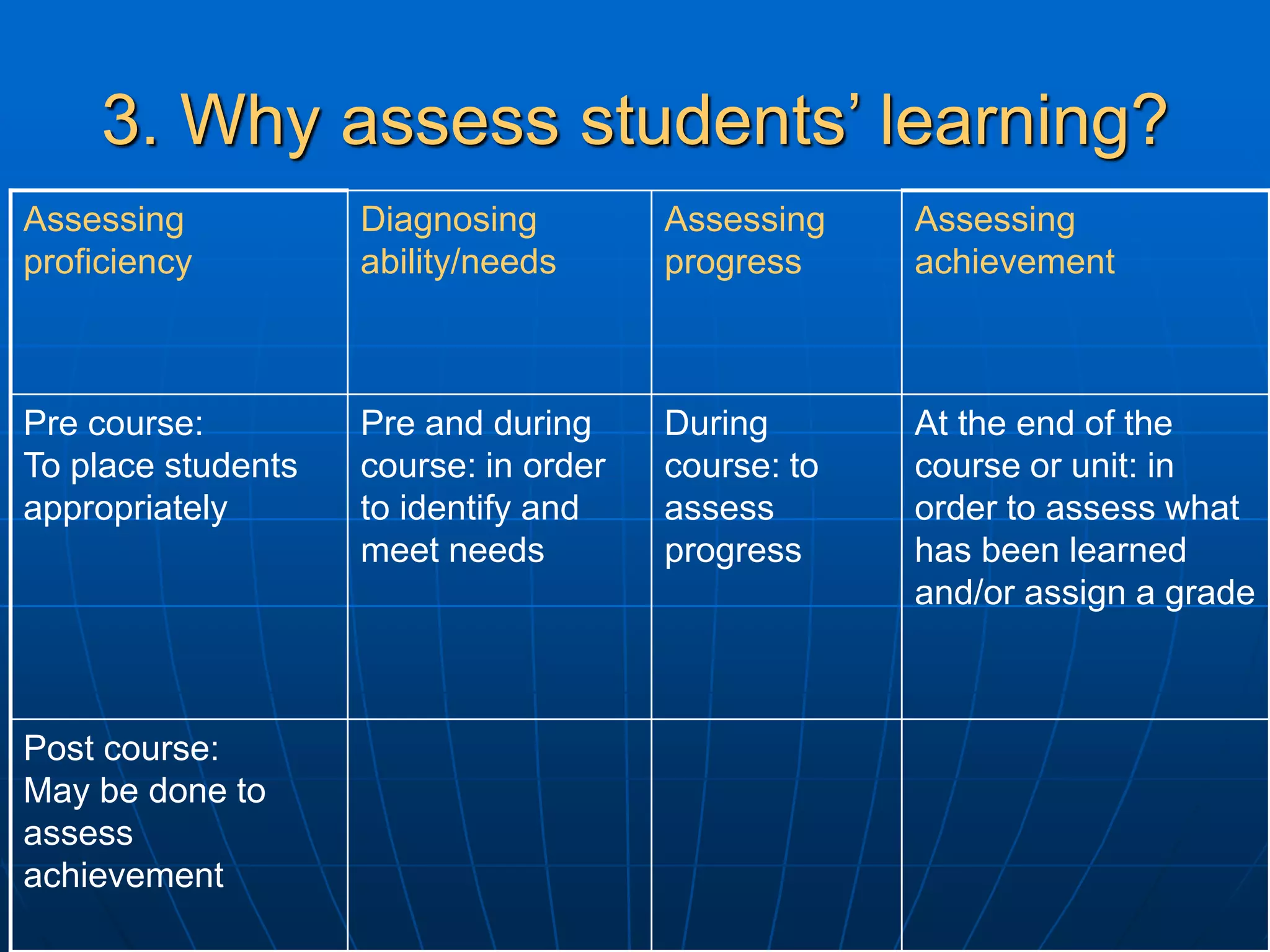
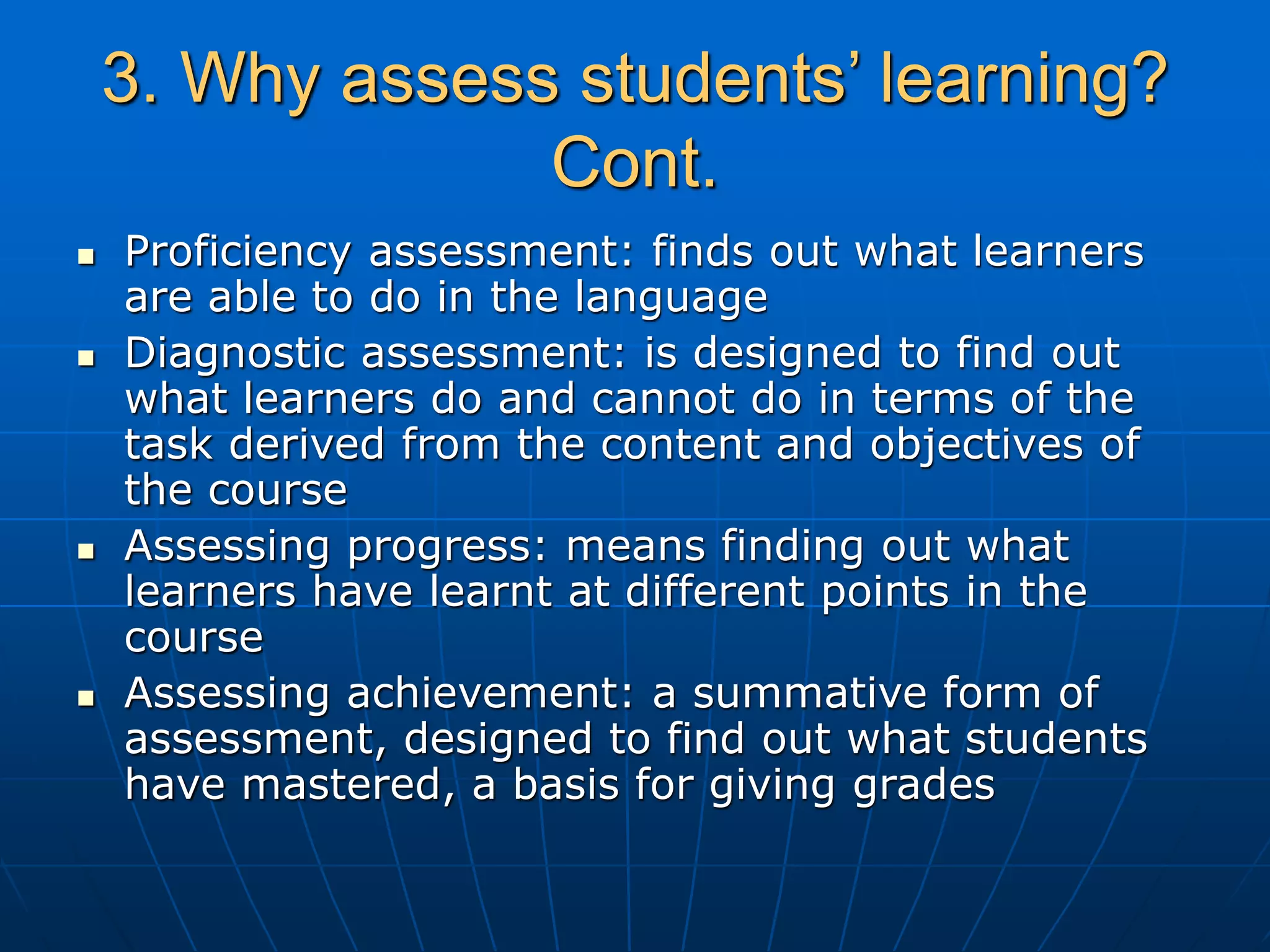
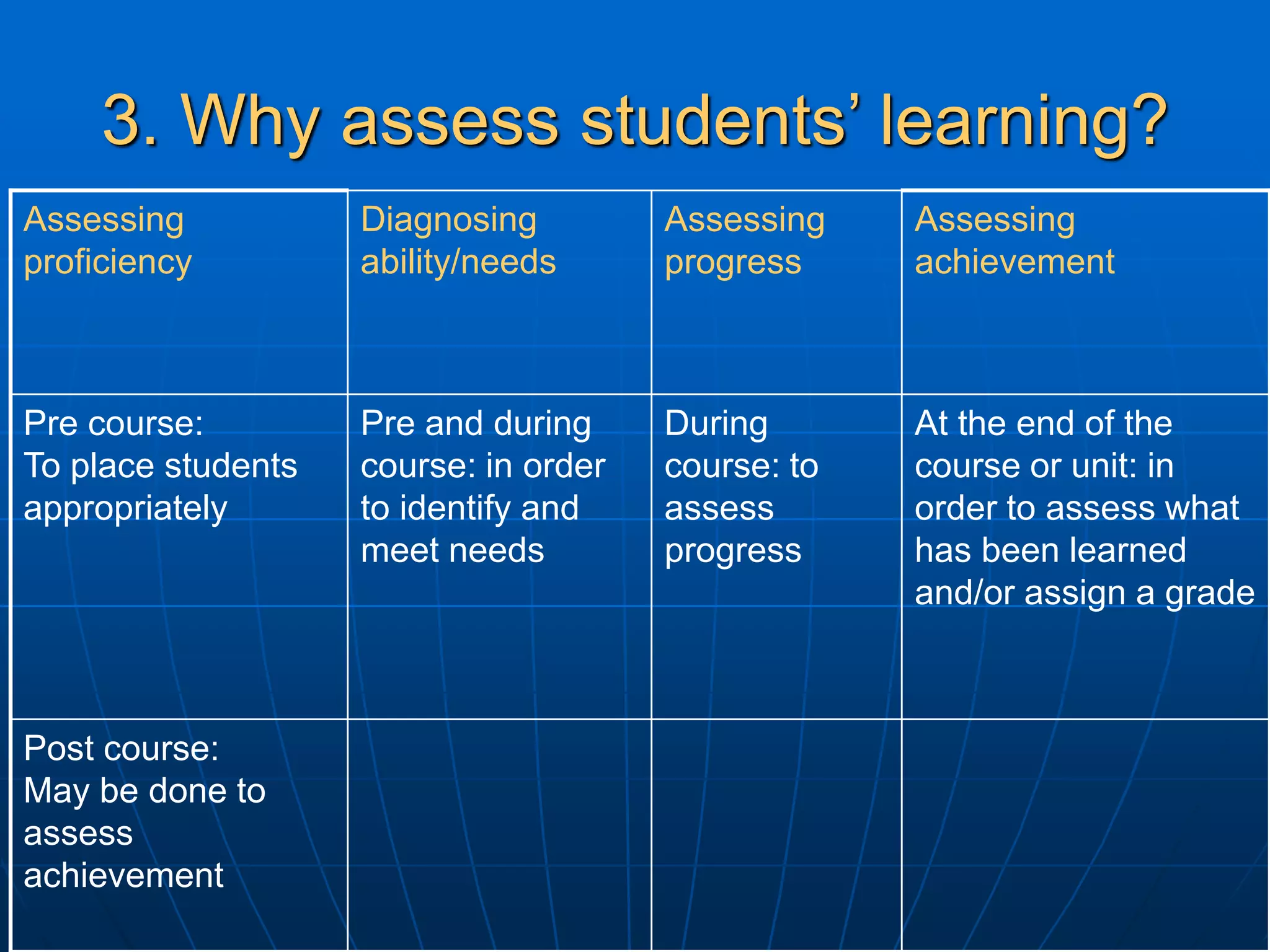
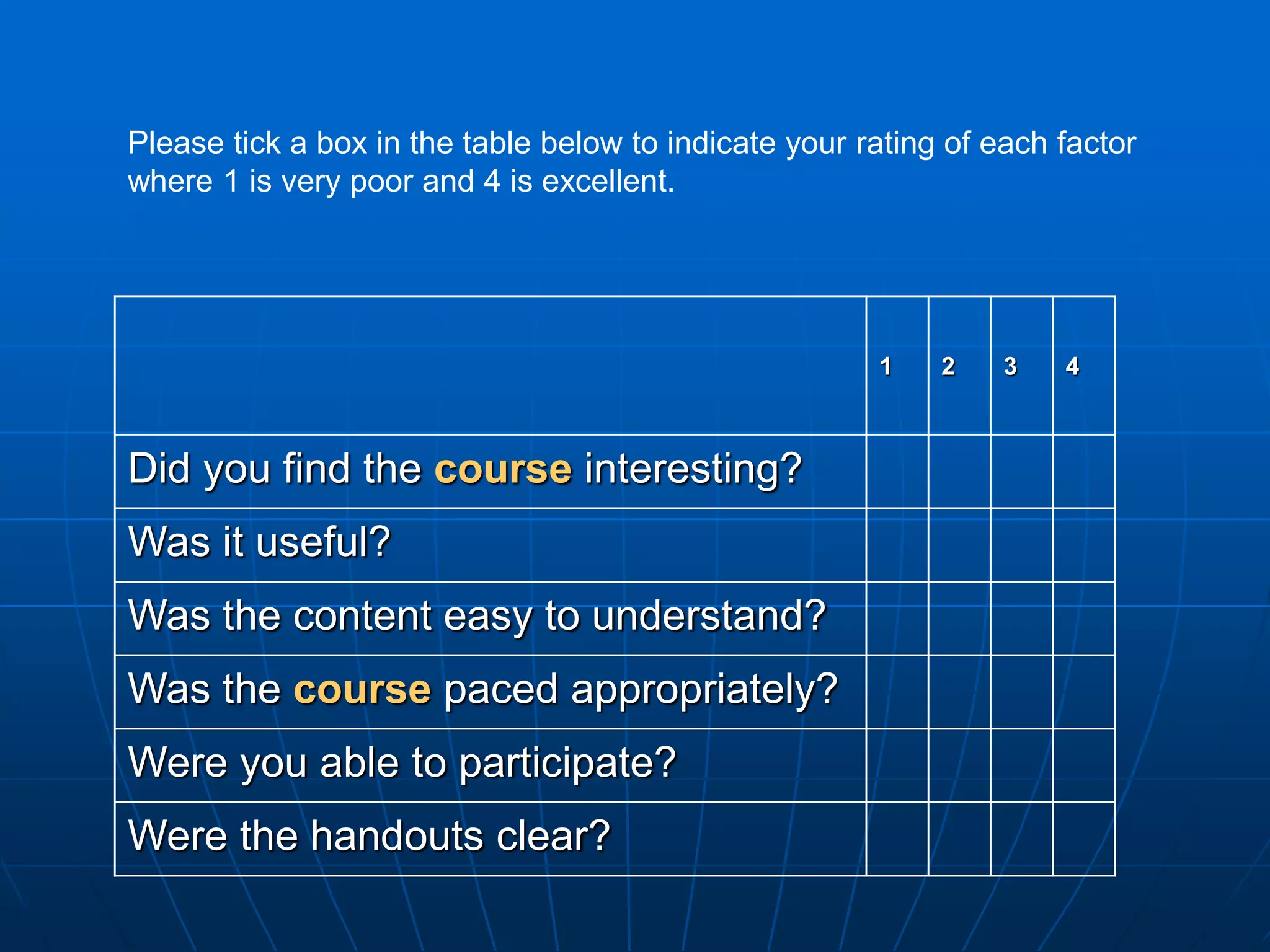
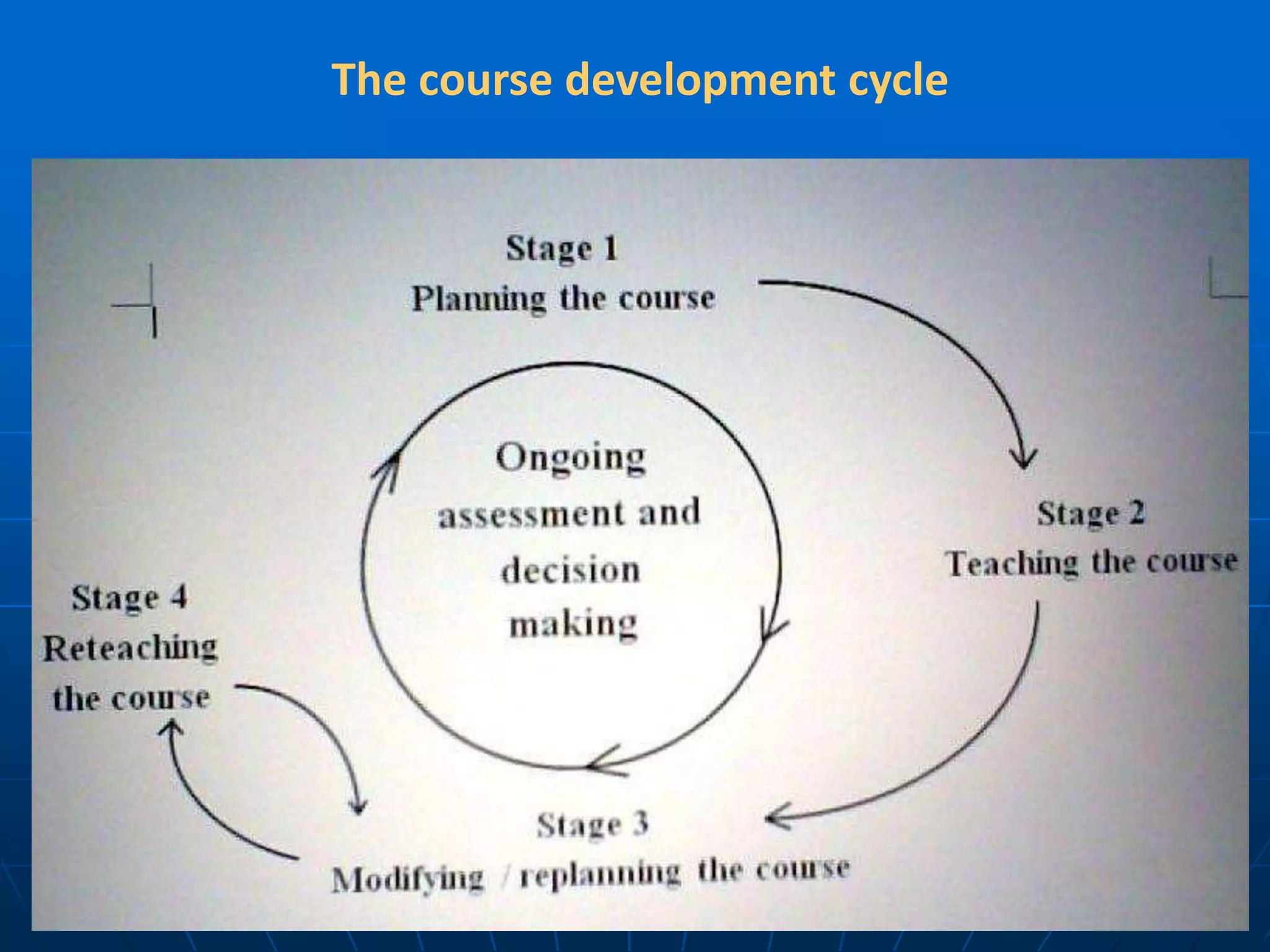
The document discusses assessment and course evaluation. It defines assessment as evaluating needs, students' learning through testing, and evaluating course design effectiveness. Assessment involves considering who, what, why, how, when, and what is done with results. Course evaluation also considers these questions to improve learning and teaching. Formative evaluation occurs during instruction while summative evaluation happens at the end to improve future courses. Both students and teachers are involved in the evaluation process.