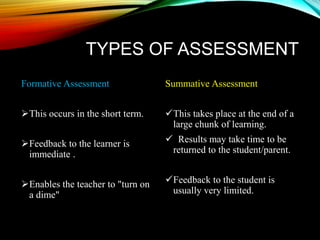
Assessment involves collecting evidence of a student's learning over time to improve teaching. It is not based on one test, but uses multiple measures to develop a deep understanding of what students know. Assessment provides feedback to students and teachers to modify instruction. It plays a key role in student learning and motivation. Assessment can be formative, to guide ongoing instruction, or summative, to evaluate learning at an endpoint. Both have important roles in the education process.